A group consensus approach for heterogeneous networked multi-agent systems with time-varying delays
A multi-agent system, time-varying time-delay technology, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems that affect the convergence speed of the system, and achieve the effect of easy solution and implementation, and fast convergence speed of the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
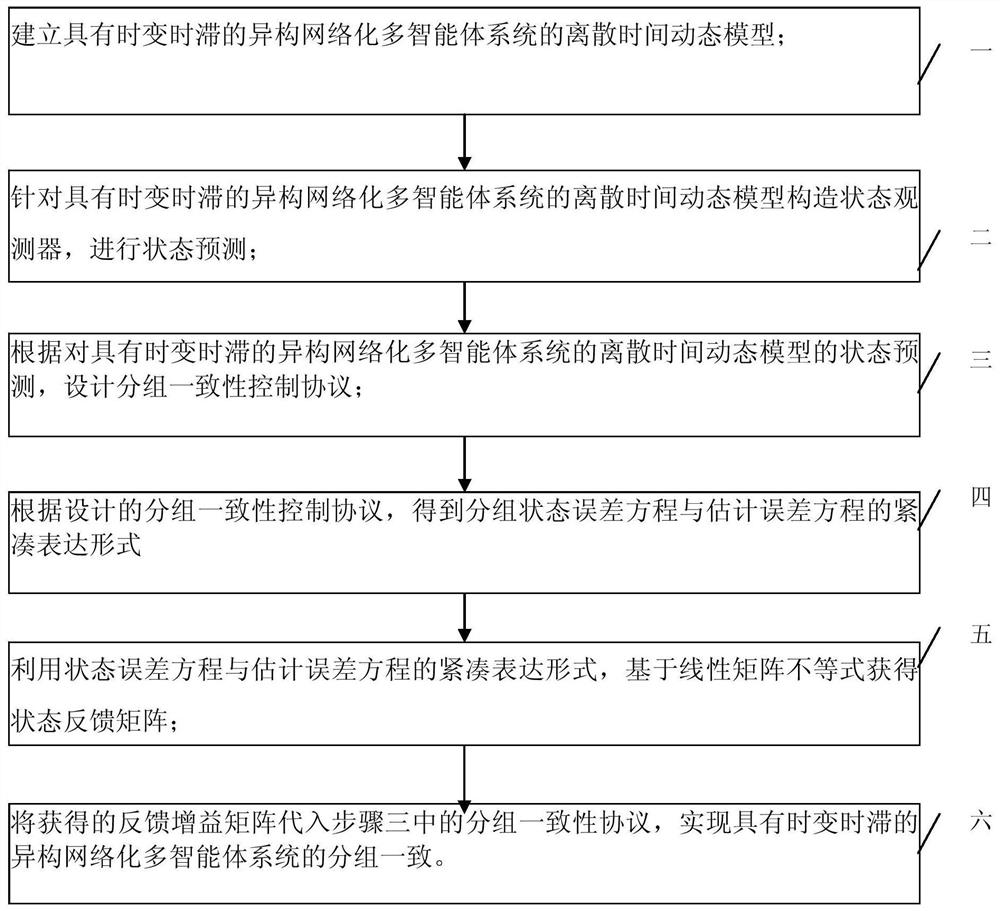
[0071] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 A pair of this embodiment will be described. The method for the group consistency of the heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with time-varying time-delay described in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0072] Step 1. Establishing a discrete-time dynamic model of a heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with time-varying time-delay;
[0073] Step 2, constructing a state observer for the discrete-time dynamic model established in step 1, and performing state prediction;
[0074] Step 3. According to the state prediction of the discrete-time dynamic model of the heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with time-varying time-delay in step 2, design a group consistency control protocol;
[0075] Step 4. According to the group consistency control protocol designed in step 3, a compact expression form of the group state error equation and estimation error equation is obtained;
[0076]...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0078] Specific implementation mode 2: The difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode 1 is that the step 1 is specifically:
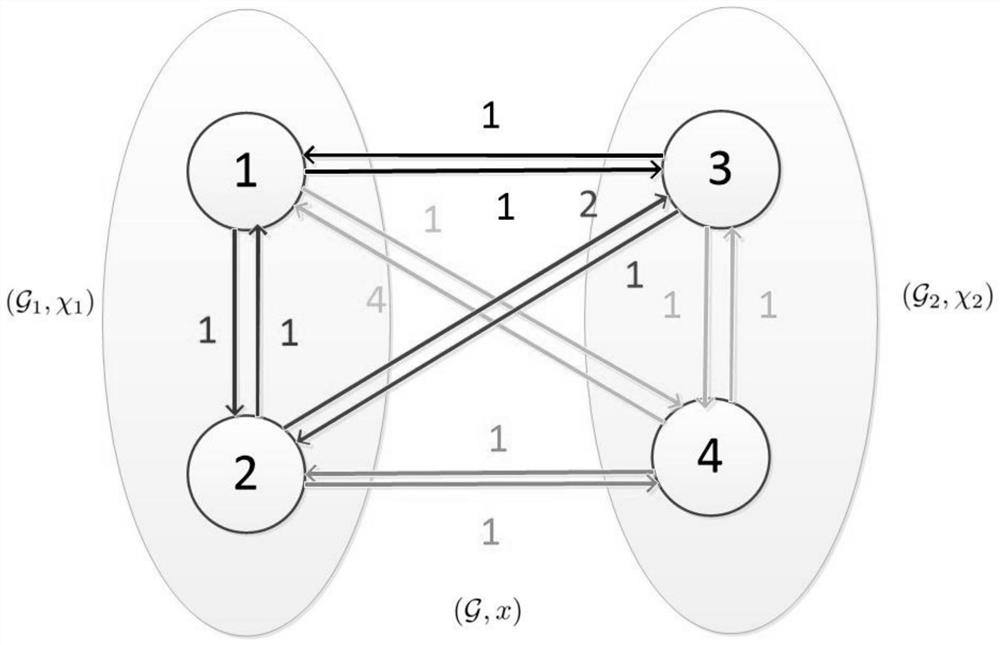
