Two-dimensional permanent magnet array type magnetic suspension gravity compensator
A permanent magnet array and gravity compensation technology, applied in the field of magnetic levitation, can solve problems such as large parasitic force and complex system structure, and achieve the effects of various forms, large optimization space, and easy implementation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
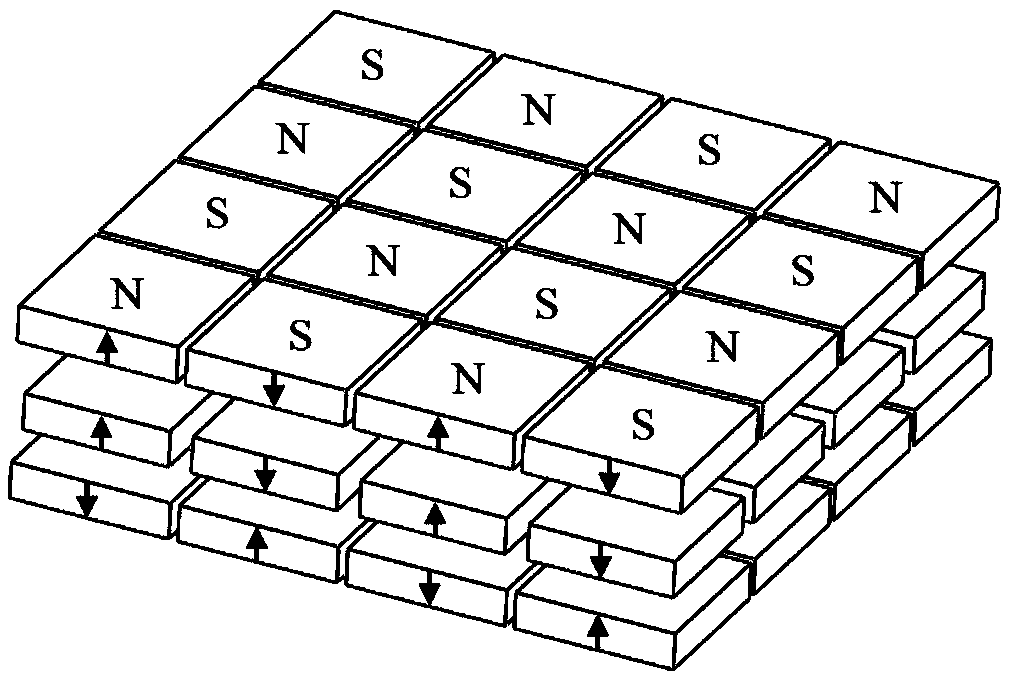
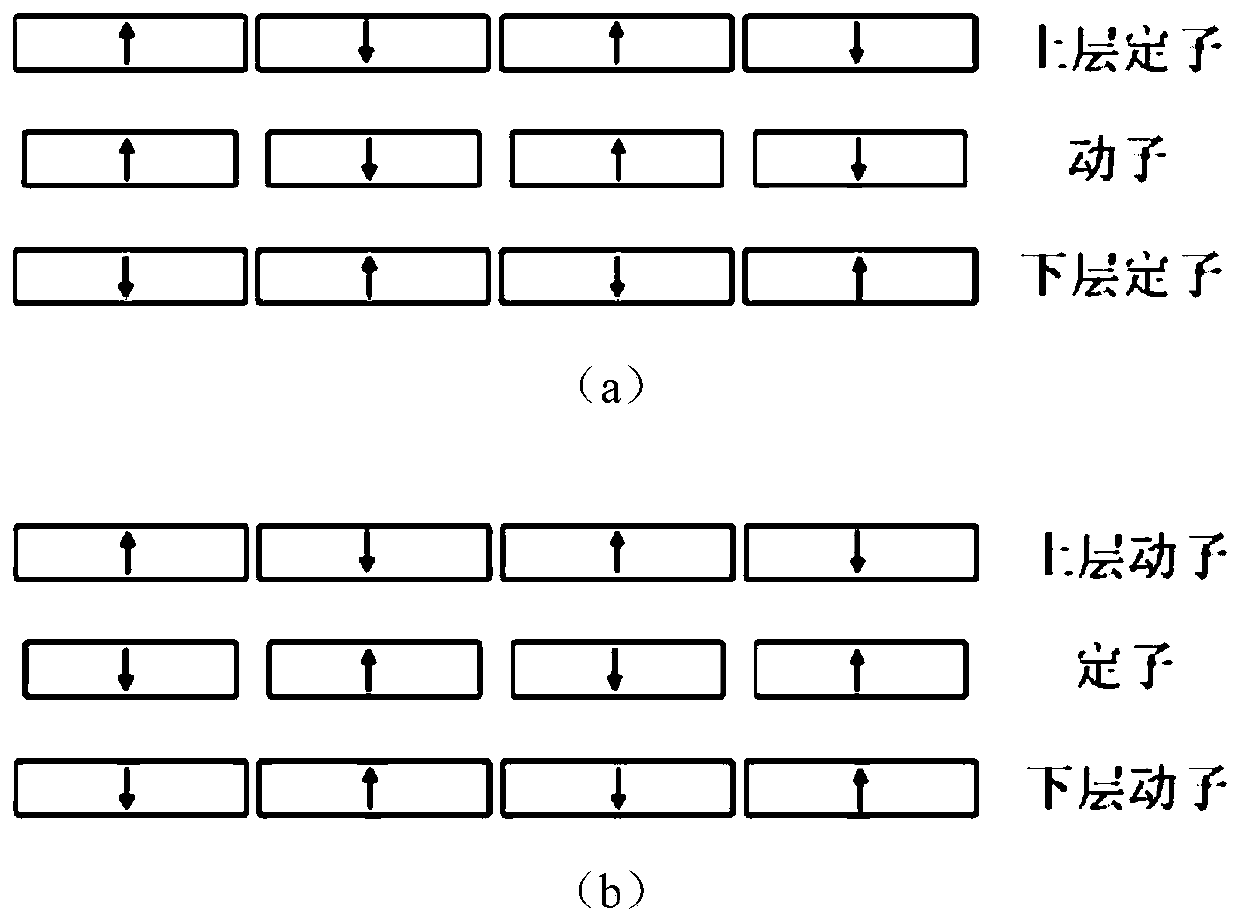
[0028] Embodiment one: see figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 , the two-dimensional permanent magnet array magnetic levitation gravity compensator comprises a stator and a mover, and the compensator of the present embodiment is divided into a single mover (see figure 2 (a) shown) or single stator (see figure 2 (b) shown).
[0029] The first single mover compensator (see figure 2 As shown in (a): The stator includes an upper stator and a lower stator, and a mover is arranged between the upper stator and the lower stator that are parallel and fixedly connected to each other, and there is a vertical air gap between the two-layer stator and the mover; the two-layer stator and the The mover is a two-dimensional array plate structure composed of N×N rectangular permanent magnets, and there is an interval between any two adjacent permanent magnets in each plate structure;
[0030] The magnetization direction of the permanent magnet is vertical, and the magnetization direction...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment two: see Figure 4 to Figure 6 To illustrate, the stator of the two-dimensional permanent magnet array magnetic levitation gravity compensator includes an upper stator and a lower stator that are parallel to each other and are fixedly connected, and the mover includes an upper mover and a lower mover that are parallel to each other and are fixedly connected. Between the upper stator and the lower stator, the two-layer stator and the two-layer mover are two-dimensional array plate structures composed of N×N rectangular permanent magnets, and there is an interval between any two adjacent permanent magnets in each plate structure , there is a vertical air gap between any two adjacent flat plate structures;
[0038] The magnetization direction of the permanent magnet is vertical, and the magnetization direction of any two adjacent permanent magnets in each flat plate structure is opposite;
[0039] The magnetization directions of the permanent magnets of the sta...
