Stabilization of hazardous materials
A hazardous, aluminum hydroxide-based technology for arsenic waste stabilization/solidification that can solve problems such as not being a long-term effective option
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
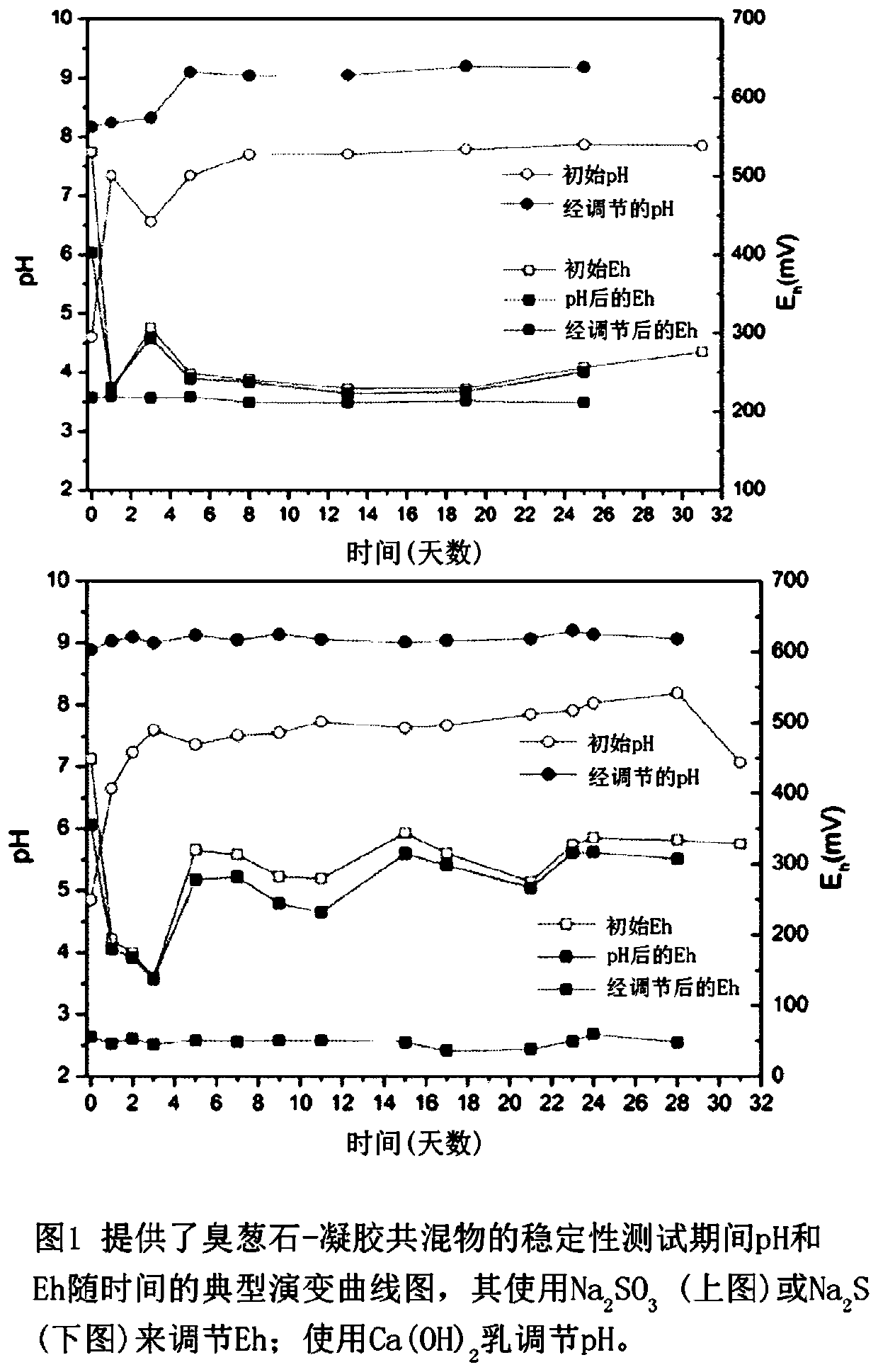
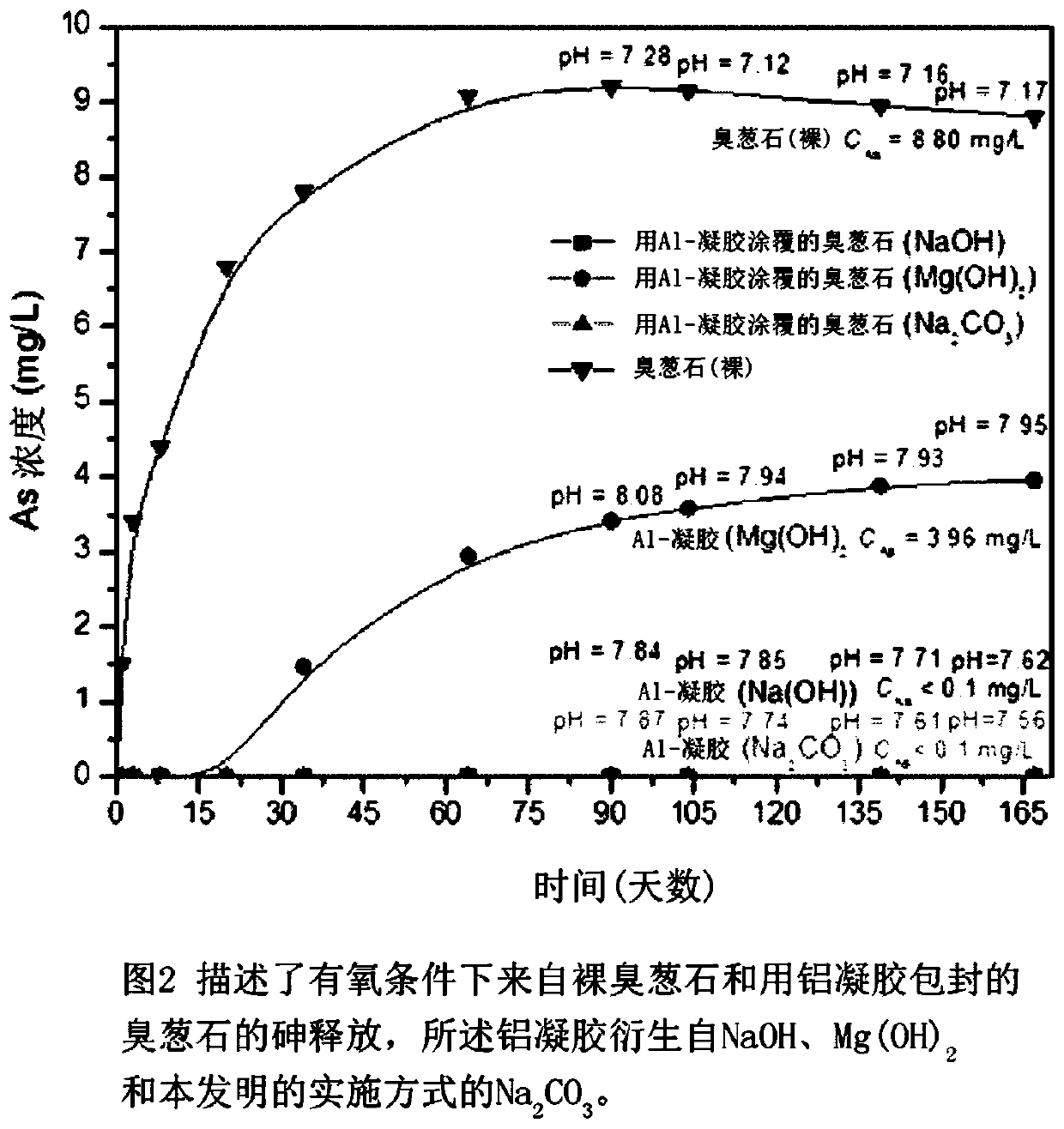
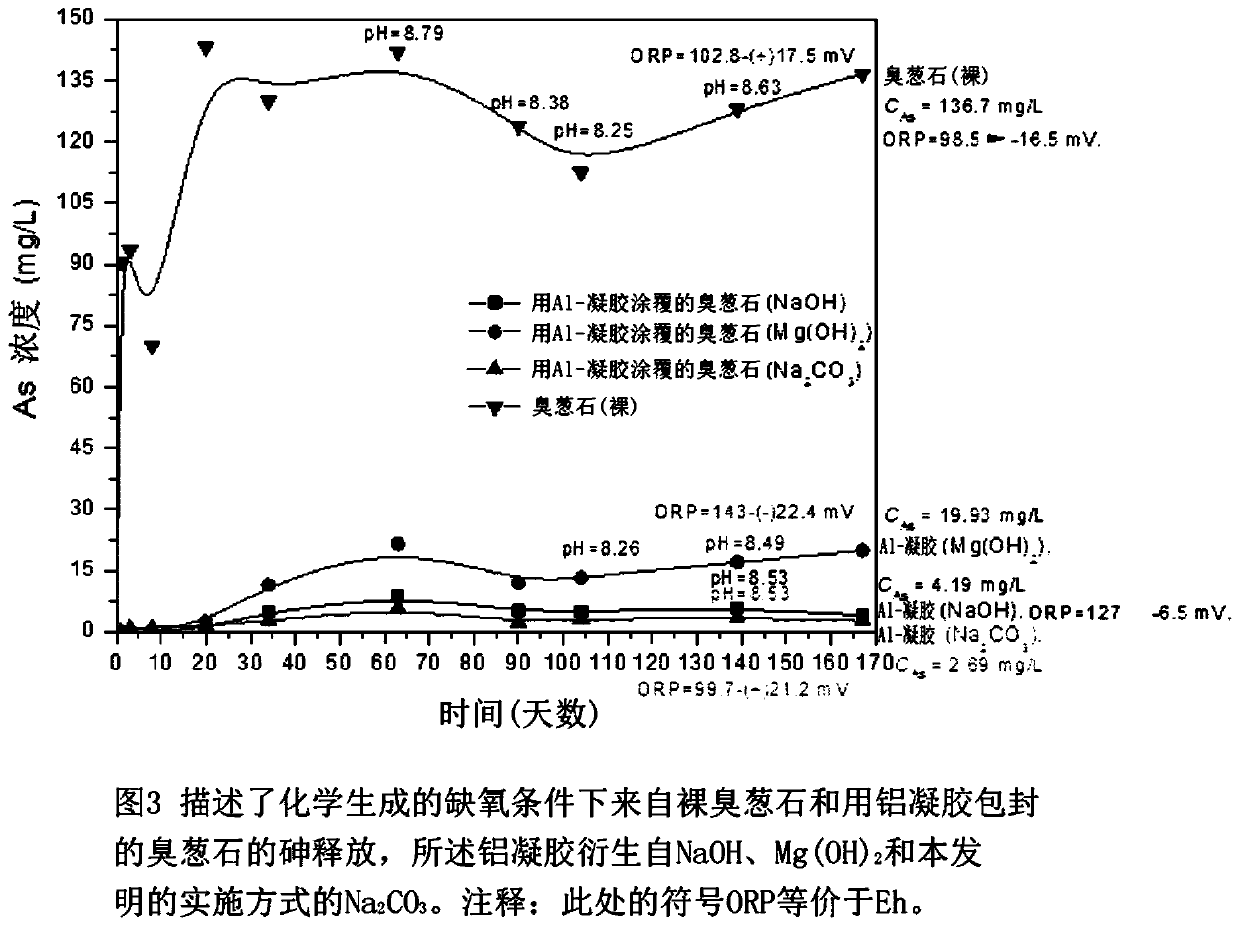
[0037] Preparation of scorodite
[0038] The scorodite base material was synthesized by atmospheric precipitation by using the seeding and supersaturation control method previously developed by the inventors. In this procedure, 0.5 L of As(V)-Fe(III)-H 2 SO 4 The solution was placed in a reactor and heated to 95°C. When the temperature inside the reactor reached about 65°C and the pH dropped to 0.45, 5 g of hydrothermally generated scorodite was seeded into the reactor. In the presence of seeds, precipitation was initiated and proceeded for 24 hours after which time the slurry was filtered using a pressure filter with a 0.22 μm pore size membrane filter. The solids were then subjected to several washes and successive TCLP type wash steps (TCLP stands for Toxic Characteristic Leachability Program method developed by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)). The freshly washed scorodite particles are then used for aging with aluminum hydroxide gel. All reagents and che...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com