A Multi-target Pose Approximation Method for Robot End Based on Joint Angle Compensation
A robot and joint angle technology, applied in the direction of manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as geometric parameter error compensation, absolute pose error, etc., to achieve faster convergence speed, more accurate calculation results, and improved approximation accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
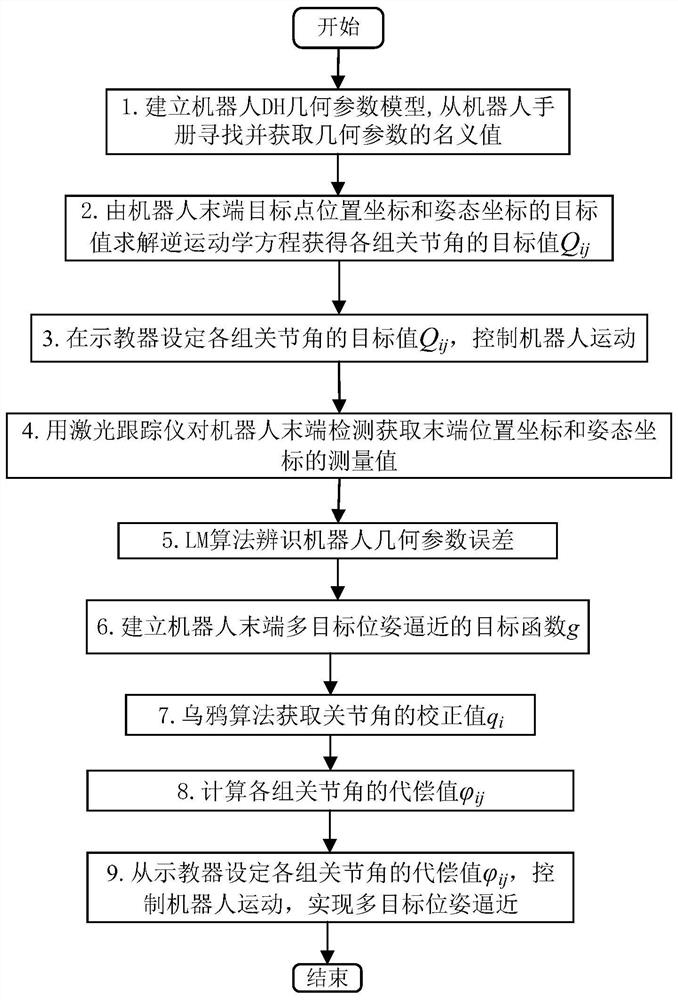
[0106] combine image 3 , the present invention refers to a multi-target pose approaching method based on joint angle compensation at the end of the robot, the method comprising:
[0107] After determining the target value of each group of joint angles according to the nominal value of the robot's geometric parameters, and controlling the movement of each joint of the robot to the target value of each group of joint angles, according to the collected robot end position and attitude data measurement values, the robot geometric parameters The error is identified, and the identified geometric parameter error of the robot is converted into the correction value of each joint angle of the robot. Combined with the correction value of the joint angle obtained through conversion, the compensation of the joint angle used to control the robot to perform the multi-target pose approximation action is calculated. value.
[0108] Preferably, the geometric parameter error of the robot refers ...
specific Embodiment 2
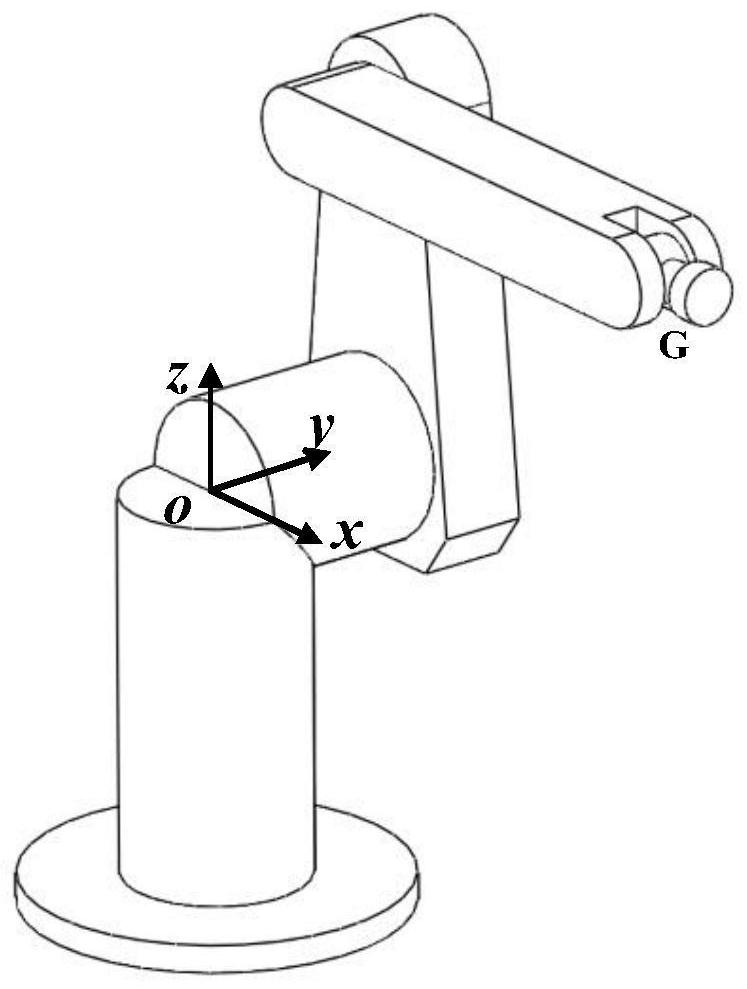
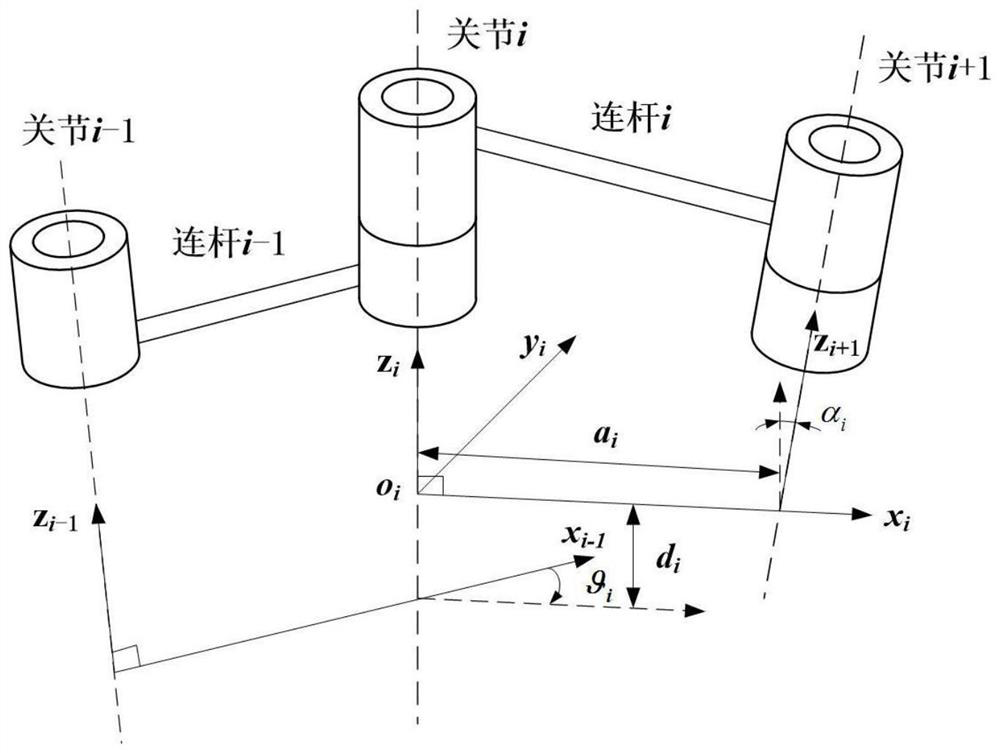
