Micromechanical device with covering bond frame
A micro-mechanical and micro-mechanical structure technology, applied in the direction of micro-structural devices composed of deformable elements, micro-structural technology, micro-structural devices, etc., can solve problems such as expensive structures, reduce manufacturing costs, improve performance, The effect of reducing chip area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
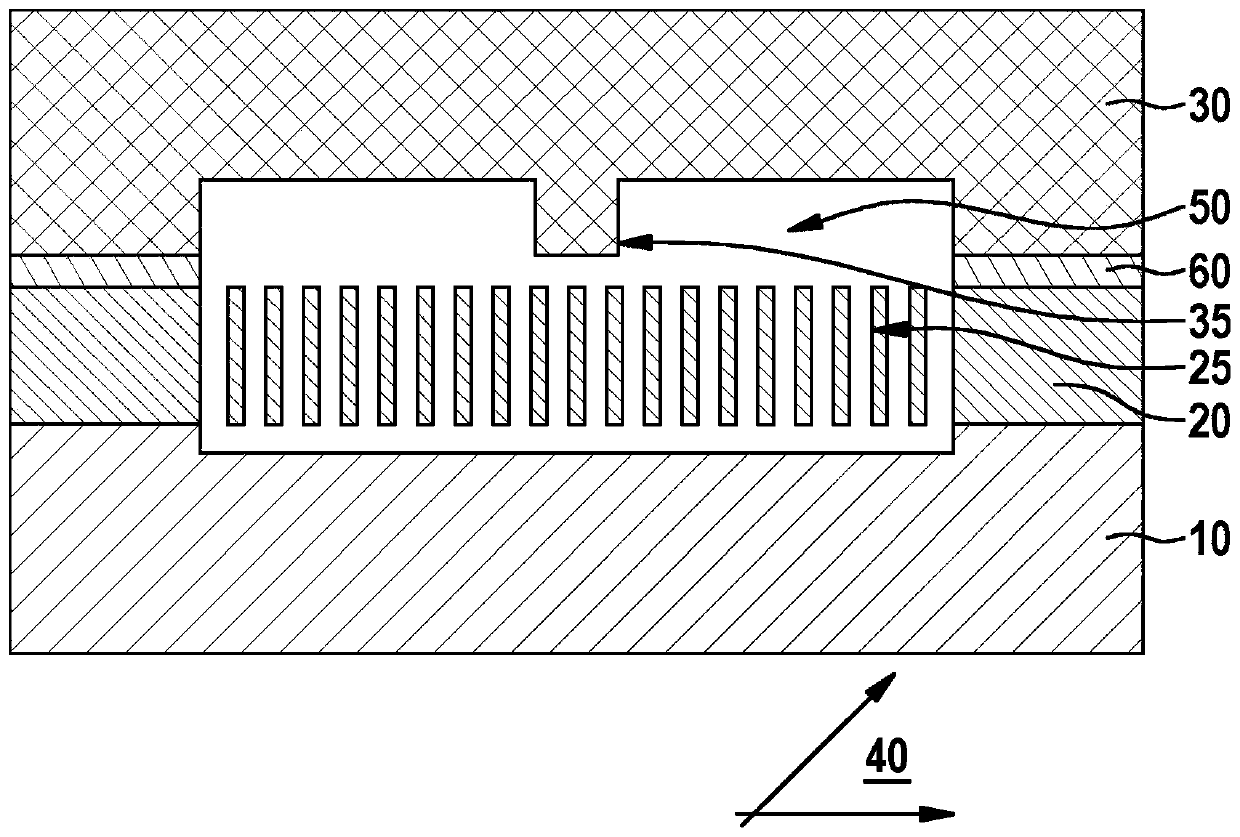
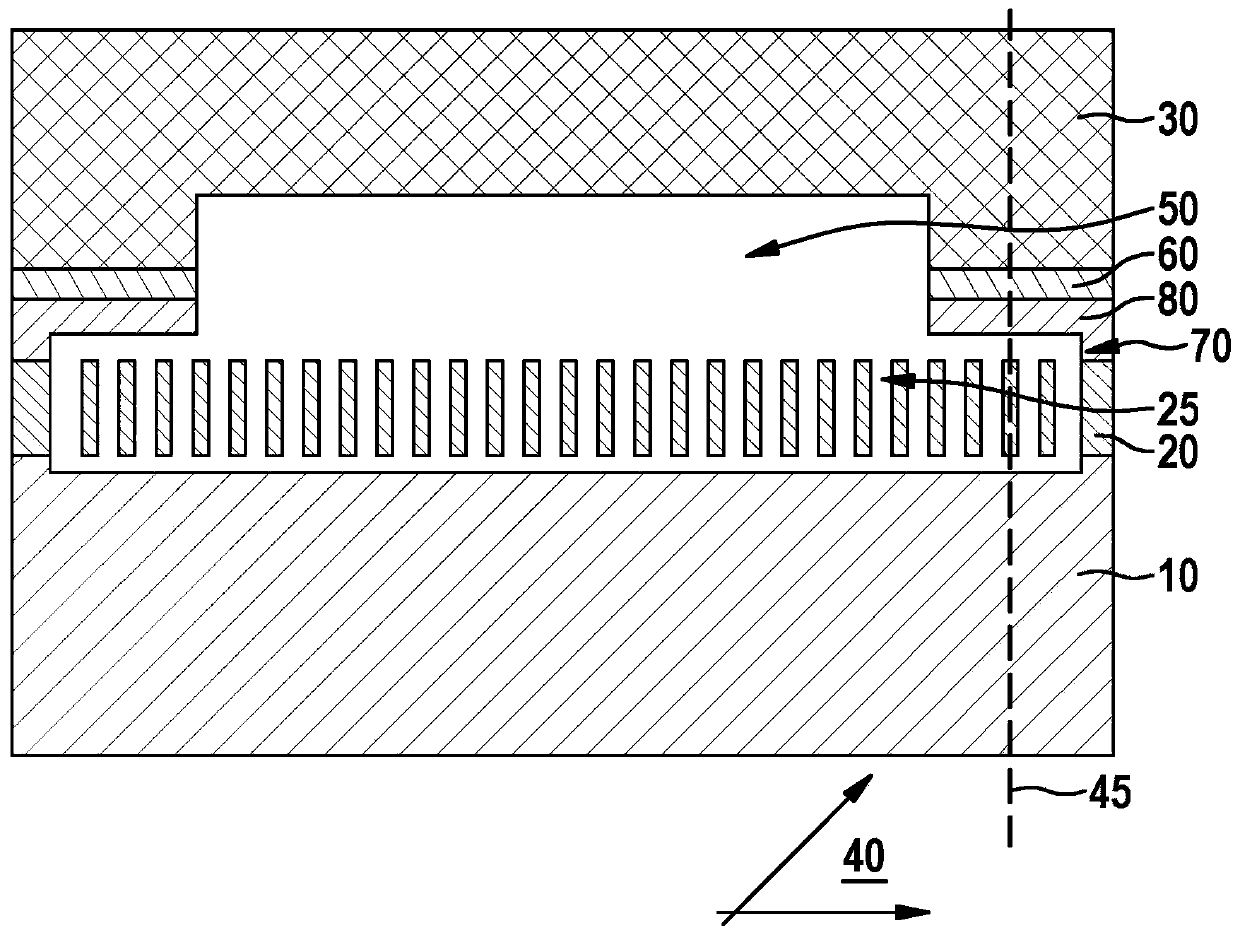
[0024] A schematic comparison of a prior art micromechanical device and a micromechanical device according to the invention with a covered bond frame is shown in cross section in FIGS. 1 and 2 .
[0025] FIG. 1 shows a prior art micromechanical device with a substrate, a micromechanical structure, a bond frame and a cover. Shown is a micromechanical device with a substrate 10 , a functional layer 20 and a cover 30 arranged one above the other parallel to the main plane of extent 40 . In this case, a cavity 50 is formed in the functional layer 20 , which cavity is surrounded by a bonding frame 60 . A micromechanical structure 25 is also formed in the functional layer 20 . The cover 30 is connected to the key frame 60 . The cover 30 has a cover stop 35 for delimiting the offset of the functional layer 20 perpendicular to the main plane of extent 40 .
[0026] figure 2 A micromechanical device according to the invention is shown with a substrate, a micromechanical structure, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com