Synchronous permanent magnet coupler with single permanent magnet rotor
A permanent magnet rotor and coupling technology, applied in the direction of synchronous clutch/brake, permanent magnet clutch/brake, magnetic circuit rotating parts, etc., to achieve the effect of small eddy current and low temperature rise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
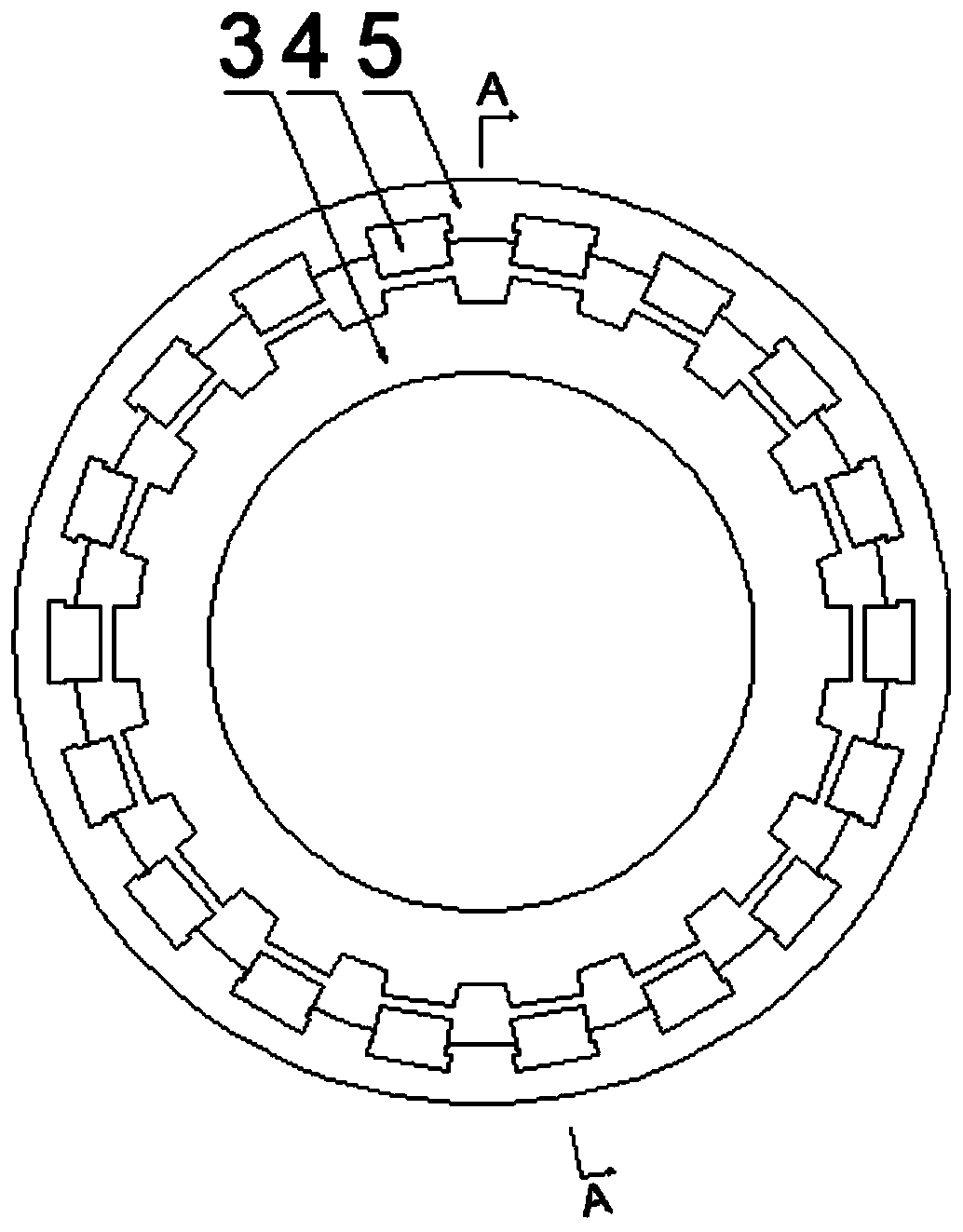
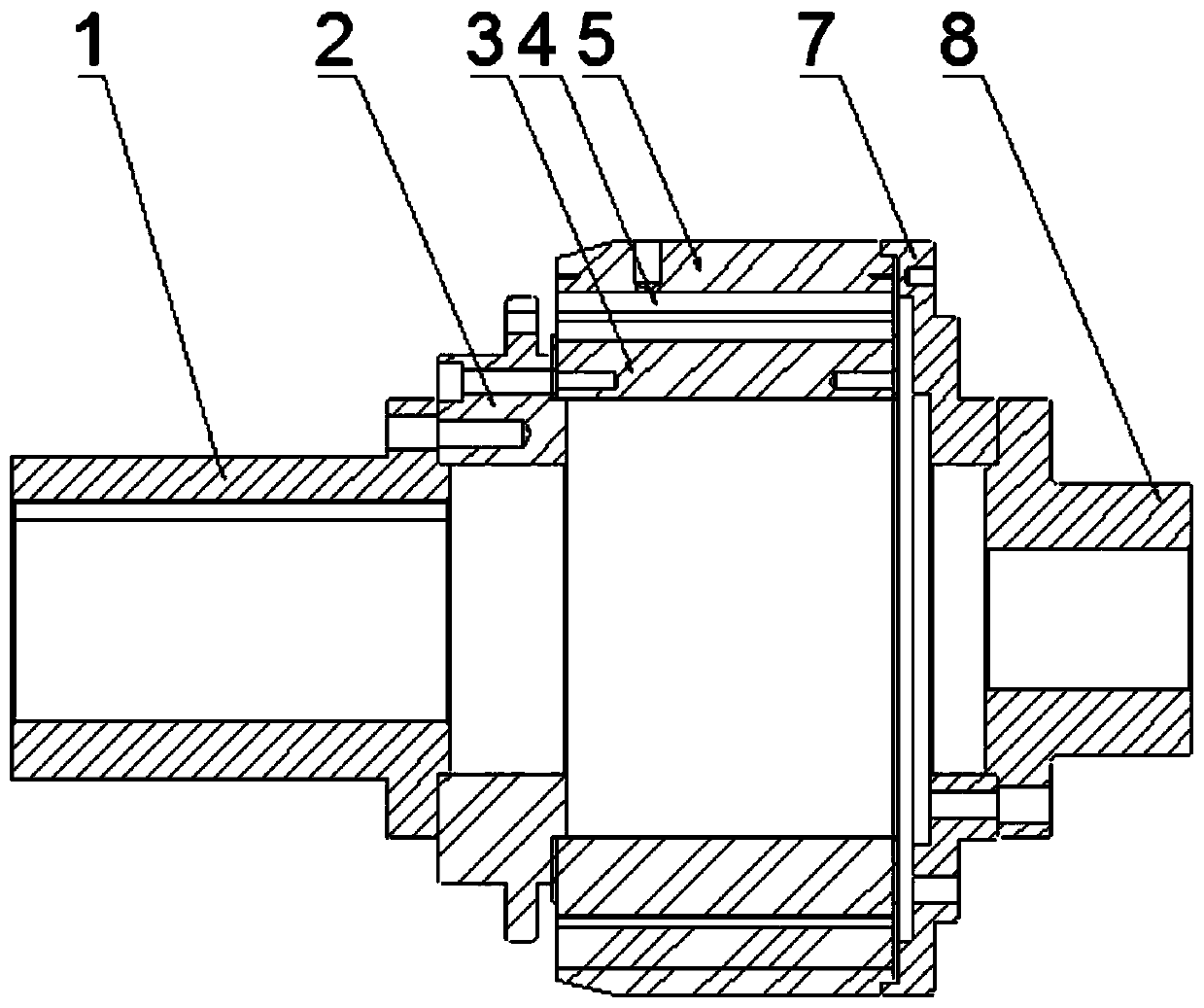
[0046] like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, the input end coupling 1 and the output end coupling 8 are used to connect the rotor of the permanent magnetic coupling with the drive system and the load, and the two can be exchanged without affecting the normal use of the equipment. The input-end adapter plate 2 and the output-end adapter plate 7 are connecting plates between the inner and outer rotors and the coupling; the reluctance inner rotor 3 has no permanent magnets 4, only a certain number of convex stages, so that the magnetic resistance of the equipment The path changes, and its number is the same as the number of salient stages on the inner rotor 3 of the reluctance. In this device, the reluctance inner rotor 3 and the permanent magnet rotor 5 can be interchanged without affecting the normal use of the device
