A method for automatically measuring the propagation delay of an irig-b timing signal, a timing slave station and a timing system
A technology for signal propagation and automatic measurement, applied in transmission systems, time-division multiplexing systems, multiplexing communications, etc., can solve problems such as manual measurement of propagation delay, facilitate practical promotion and application, and reduce technical requirements Good level and compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
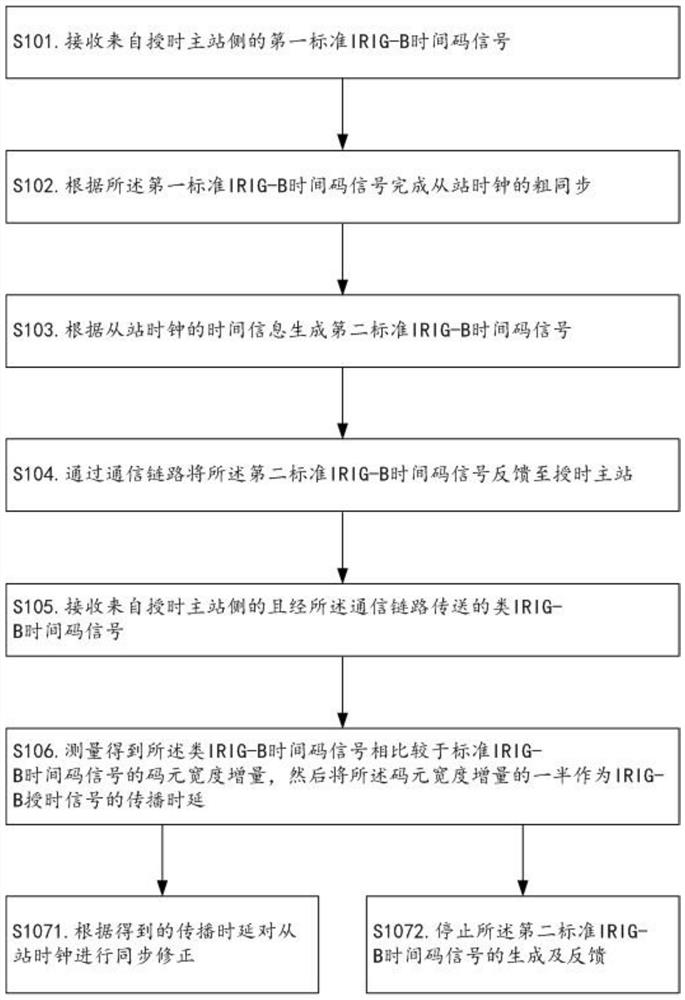
[0051] like Figures 1 to 3 As shown, the method for automatically measuring the propagation delay of an IRIG-B timing signal provided in this embodiment may, but is not limited to, include the following steps S101 to S106.
[0052] S101. Receive a first standard IRIG-B time code signal from the timing master station side, wherein the first standard IRIG-B time code signal is generated on the timing master station side according to the time information of the master station clock.
[0053] In the step S101, the first standard IRIG-B time code signal is a standard IRIG-B (DC) serial time code signal, and the generation method is an existing conventional method.
[0054] S102. Complete the coarse synchronization of the slave station clocks according to the first standard IRIG-B time code signal.
[0055] In the step S102, the method of performing coarse synchronization is the existing conventional time synchronization method, which may be but not limited to the following steps:...
Embodiment 2
[0072] like Figure 4As shown, based on the technology of the first embodiment, this embodiment provides a timing slave station for implementing the method described in the first embodiment, including a signal transceiver unit, a coarse synchronization processing unit, a signal generation unit, and a delay measurement unit unit; on the one hand, the signal transceiver unit is used to receive the first standard IRIG-B time code signal and IRIG-B-like time code signal from the timing master station side, and on the other hand, it is used to feed back to the timing master station through the communication link The second standard IRIG-B time code signal, wherein the first standard IRIG-B time code signal is generated on the side of the timing master station according to the time information of the master station clock, and the second standard IRIG-B time code signal is generated according to the time information of the master station clock. The first standard IRIG-B time code sig...
Embodiment 3
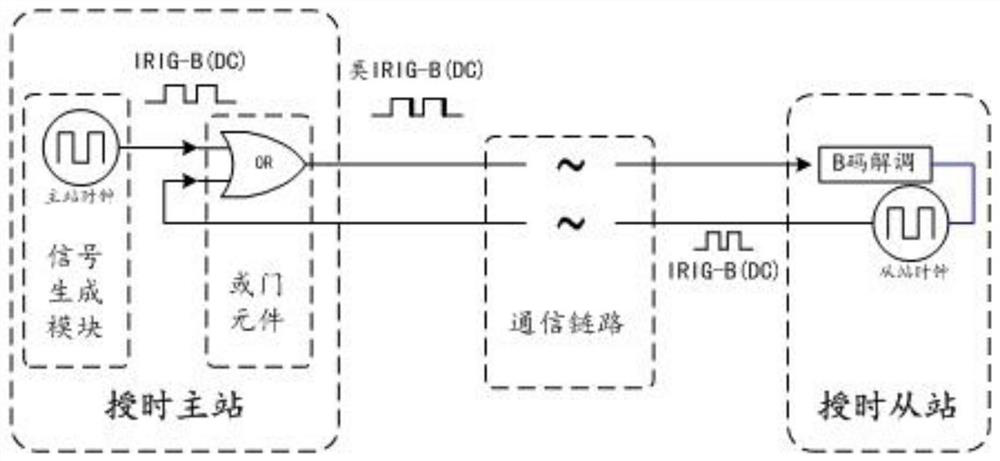
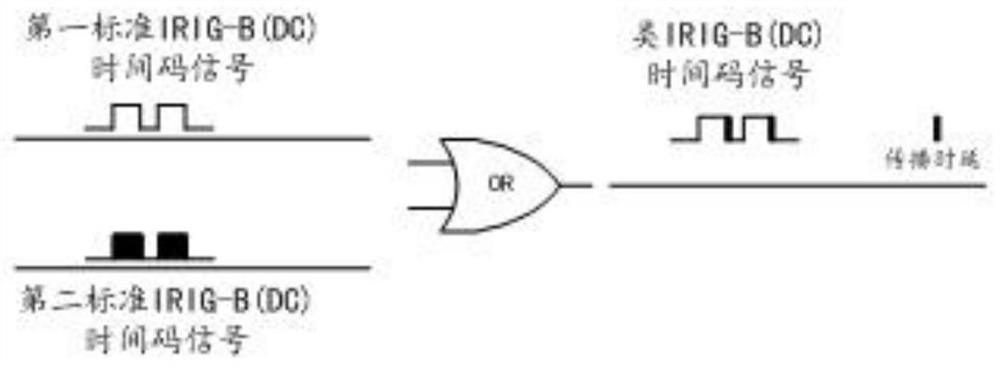
[0076] like Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment further provides a timing system based on the technology of the second embodiment, including a timing master station and a timing slave station as described in the second embodiment, wherein the timing master station includes a signal generation module an OR gate element; the signal generation module is configured to generate a first standard IRIG-B time code signal according to the time information of the master clock, and transmit the first standard IRIG-B time code signal to the OR gate element The first input end of the OR gate element; the second input end and the output end of the OR gate element are respectively connected to the signal transceiver unit of the timing slave station through the same communication link.
[0077] Preferably, the signal generation module is further configured to stop the generation of the first standard IRIG-B time code signal when it is found that the second input end of the OR gate element is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com