Unmanned aerial vehicle flight path planning method based on improved clustering algorithm
A technology of track planning and clustering algorithm, which is applied to computer parts, computing, navigation computing tools, etc. It can solve the problems of large amount of calculation and low accuracy, and achieve the goal of small amount of calculation, high accuracy, and enhanced exploration and efficiency. The effect of mining
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0042] Specific implementation mode one: the specific process of a UAV trajectory planning method based on an improved clustering algorithm in this implementation mode is as follows:
[0043] Problem description of UAV trajectory planning
[0044] UAVs have demonstrated their advantages and potential in military and civilian fields. In order to achieve autonomous navigation of UAVs, aspects such as modeling, trajectory planning, and control system design must be considered. Among them, trajectory planning is an important problem that has been extensively studied.
[0045]UAV trajectory planning is to find the optimal or suboptimal trajectory from the starting point to the destination under the condition of satisfying multiple constraints (including UAV attributes and terrain constraints). The quality of the flight path is measured by indicators such as flight length, flight altitude, and probability of being destroyed. Therefore, the trajectory planning problem can be descr...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0109] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the expression for calculating the P target value in the step 1 is:
[0110]
[0111] x=(x 1 ,y 1 ,z 1 ,...,x w ,y w ,z w ) T
[0112] s.t.x j ∈[x a ,x b ],y j ∈[y a ,y b ],z j ∈[z a ,z b ],j=1,...,w
[0113] where x is x 1 or x N , f 1 (x) is the minimum total track length, f 2 (x) is the total flight altitude, g k is the constraint function, k is the number of clusters; x 1 ,y 1 ,z 1 is the coordinate value of the first path point, x w ,y w ,z w is the coordinate value of the wth path point, w is the number of paths in the track; x j ,y j ,z j is the coordinate value of the jth waypoint, and j is the serial number of the waypoint in the track; [x a ,x b ],[y a ,y b ] and [z a ,z b ] denote the lower and upper bounds for the x, y and z coordinates, respectively.
specific Embodiment approach 3
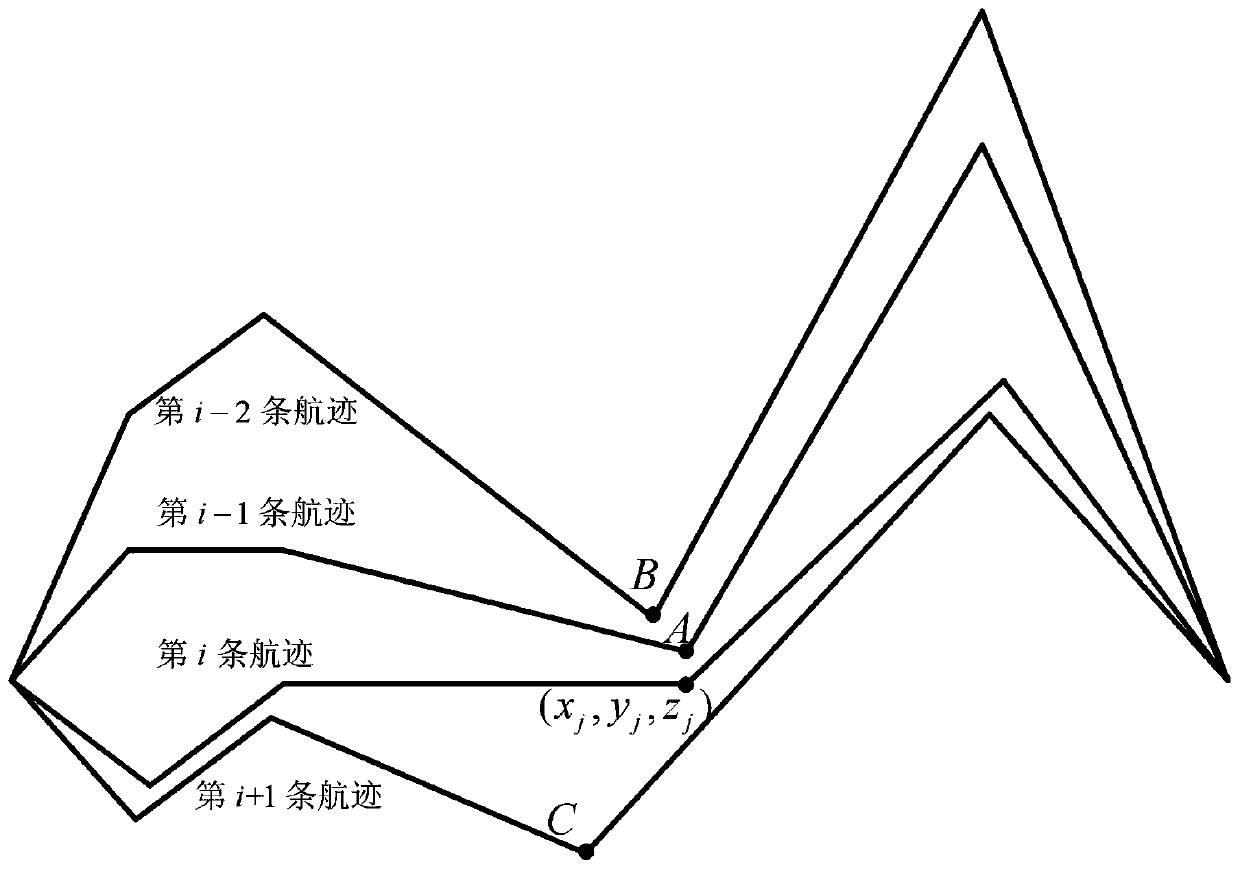
[0114] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in the step three, a clustering algorithm is used to find the neighbor path point S of each path point, S=Clustering (P, w, K); The specific process is:
[0115] Step 31. Set the population P, the number of path points w, and the maximum number of clusters K;
[0116] Let j = 2;
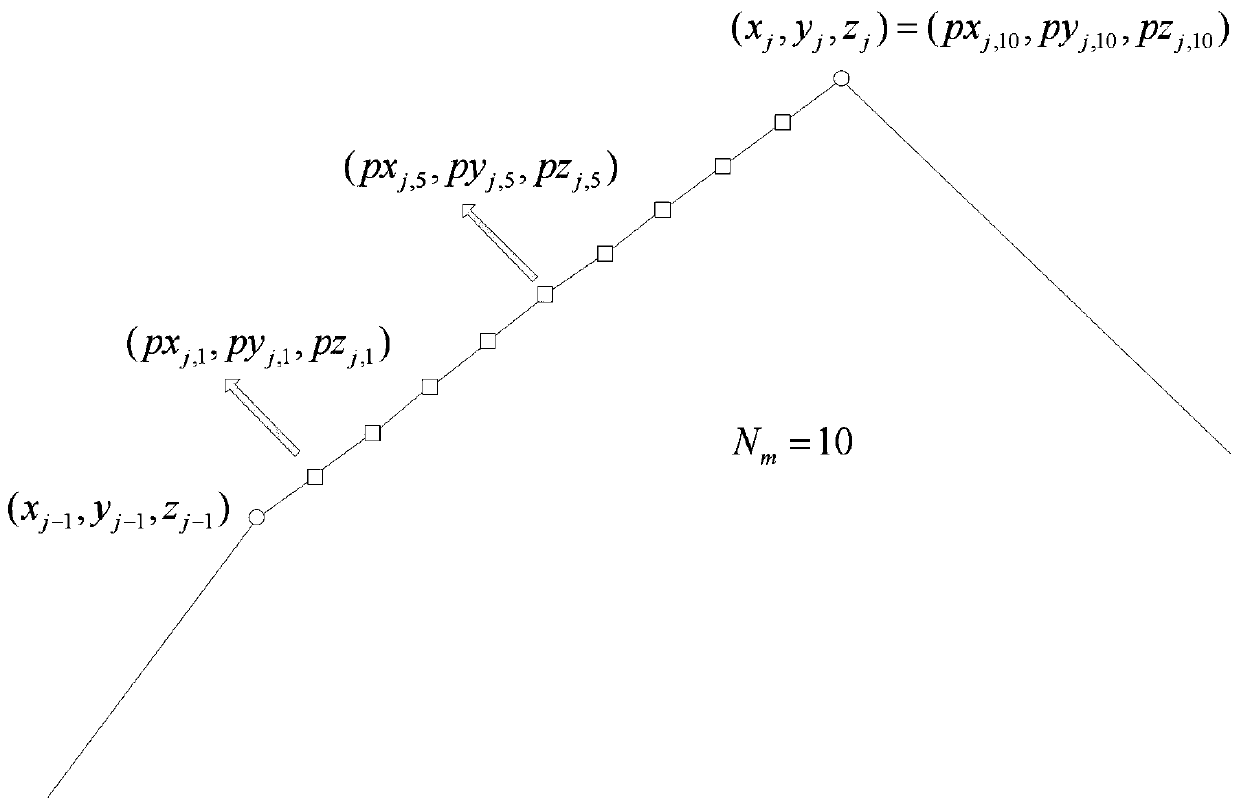
[0117] Step 32. Find the waypoints with sequence number j in all tracks to form global waypoints
[0118] In the formula, is the x-coordinate value of the jth waypoint of the first track, is the x-coordinate value of the jth waypoint of the Nth track, is the y-coordinate value of the jth waypoint of the first track, is the y-coordinate value of the jth waypoint of the Nth track, is the z-coordinate value of the jth waypoint of the first track, is the z-coordinate value of the jth waypoint of the Nth track;
[0119] Step 33, use the K-means algorithm to convert the global...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com