Map construction method and device and terminal equipment
A map construction and sub-map technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, 3D modeling, image data processing, etc., can solve problems such as errors, cumulative errors, and poor mapping effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
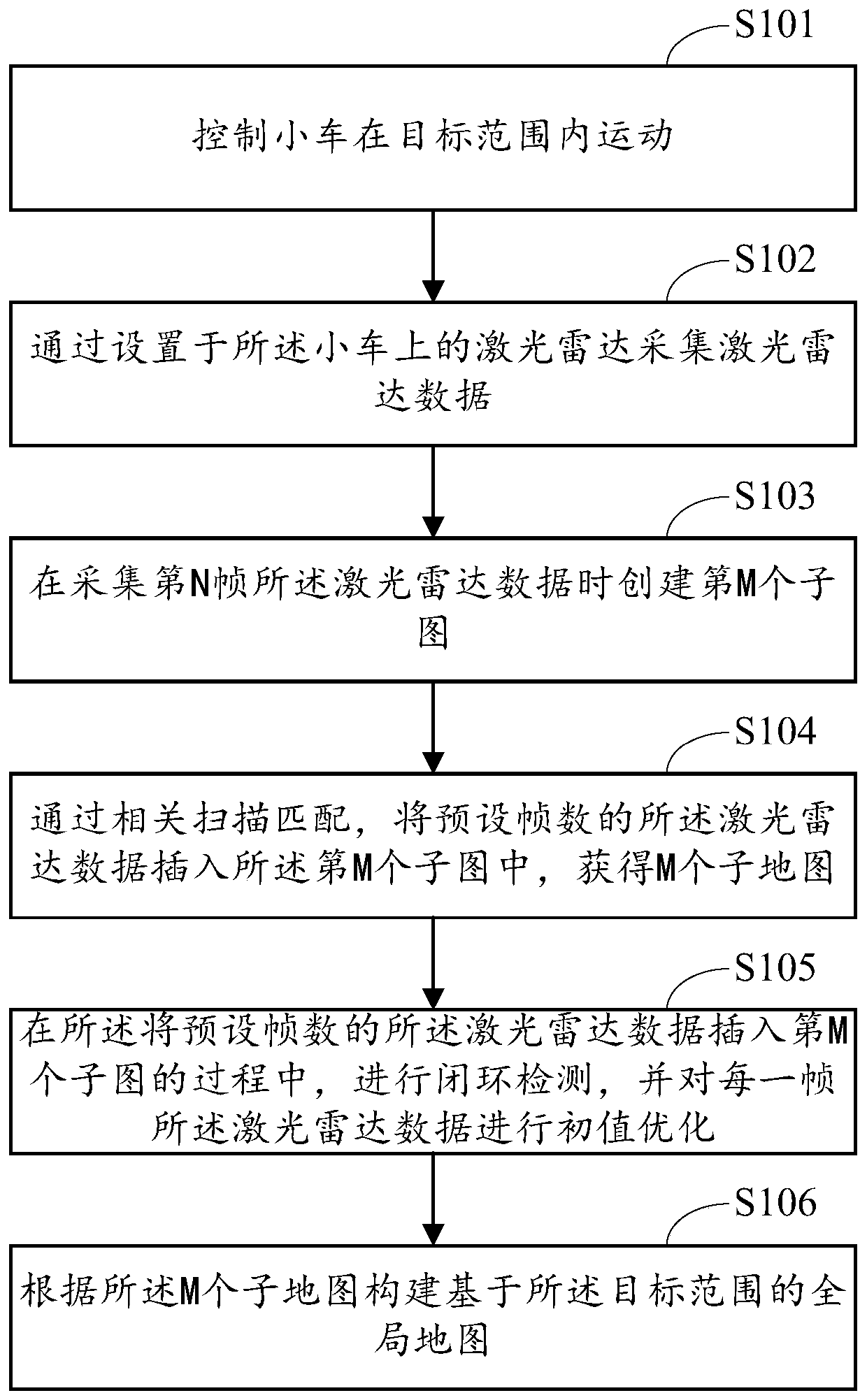
[0066] Such as figure 1 As shown, Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for constructing a map, including:
[0067] S101. Control the car to move within the target range.