Embodiment 2
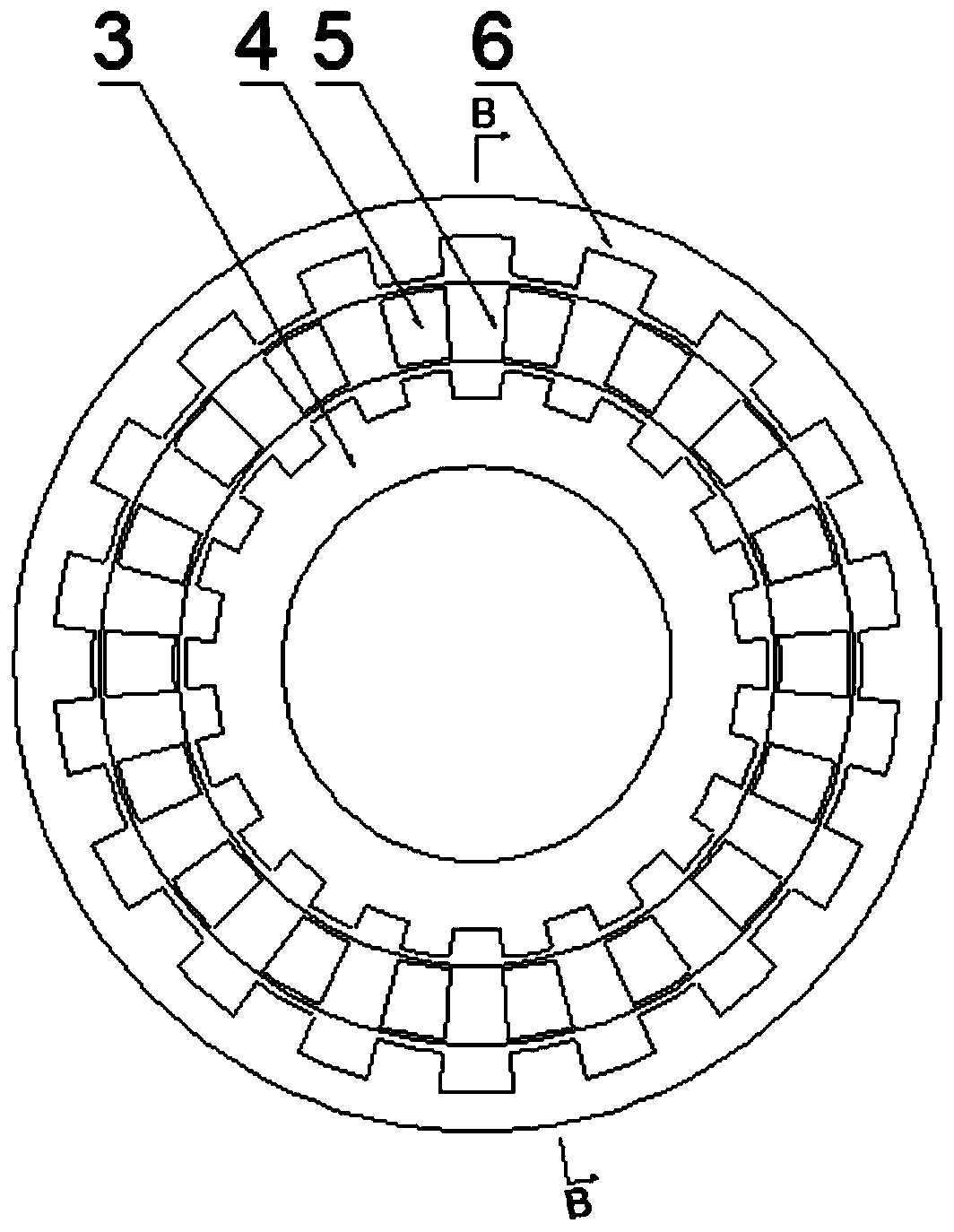
[0048] The permanent magnetic coupling in this embodiment is similar to the permanent magnetic coupling in Embodiment 1, the difference lies in the structure of the reluctance rotor. like image 3 , Figure 4 As shown, the input end coupling 1 and the output end coupling 8 are used to connect the rotor of the permanent magnetic coupling with the drive system and the load, and the two can be exchanged without affecting the normal use of the equipment. The reluctance inner rotor 3 and the reluctance outer rotor 6 are both arranged on the right end face of the input adapter plate 2, the permanent magnet rotor 5 is arranged on the left end face of the output end adapter plate 7, and the reluctance inner rotor 3 and the reluctance outer rotor No permanent magnet 4 is placed on 6, only the same number of salient stages, and the salient stages of the inner and outer rotors of the reluctance are opposite one by one, and the salient stages are axially overlapped, so that the magnetic ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] like Figure 5 As shown, the input end coupling 1 and the output end coupling 8 are used to connect the rotor of the permanent magnetic coupling with the drive system and the load, and the two can be exchanged without affecting the normal use of the equipment. The input side reluctance rotor 9 is a reluctance rotor and it is a disc-shaped convex structure, and the size of the convex is related to the size of the permanent magnet 4 and the transmission torque. In the permanent magnet rotor fixed plate 10, the magnet mounting plate 11 is made of non-magnetic material. The magnet mounting plate 11 is slotted on one side, and the permanent magnet 4 is placed in the groove. The magnet mounting plate 11 and the magnet cover 13 seal the permanent magnet 4 together. . The sleeve 12 is used to connect the double-disc reluctance rotors so that the two rotors can run synchronously. The permanent magnet rotor fixing disc 10 is used together with the permanent magnet rotor connect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com