[0079] For a network containing N+M agents N≥2, M≥2; the state of agent i is expressed as x i , i=1,2,…,N+M; each agent is a network A node of , the state of each node can represent the actual physical quantity, such as attitude, position, temperature, voltage, etc. The topology of this networked multi-agent system is a weighted directed graph, is the vertex set, is the edge set, is a non-negative weighted adjacency matrix; the index set of vertices is from vertex v i to vertex v j The directed edge of is denoted as ε ij =(v i ,v j ), j=1,2,…,N+M; corresponding to ε ij The adjacency matrix element a of ij is a non-zero real number, the vertex v i The neighborhood node set of is Laplace matrix Indicates that the element is l ij The (N+M)×(N+M) dimensional matrix, where,
[0080] The weighted ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0086] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 2 is that the specific process of state prediction described in step 2 includes:
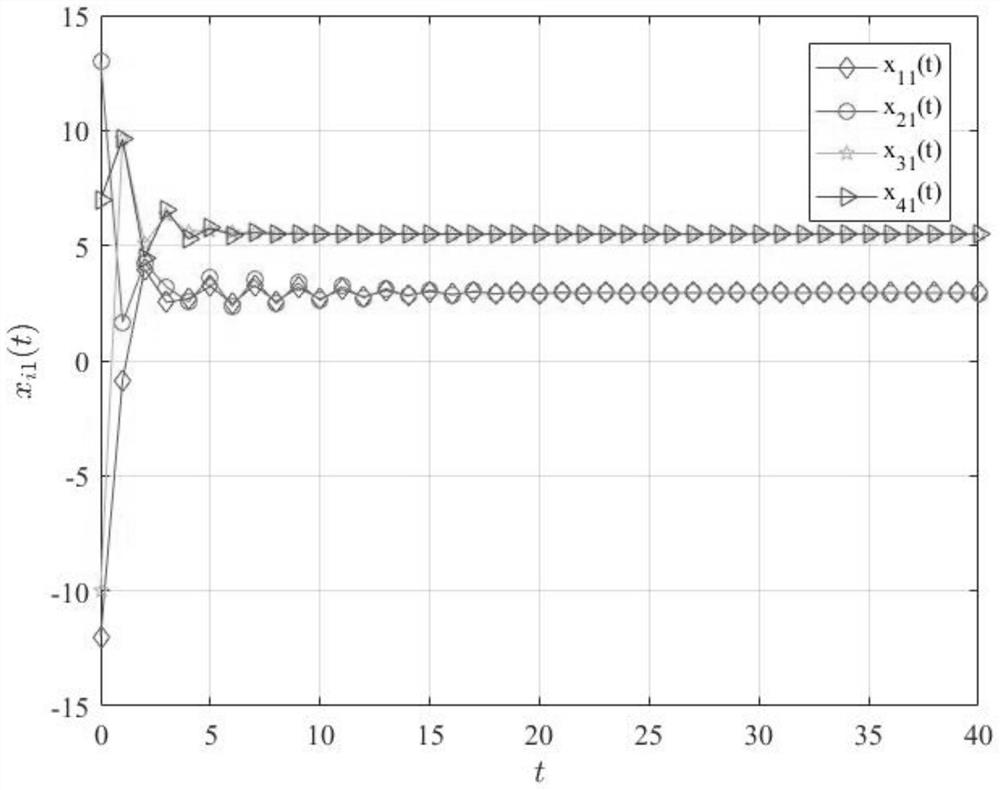
[0087] In a networked multi-agent system, agent i can receive information from itself and neighboring agent j, but there is a time-varying delay τ in the communication network ij (t); and is a known bounded function, τ 0 and τ are the lower and upper bounds respectively; the state prediction from time t-τ to time t is:
[0088]
[0089] in, R s is the s-dimensional real number space; Represents the predicted state of agent i at time t based on the information of agent i up to time t-τ, y i (t-τ) represents the output function of the i-th agent at time t-τ, L iDenotes the i-th observer gain matrix, Indicates the predicted output function of the i-th agent at time t-τ, L i Denotes the i-th observer gain matrix.
[0090] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the second embodiment. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com