Server, equipment and method and system for monitoring survival state of server
A technology for monitoring servers and servers, which is applied in the field of servers, equipment, and monitoring server survival status. It can solve the problems of high power consumption of heartbeat packets, shortening the battery life of equipment, and affecting the service life of equipment, so as to prolong the service life and save the overall power. consumption effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
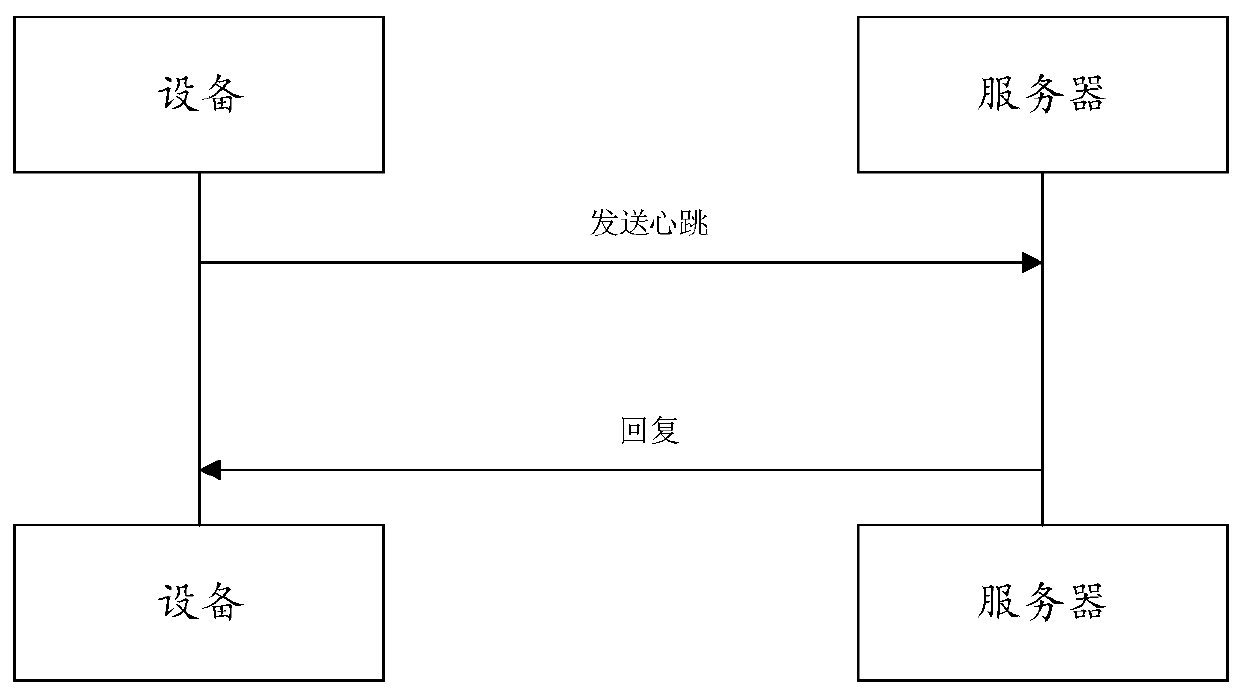
[0056] see figure 2 , figure 2 It is a schematic flow chart of an embodiment of the method for monitoring server survival status in this application. Such as figure 2 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0057] S11: The server 10 establishes a communication connection with the device 20;
[0058] In step S11, there are many ways for the server 10 to establish a communication connection with the device 20. Two common ways to establish a communication connection are introduced below.
[0059] 1. A communication connection is established between the server 10 and the device 20 by sending a handshake packet. Specifically, the process of establishing a communication connection includes the following steps:
[0060] (1) The server 10 sends a handshake packet to the device 20;
[0061] Wherein, the handshake packet conforms to a predetermined communication protocol format.
[0062] (2) The device 20 continues to receive the handshake packet. If the device 2...