[0068] In the above step S101, the target range represents the range where map construction needs to be performed.
[0069] In a specific application, the trolley can be an AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle), and the AGV is equipped with an automatic guidance device such as electromagnetic or optical, and travels along a prescribed guidance path.
[0070] In the embodiment of the present invention, the guidance path can be planned within the target range, so that the car can acquire information in the target range that can be used for map construction during driving.
[0071] S102. Collect laser radar data through the laser radar installed on the trolley.
[0072] In the above step S102, the lidar can directly acquire data such as distance, angle, reflection intensity, and speed from the ta...
Embodiment 2
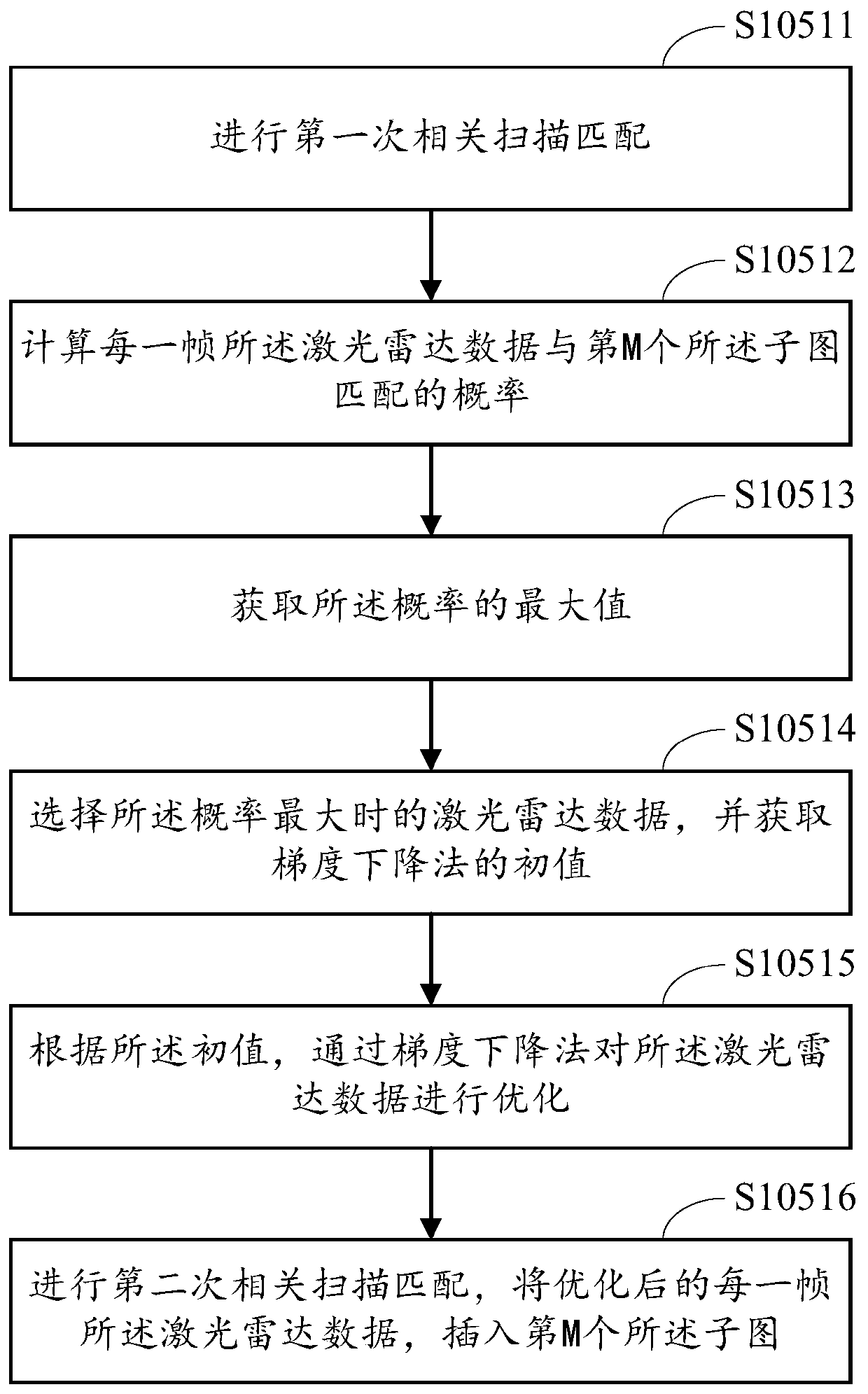
[0090] The embodiment of the present invention explains the implementation of sub-step S1051 of step S105 in the first embodiment above, and illustrates the detailed process of initial value optimization therein.
