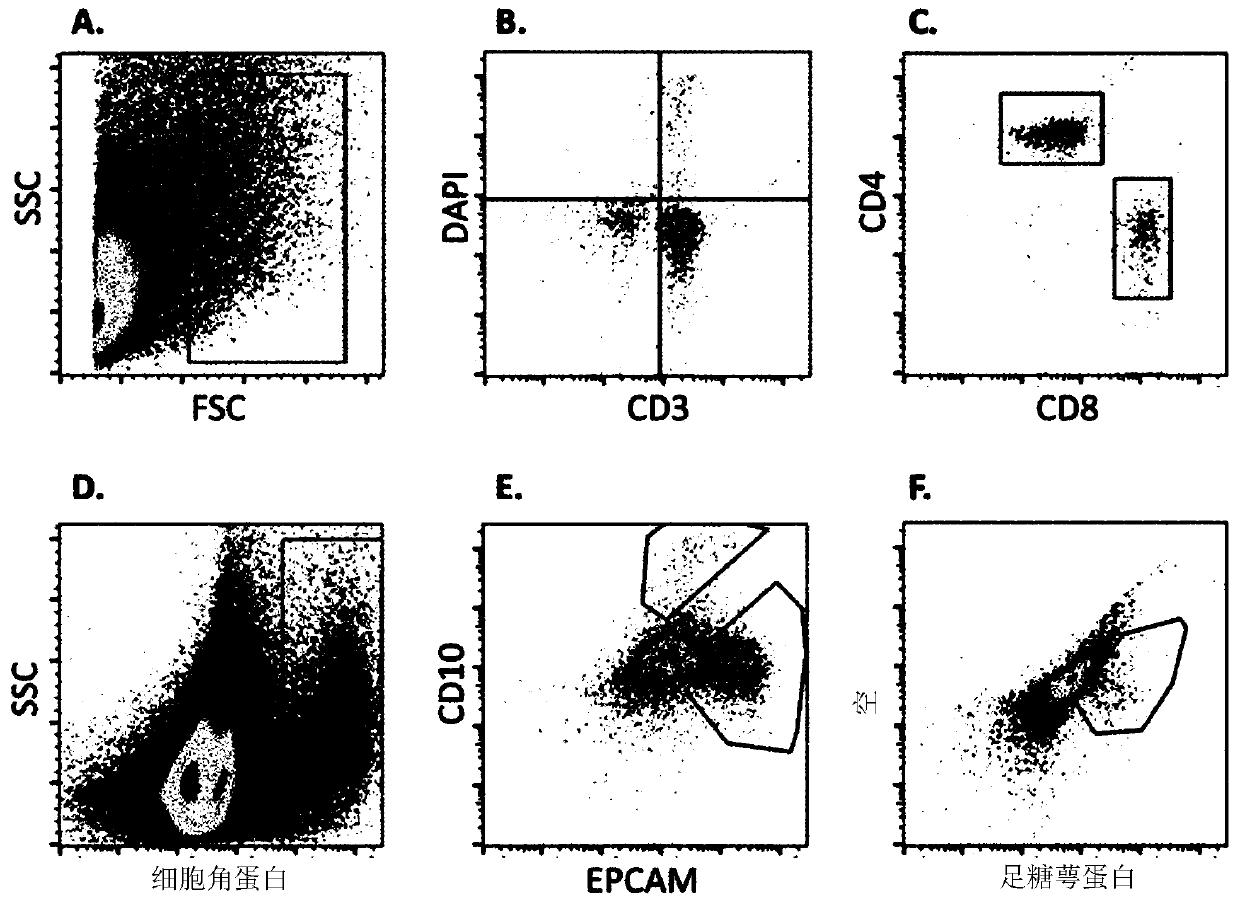
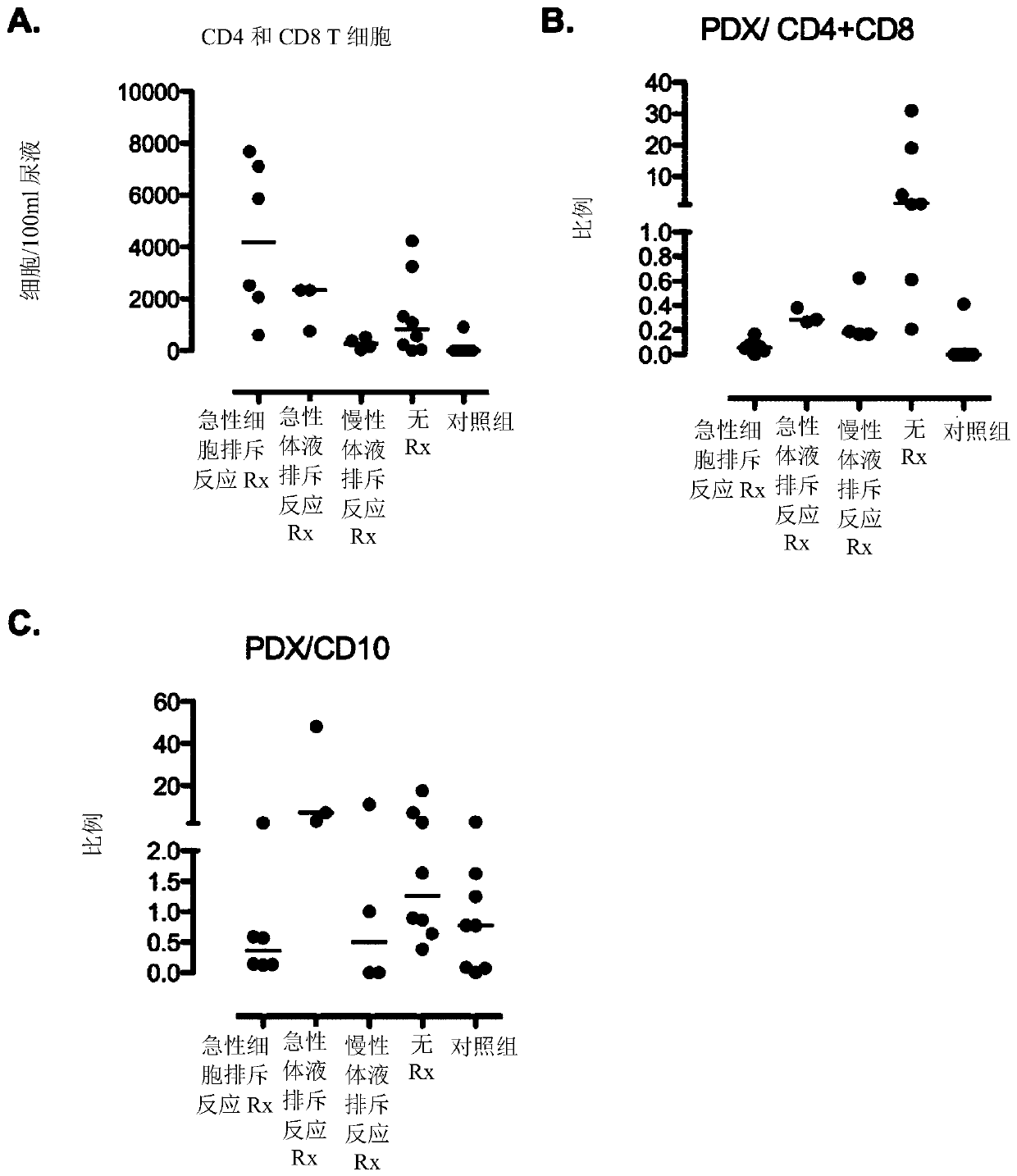
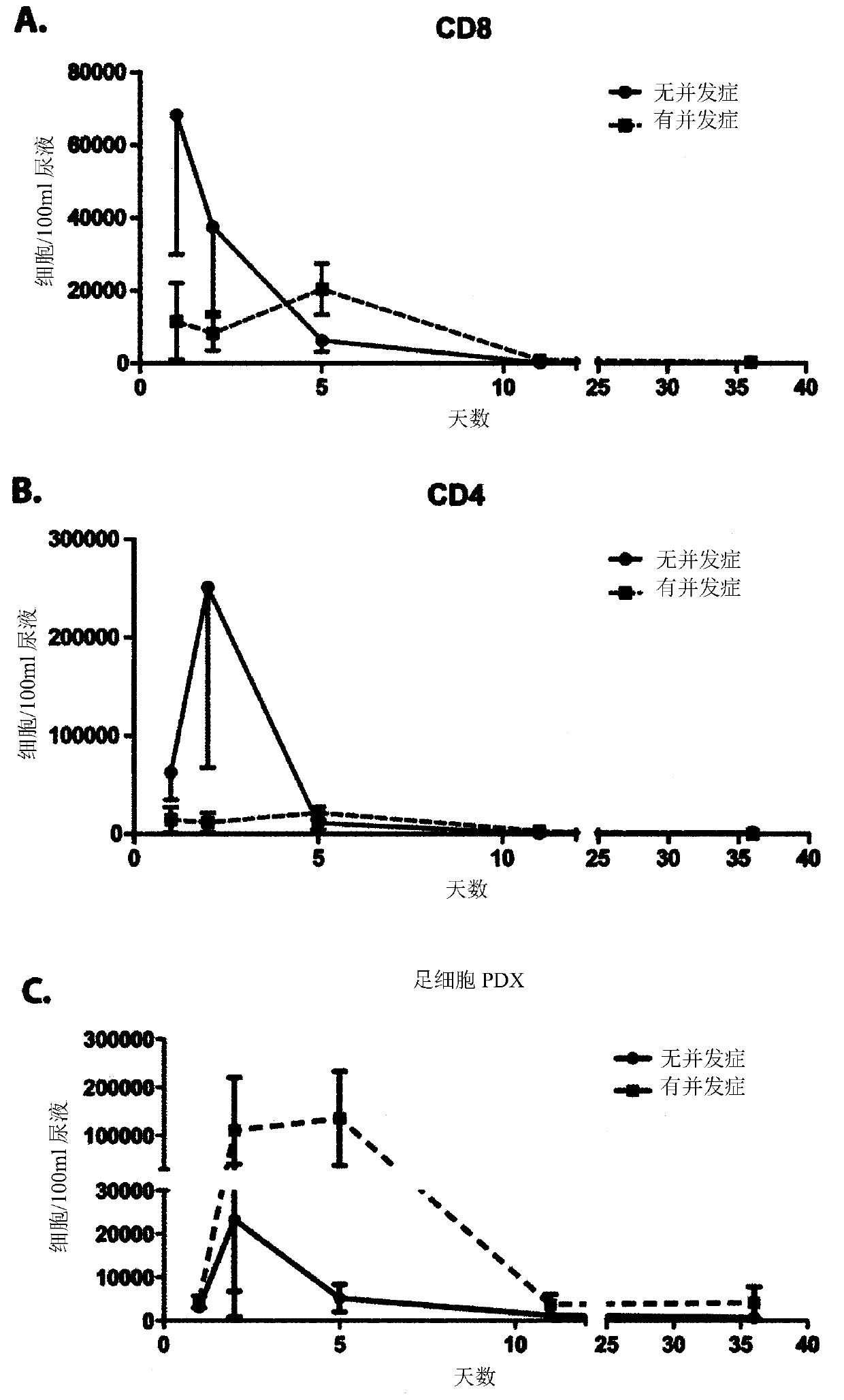
Urine flow cytometry as biomarker of renal diseases
A cell and kidney disease technology, applied in the field of urine flow cytometry as a biomarker of kidney disease, can solve the problems of potential disease recurrence, chronic transplant injury, transplant rejection, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0166] example
[0167] 1. Method
[0168] sample collection
[0169] Urine samples from patients undergoing kidney transplantation were collected by catheter or spontaneously. Store samples in sterile beakers and be ready for analysis within 6 hours of collection.
[0170] cell separation
[0171] Samples were dispensed in 50 ml tubes and centrifuged at 4 °C and 1300 g for 8 min. The supernatant was discarded and the pellets were resuspended and combined in PBS / BSA buffer to give 40ml per sample. Unfixed cells (T cells) were analyzed on the day of sample collection. Fixed cells were analyzed within 7 days of sample collection.
[0172] Fixed cells: For staining for intracellular markers, transfer 10 ml of detached cells to a 15 ml tube and centrifuge at 1300 g for 8 min at 4 °C. Discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in PBS / BSA buffer. The solution was transferred to a 1.5 ml tube and centrifuged at 4 °C and 2300 g for 8 min. Discard the supernatant. T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com