Embodiment 3
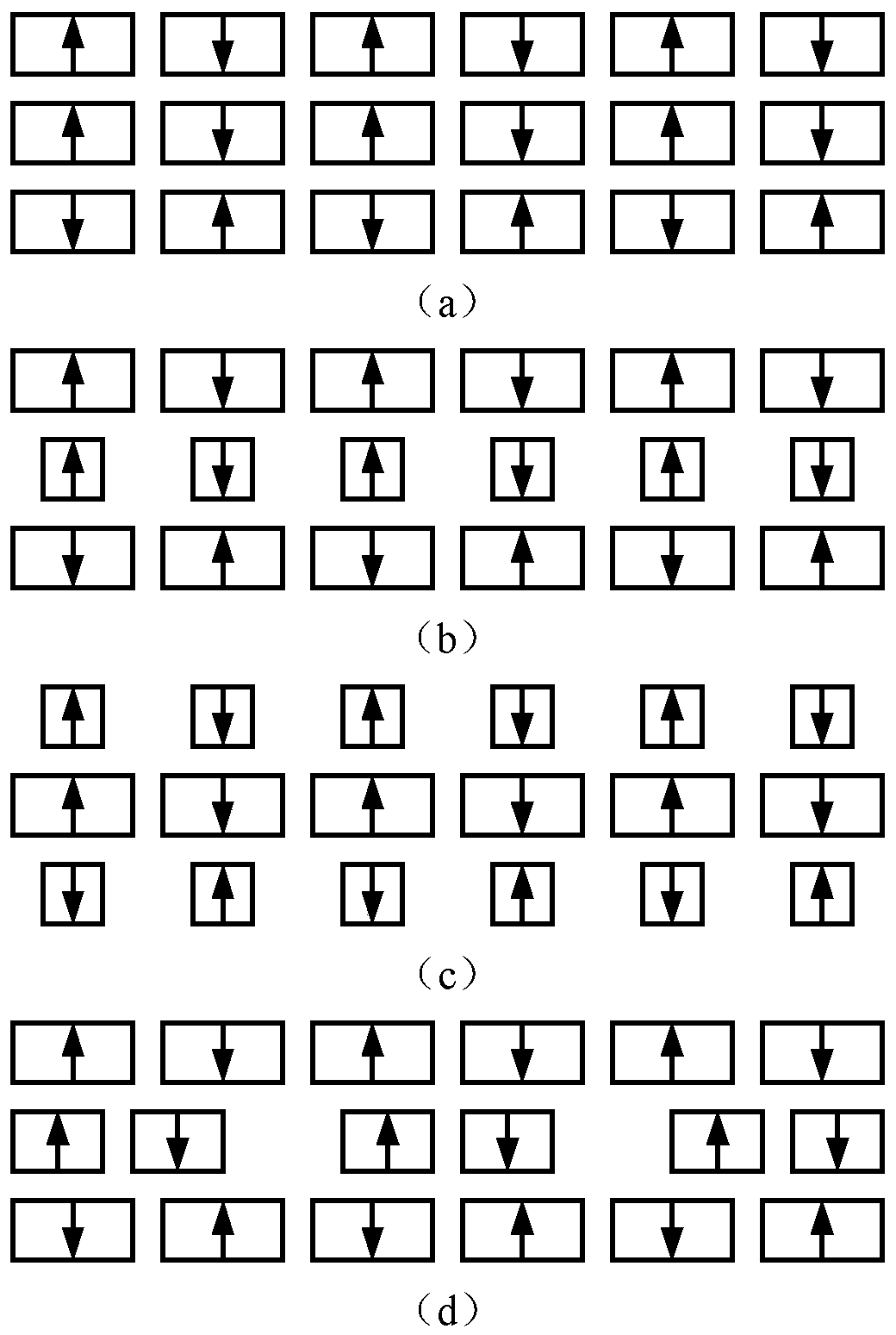
[0045] Embodiment three: see Figure 7 with Figure 8 To illustrate, each planar structure of the compensator in this embodiment is a two-dimensional Halbach permanent magnet array planar structure, and the two-dimensional Halbach permanent magnet array planar structure includes N×N vertically magnetized rectangular permanent magnets and 2N( N-1) horizontally magnetized rectangular permanent magnets, a horizontally magnetized permanent magnet is arranged between any two adjacent vertically magnetized permanent magnets, and the magnetization direction of the horizontally magnetized permanent magnet is from a vertical The magnetization permanent magnet points to another adjacent vertical magnetization permanent magnet, and the magnetization directions of any two adjacent horizontal magnetization permanent magnets are opposite.
[0046] The two-dimensional Halbach permanent magnet arrays are distributed in such a way that the adjacent vertical stator permanent magnets are magnet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com