Embodiment 2
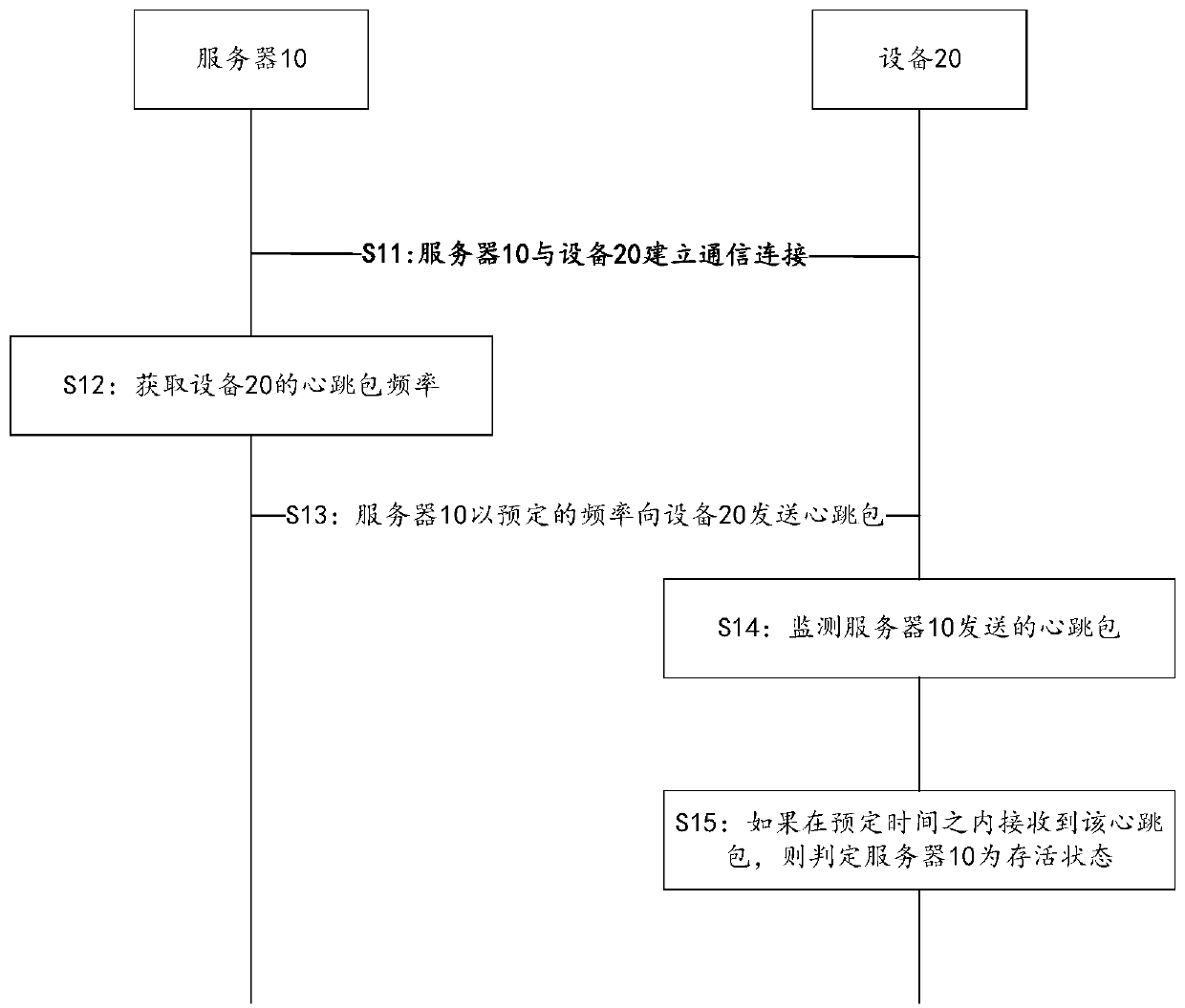
[0094] see Figure 4 , Figure 4 It is a schematic flow chart of the second embodiment of the method for monitoring the survival status of the server in this application. The multiple devices connected to the server can be of different types, such as cameras, TVs, groundwater meter detectors, etc. These devices have different functions, different working modes in the working scene, and different requirements for timely response of the devices. Therefore, different devices can set different heartbeat packet frequencies. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the heartbeat packet frequency of the device is set by obtaining the static device parameters of the device.
[0095] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0096] S21: The server 10 establishes a communication connection with the device 20;
[0097] Wherein, step S21 is the same as step S11 in the first embodiment.
[0098] S22: The server 10 obtains th...