[0112] See figure 1 and figure 2 , figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the serial robot structure, figure 2 is the schematic diagram of the robot DH geometric parameter model. The robot includes a robot base, a first joint, a second joint, ..., an Mth joint and a robot end connected in series in sequence, two adjacent connecting rods are connected through the joint, and the robot base is connected in series with the first joint. connected, the Mth joint is connected in series with the end of the robot.
[0113] Based on the aforementioned robot structure, see image 3 , in this embodiment, the multi-target pose approximation method for the end of the robot based on joint angle compensation specifically includes the following steps:
[0114] Step 1. Establish base coordinate system oxyz and joint coordinate system o i x i the y i z i The following robot DH geometric parameter model, the geometric parameters of the DH geometric parameter model include connecting rod o...
specific Embodiment 3
[0189] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention is described further, as an embodiment of the present invention, what use is Staubli-TX60 six degrees of freedom serial industrial robot, concrete steps are as follows:
[0190] 1. Establish the base coordinate system oxyz and the joint coordinate system o for the Staubli-TX60 six-degree-of-freedom serial robot i x i the y i z i Find and obtain the nominal value of the robot's DH geometric parameter from the robot manual As shown in Table 1, i=1, 2, . . . , M, where M=6.
[0191] Table 1 Nominal values of DH geometric parameters of Staubli-TX60 robot
[0192]
[0193] 2. In order to confirm the correctness of the method of the present invention, the target value p of the 30 target point position coordinates at the end of the Staubli-TX60 robot oj Coordinate component p along the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis in the base coordinate system oxyz oxj ,p oyj ,p ozj and the target value r of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com