[0091] Such as image 3 As shown, in the embodiment of the present invention, step S1051 may include the following implementation steps:
[0092] S10511. Perform the first correlation scan matching.
[0093] In the above step S10511, after the first correlation scan matching, the result will be processed, and the processed result will be used as the input of the second correlation scan matching.
[0094] S10512. Calculate the probability that the lidar data of each frame matches the Mth sub-image, the formula is:
[0095]
[0096] where x i Indicates the pose of the car at the current moment, and the pose of the car at the previous moment is x i-1 , z represents any frame of lidar data, j represents the preset number of frames, m represents the world model, a...
Embodiment 3
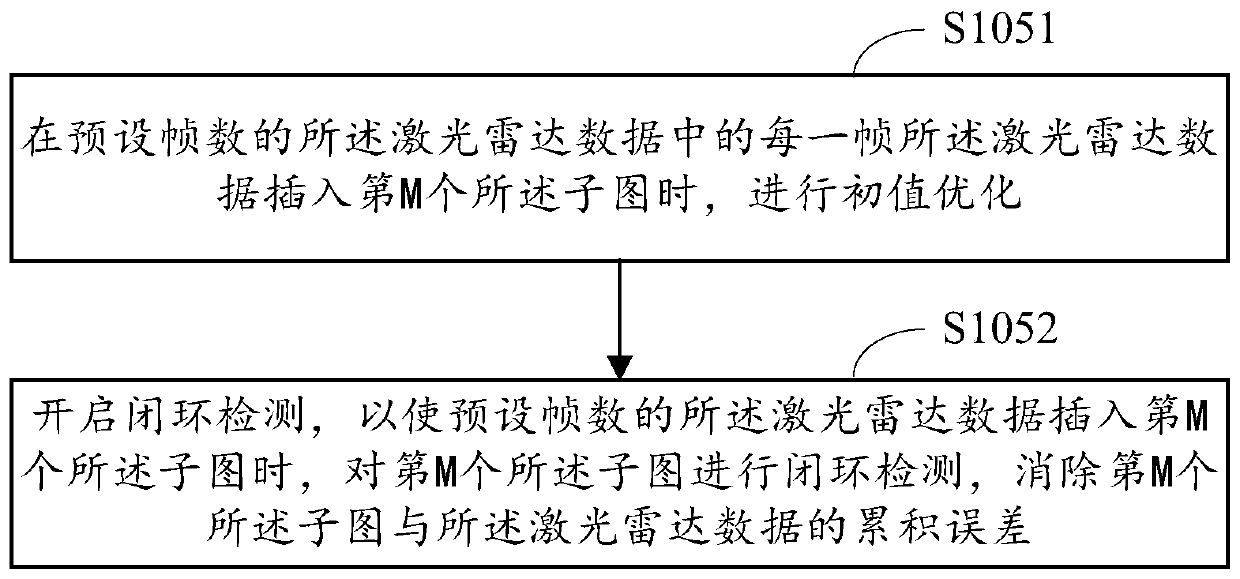
[0112] In this embodiment of the present invention, an implementation manner of sub-step S1052 of step S105 in the first embodiment is explained, and a detailed process of closed-loop detection therein is described.
[0113] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in the embodiment of the present invention, step S1052 may include the following implementation steps:
[0114] S10521. Set the detection period.
[0115] S10522. At each interval of the detection cycle, search for a key frame in the lidar data of the preset number of frames, and perform closed-loop detection through the lidar data of the key frame, and eliminate the Mth sub-image and the difference according to the closed-loop detection result The cumulative error of the lidar data.
[0116] Wherein, the lidar data whose detection period is shorter than the preset number of frames is inserted into the Mth subimage, and the lidar data of the preset number of frames is inserted into the period of the M+1th subimage.
[0117] I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com