Method for separating liver cells and hepatic stellate cells in animals infected with echinococcus multilocularis
A technology of hepatic stellate cells and separation method, which is applied in the field of separation of hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells in animals infected with alveoli, can solve the problem that the separation effect of hepatocytes or hepatic stellate cells is poor, and it is impossible to obtain hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells at the same time. Hepatic stellate cells, low survival rate and purity, etc., to achieve the effect of low survival rate and purity, ensuring survival rate and purity, and promoting digestion and detachment
Inactive Publication Date: 2019-10-15
THE FIRST TEACHING HOSPITAL OF XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIVERCITY
View PDF2 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0005] However, using the above-mentioned existing methods to isolate hepatocytes or hepatic stellate cells in the animal model infected with alveolar coccidia, there is not only the technical problem of not being able to obtain hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells at the same time, but also obtaining the same number of viable cells. There are also disadvantages of poor separation effect of hepatic cells or hepatic stellate cells, low survival rate and purity
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0048] 1. Materials and methods
[0049] (1) Experimental animals
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
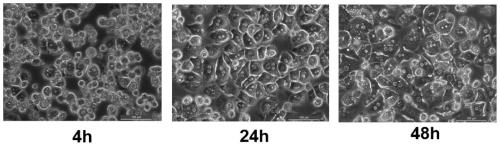
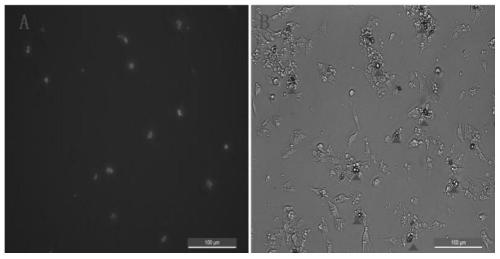
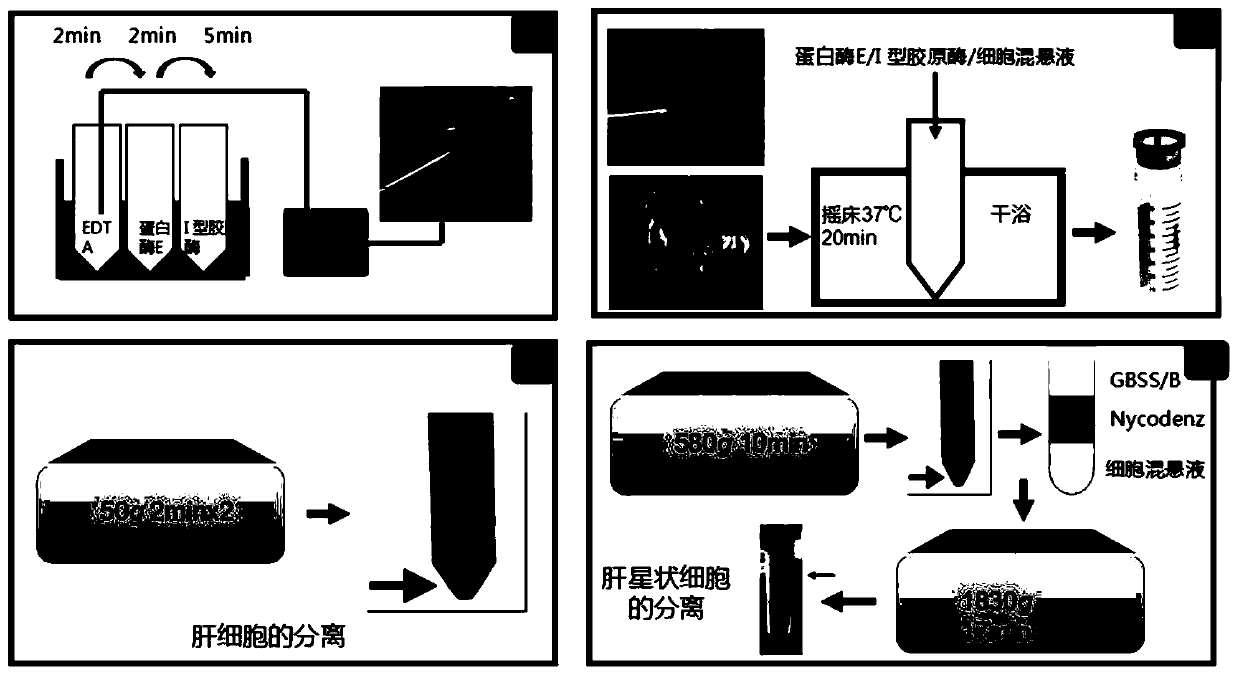
The invention relates to a method for separating liver cells from hepatic stellate cells in animals infected with echinococcus multilocularis. The method for separating liver cells from hepatic stellate cells in animals infected with echinococcus multilocularis comprises the following steps of: (1) in-situ perfusion: performing in-situ perfusion in the liver of animals infected with echinococcus multilocularis by sequentially using a pre-perfusion liquid, a post-perfusion liquid 1 and a post-perfusion liquid 2 through a portal vein, and taking off the liver to prepare an intrahepatic cell suspension; and (2) gradient centrifugation: centrifuging the intrahepatic cell suspension to obtain a supernatant 1 and a precipitate 1 at the lower layer, centrifugally washing the precipitate 1 with D-Hanks solution to obtain hepatocytes, centrifuging the supernatant 1, collecting a precipitate 2 at the lower layer, sequentially adding GBSS-B, Nycodenz separation solution and GBSS-B into the precipitate 2, performing centrifuging, collecting white annular layer, centrifugally centrifugal washing with GBSS-B, and discarding supernatant to obtain the hepatic stellate cells. The method for separating liver cells from hepatic stellate cells in animals infected with echinococcus multilocularis can extract and separate the liver cells and the hepatic stellate cells in the animals infected with echinococcus multilocularis at the same time.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of liver cell separation, and in particular relates to a method for separating hepatic cells and hepatic stellate cells in alveolar coccidia infected animals. Background technique [0002] Liver fibrosis is a complex disease involving multiple cell types and cytokines in the liver. The liver is composed of hepatic parenchymal cells and hepatic non-parenchymal cells, such as hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells, Kupffer cells, and endothelial cells. Hepatic cell apoptosis is rare in normal liver tissue. With the occurrence and development of liver fibrosis, the apoptosis of hepatic cells will change significantly. . There is a close causal relationship between hepatocyte apoptosis, HSC activation and liver fibrosis. It has been reported in the literature that under the action of some injury factors, apoptosis of hepatocytes becomes the first response of cells to toxins, and these apoptotic hepatocytes relea...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C12N5/071
CPCC12N5/067C12N2509/00
Inventor 林仁勇毕晓娟李亮吕国栋杨宁刘辉
Owner THE FIRST TEACHING HOSPITAL OF XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIVERCITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com