A common anode micro-display pixel driving circuit and driving method
A pixel drive circuit and common anode technology, applied in static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to improve the accuracy of micro-displays, and achieve the effects of eliminating screen flicker, wide adjustable range, and saving area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
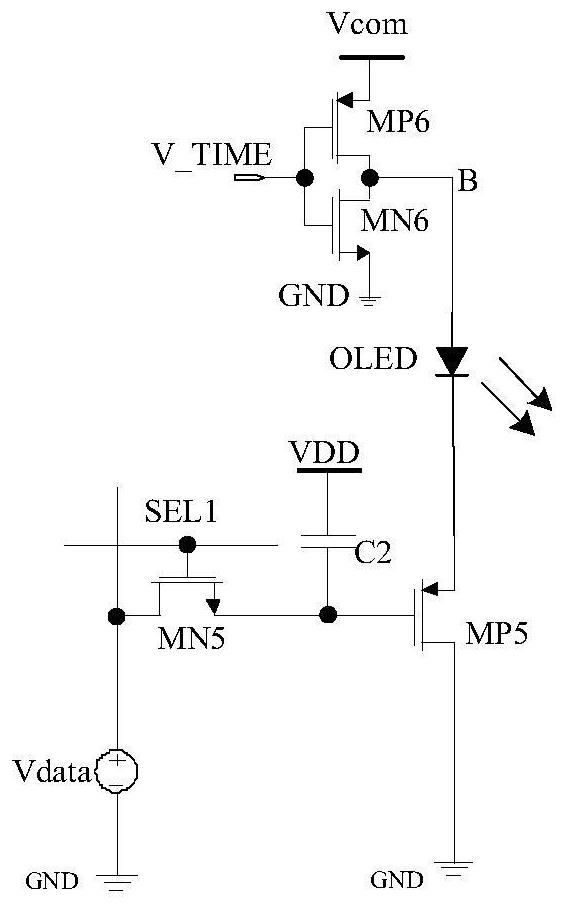
[0020] Such as figure 1 shown.
[0021] A common anode micro-display pixel drive circuit, the drain of the N-type MOS transistor MN5 is connected to the positive terminal of the input voltage source Vdata, the source of the N-type MOS transistor MN5 is connected to one end of the capacitor C2, and the gate of the P-type MOS transistor MP5 connected. The gate of the N-type MOS transistor MN5 is connected to the external control signal SEL1. The negative end of the voltage source Vdata is connected to the ground GND. The source of the P-type MOS transistor MP5 is connected to the cathode of the OLED, and the drain of the P-type MOS transistor MP5 is connected to GND. The OLED anode is connected to point B with the drain of the P-type MOS transistor MP6 and the drain of the N-type MOS transistor MN6. The source of the P-type MOS transistor MP6 is connected to VCOM, the gate of the P-type MOS transistor MP6 and the gate of the N-type MOS transistor MN6 are connected to V_TIME,...
Embodiment 2
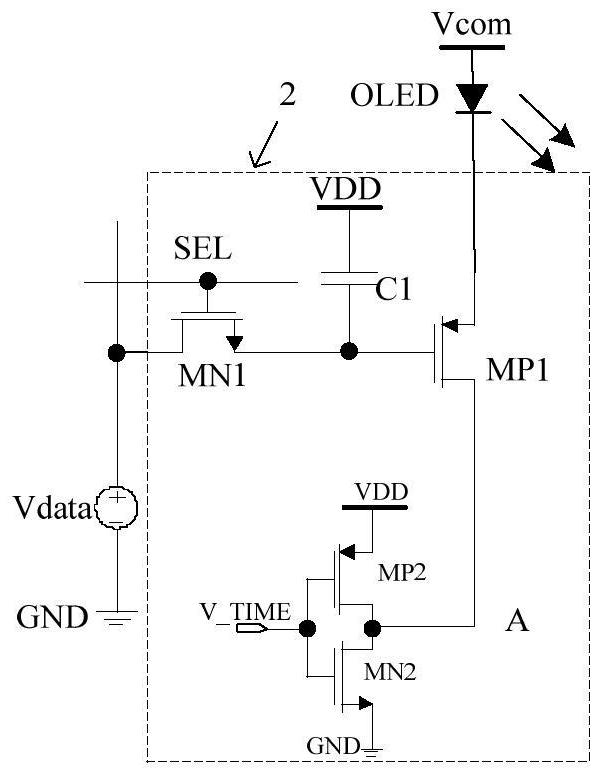
[0026] Such as image 3 .
