A stress-free assembly method for optical components
A technology for optical components and assembly methods, applied in optical components, optics, installation, etc., can solve problems such as stress concentration, poor surface deformation of optical components, poor stability, etc., to alleviate clamping stress concentration, reduce detection errors, and reduce assembly. cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with embodiment and accompanying drawing, but should not limit protection scope of the present invention with this.
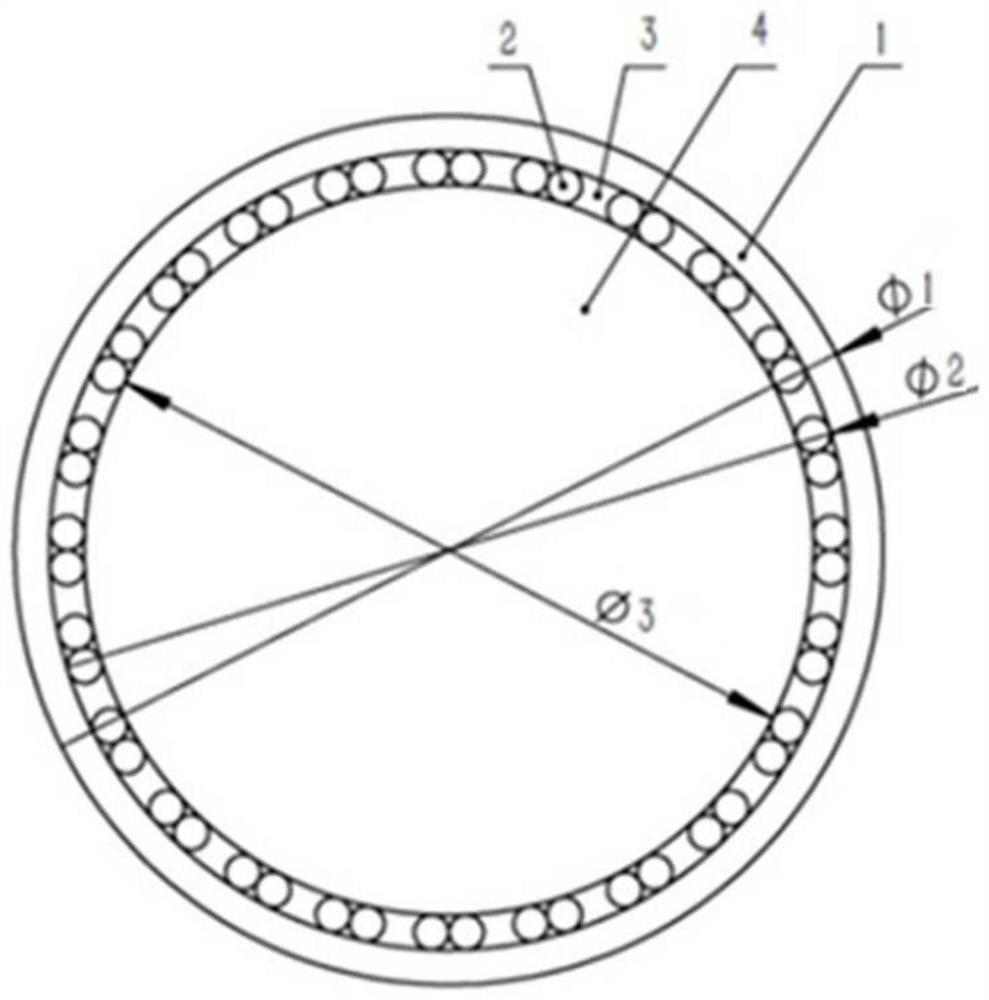
[0023] Refer to actual figure 1 , is a stress-free assembly method for optical elements of the present invention, characterized in that the method mainly includes an aluminum mirror frame 1, some polytetrafluoroethylene rods 2, molten silicone rubber 3 and optical elements 4;
[0024] The inner diameter of the aluminum mirror frame 1 is slightly larger than the diameter of the optical element 4 to be assembled and the sum of the diameters of the polytetrafluoroethylene rods 2, and the assembled optical element 4 is placed in the aluminum mirror frame 1, and then clings to the inner wall of the aluminum mirror frame 1 Evenly place several polytetrafluoroethylene rods 2 to support the optical element 4. The diameter of the polytetrafluoroethylene rod 2 is slightly smaller than the differe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Poisson's ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com