Embodiment 3
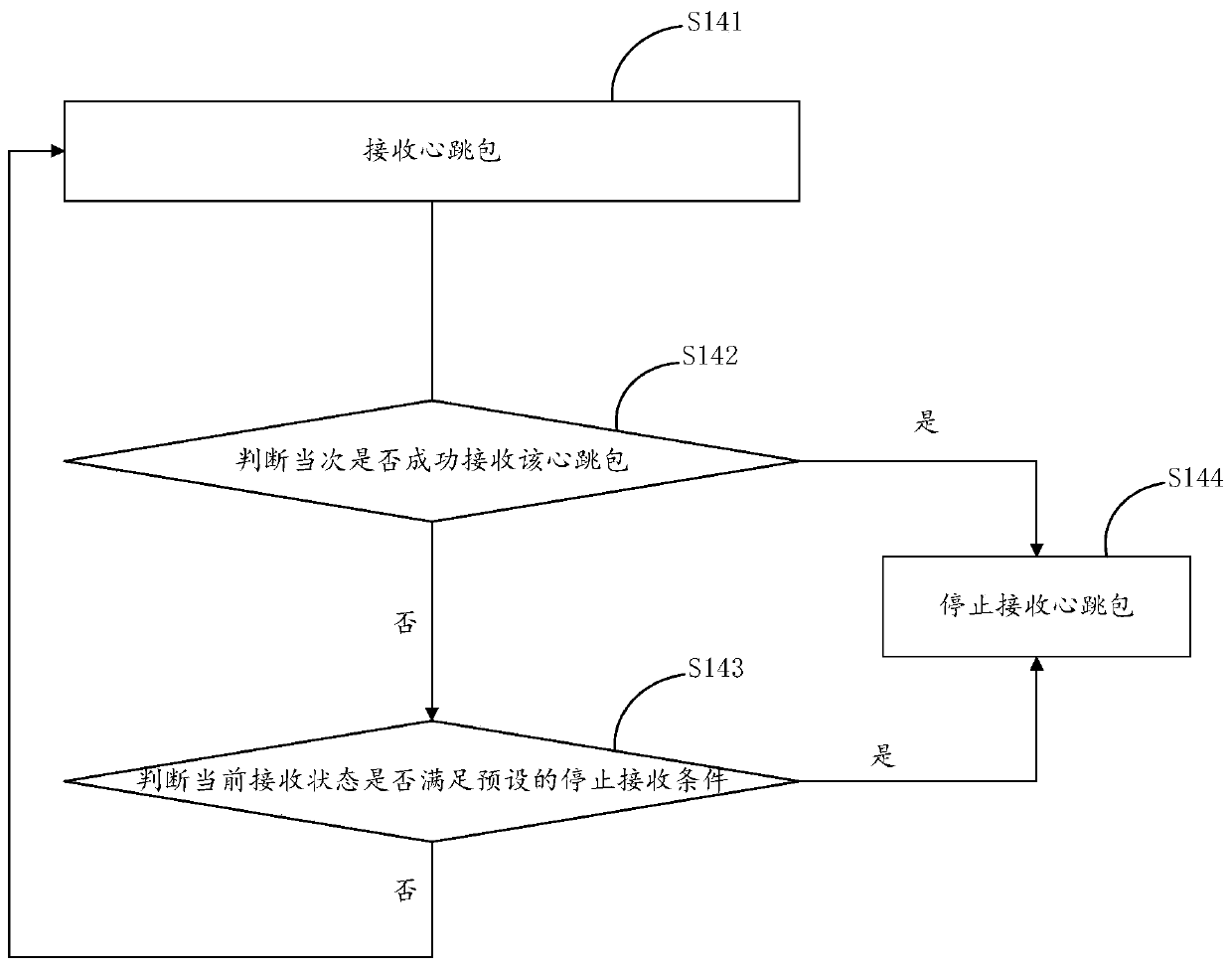
[0115] see Figure 5 , Figure 5 It is a schematic flowchart of the third embodiment of the method for monitoring the survival state of the server in this application. The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is that, further, after the server sends heartbeat packets with a fixed frequency to the device for a period of time, the dynamic device parameters of the device are obtained in real time, and the heartbeat packet frequency of the device is adjusted according to the dynamic device parameters.
[0116] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0117] S31: same as step S21 of the second embodiment;
[0118] S32: The server 10 obtains the static device parameters of the device 20, and calculates the first heartbeat packet frequency of the device 20 according to the static device parameters;
[0119] Wherein, this step S32 is the same as the step S22 of the second embodiment, the first heartbeat packet frequency is the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com