APT detection correlation analysis method based on graph algorithm
A technology of correlation analysis and graph algorithm, which is applied in the field of information security, can solve the problems of lack of APT attacks, high false alarm rate, and inability to attack event correlation, etc., and achieve the effect of visualization, high accuracy, and low false alarm rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
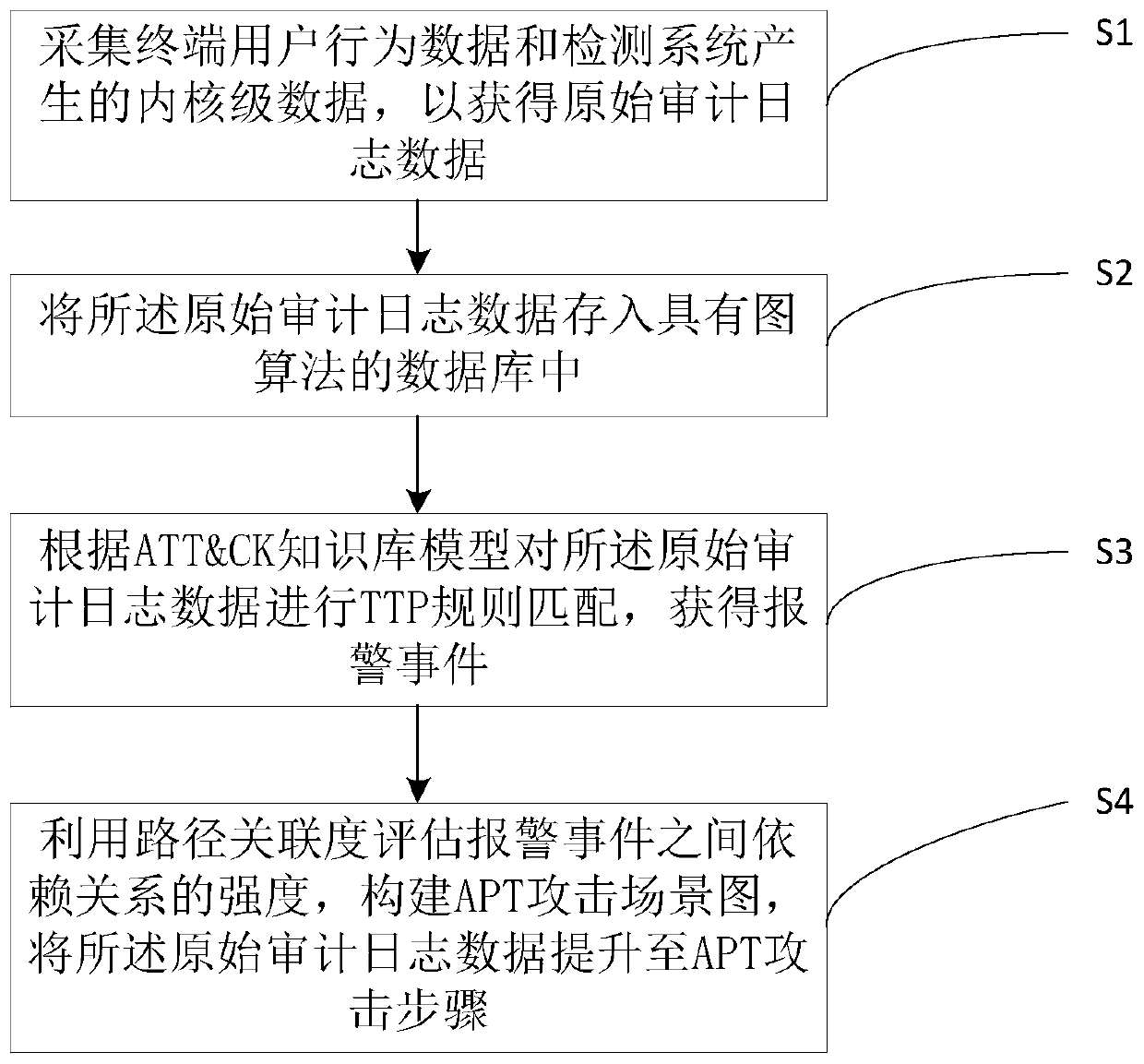
[0051] A graph algorithm-based APT detection association analysis method, see figure 1 , including the following methods:
[0052] S1: Collect end user behavior data and kernel-level data generated by the detection system to obtain original audit log data; specifically, the kernel-level data generated by the detection system includes real-time operation information of processes in the file or network dimension.