[0027] A common anode micro-display pixel driving circuit is composed of a specific pixel circuit in the dotted line frame 2, an external voltage source Vdata, and an external OLED. The drain of the N-type MOS transistor MN1 is connected to the positive terminal of the input voltage source Vdata, and the source of the N-type MOS transistor MN1 is connected to one end of the capacitor C1 and the gate of the P-type MOS transistor MP1. The gate of the N-type MOS transistor MN1 is connected to the external control signal SEL. The negative end of the voltage source Vdata is connected to the ground GND. The source of the P-type MOS transistor MP1 is connected to the cathode of the OLED, and the anode of the OLED is connected to the VCOM voltage. The drain of the P-type MOS transistor MP1 is connected to the drain of the P-type MOS transistor MP2 and the drain of the N-type MOS transistor MN2 at point A. The source of the P-type MOS transistor MP2 is c...
Embodiment 3
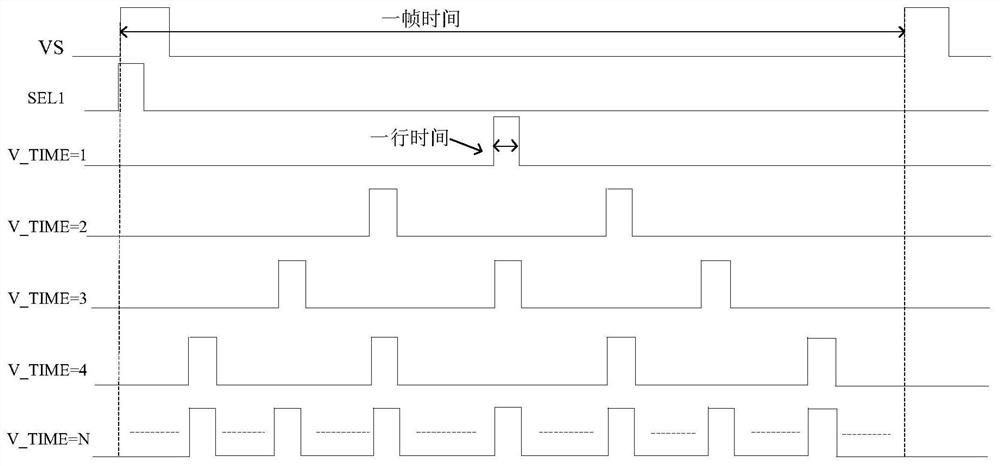
[0032] A common anode micro-display pixel driving method, using PFM control mode, when V_TIME=N, after the field synchronization signal becomes high level, N V_TIME high pulses are generated on average within one field time, and the width of one pulse is one line time , MN6 is turned on when the V_TIME pulse is at a high level, the voltage at point B is equal to the GND voltage, MP5 is turned off, and after the V_TIME pulse becomes low level, the voltage at point B is equal to the VCOM voltage, the current generated by MP5 flows through the OLED, and the OLED starts Lighting; such a cycle, OLED from extinguishing to luminous and then to luminous to extinguished, thus realizing the precise control of the light emitting time of the OLED device, in the case of a fixed pulse width, the precise adjustment of the brightness of the OLED light is realized by adjusting the pulse frequency. The VPLUSE signal is divided into N levels, and regulates the common anode voltage VCOM or the pow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com