Method for improving stability of super-hydrophobic surface underwater air layer
A super-hydrophobic surface and air layer technology, which is applied in the process, coating, gaseous chemical plating and other directions for producing decorative surface effects, can solve the problems of complex methods, high cost, complex equipment, etc., and achieve simple equipment and reliable The effect of good control and wide substrate selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] This embodiment provides a method for stabilizing the underwater air layer on an aluminum sheet as a substrate.
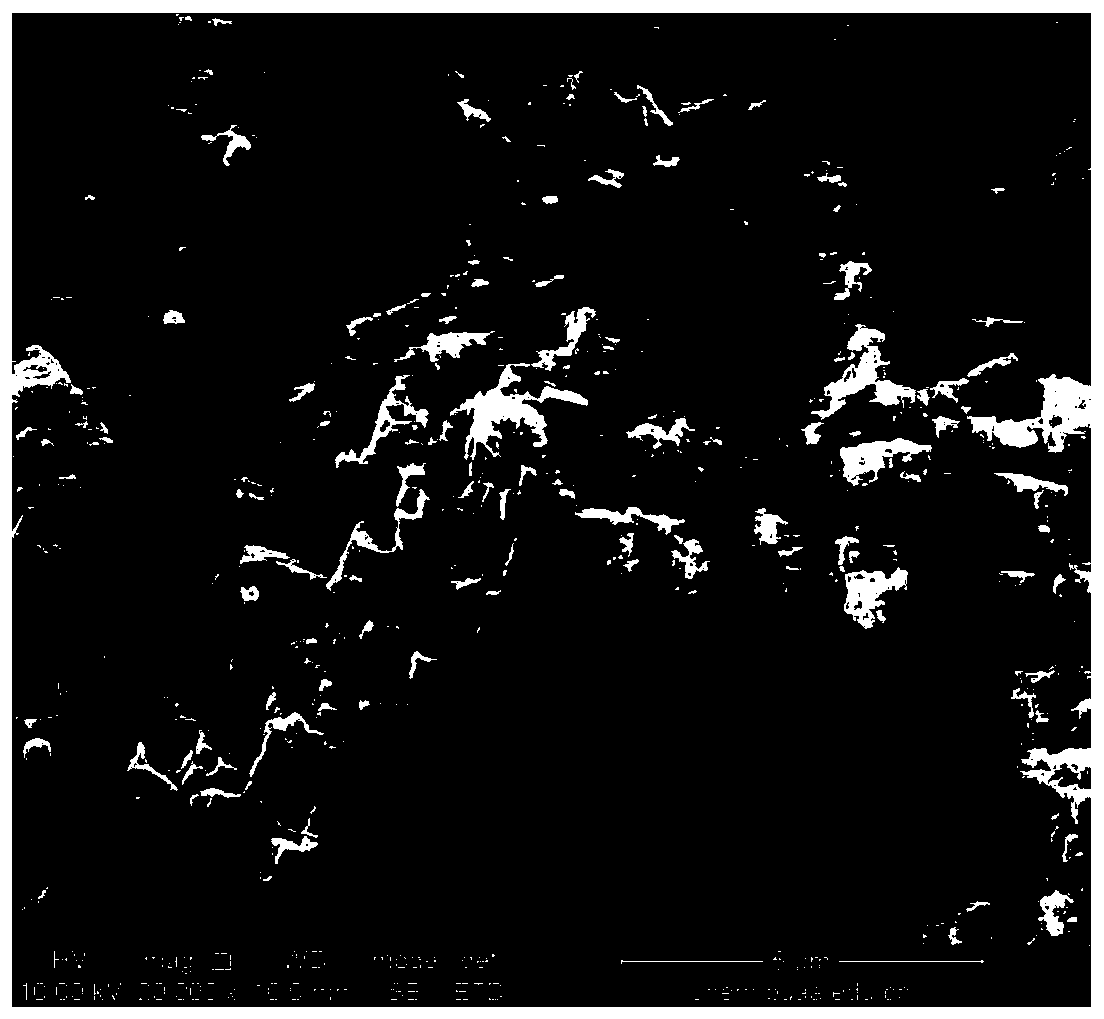
[0038] The aluminum sheet is selected as the substrate, and the rough surface is obtained by chemical etching. The aluminum sheet was corroded with 3 mol / L hydrochloric acid for 10 minutes, ultrasonically cleaned in deionized water for 5 minutes, and blown dry with nitrogen gas. Afterwards, it was modified with perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane and dried in an oven at 120°C for 2 hours to obtain a superhydrophobic surface. The superhydrophobic surface was immersed in 0.1 mol / L Tris-dopamine buffer solution for 10 minutes, and then dried at room temperature to obtain a rough structure superhydrophobic surface modified by the top hydrophilic substance-polydopamine. SEM photographs of the surface (eg figure 1 ) indicates that the surface has a micro-nano composite structure, and its size is from 10 nanometers to 10 microns. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (such...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This embodiment provides a method for stabilizing the underwater air layer on a superhydrophobic surface with polystyrene as the substrate.
[0041] Polystyrene is selected and the rough structured surface is obtained by phase separation method. Chloroform is used as a solvent to prepare a polystyrene solution with a weight fraction of 20%. The solution is spin-coated on a polystyrene substrate at a humidity of 80%, and then dried at 25°C for 24 hours to obtain a superhydrophobic surface. . The superhydrophobic surface was soaked in 0.15 mol / L Tris-dopamine buffer solution for 8 minutes, and then dried at room temperature to obtain a rough-structured superhydrophobic surface modified with hydrophilic substances at the top.
Embodiment 3
[0043] This embodiment provides a method for stabilizing the underwater air layer on a superhydrophobic surface using polydimethylsiloxane as a substrate.
[0044] Polydimethylsiloxane was selected to obtain rough structured surface by template method. Prepare dimethylsiloxane and curing agent in a weight ratio of 10 / 1, stir evenly and remove air bubbles. Select 800 mesh sandpaper and drop-coat trimethylchlorosilane as an anti-adhesive agent. Then pour the prepared mixture onto the sandpaper surface treated with the anti-adhesive agent above, vacuumize in the vacuum container, and then transfer to an oven with a temperature of 60° C. for curing for 4 hours. The cured polydimethylsiloxane film and sandpaper are peeled off to obtain a micro-nano composite rough structure polydimethylsiloxane surface with a reverse structure of sandpaper. The surface is treated with a weight fraction of 0.1% methyltrichlorosilane- Hydrophobic modification was carried out in toluene solution, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com