[0053] S2: Store the original audit log data into a database with a graph algorithm; the database with a graph algorithm includes a graph database, wherein nodes in the database represent entities, including processes, files (including PE files) and networks ;Relationships represent relationships between entities in this database.
[0054] Specifically, the method can store the original audit log data into a graph database or other databases with a graph structure. In this database, nodes can have their own attributes, such as the name of the process, startup paramete...
example 1
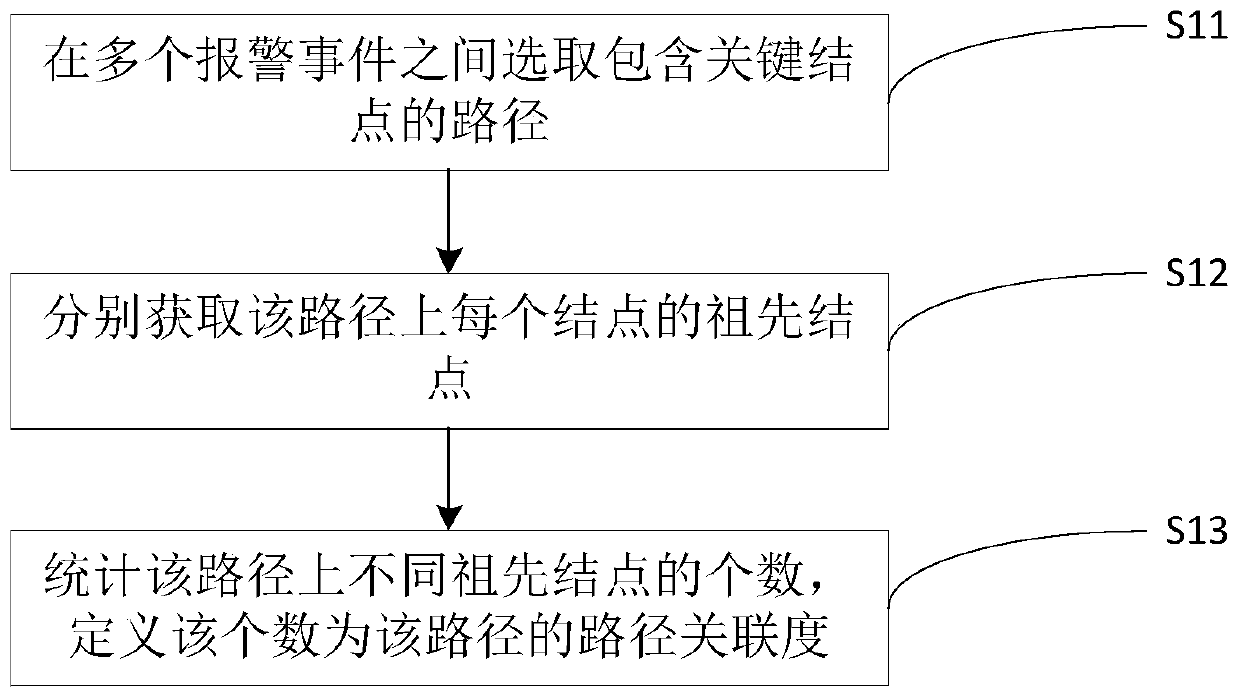
[0068] Example 1: The path P1->P2->P3->P4->P5 represents the creation process of a series of processes. The ancestor node of all nodes in this path is P1, so path correlation (P1, P5) = 1, indicating that the nodes of this path only contain one ancestor node. From the actual situation, P1 to P5 are in the information have a strong correlation.
example 2
[0069] Example 2: In the path P1->F1->P2->P3->F2->P4, P1 writes data to F1, P2 reads data from F1, then creates a child process P3, P3 writes the file F2, and F2 starts process P4. In this path, the ancestor nodes of each node are P1, P1, P2, P2, P2, P4 respectively, and the number of ancestor nodes (coverage) is 3, therefore, path correlation(P1,P4)=3 , indicating that the nodes of this path only contain three ancestor nodes. From the actual situation, the information correlation between P1 and P4 is relatively weak. If in the above example (path correlation(P0,F)<=path thres), path thres is set to 2, then the path correlation degree of the path is 3, which is greater than 2, indicating that the nodes in the path do not satisfy the TTP rule.
[0070] In addition, since there may be multiple paths between two nodes in the graph database, this method prefers the shortest path with key nodes. Key nodes mainly refer to files and networks operated by processes. The addition of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com