Multipolar quantum cascade ring laser
A technology of ring lasers and quantum cascades, applied in lasers, phonon exciters, semiconductor lasers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
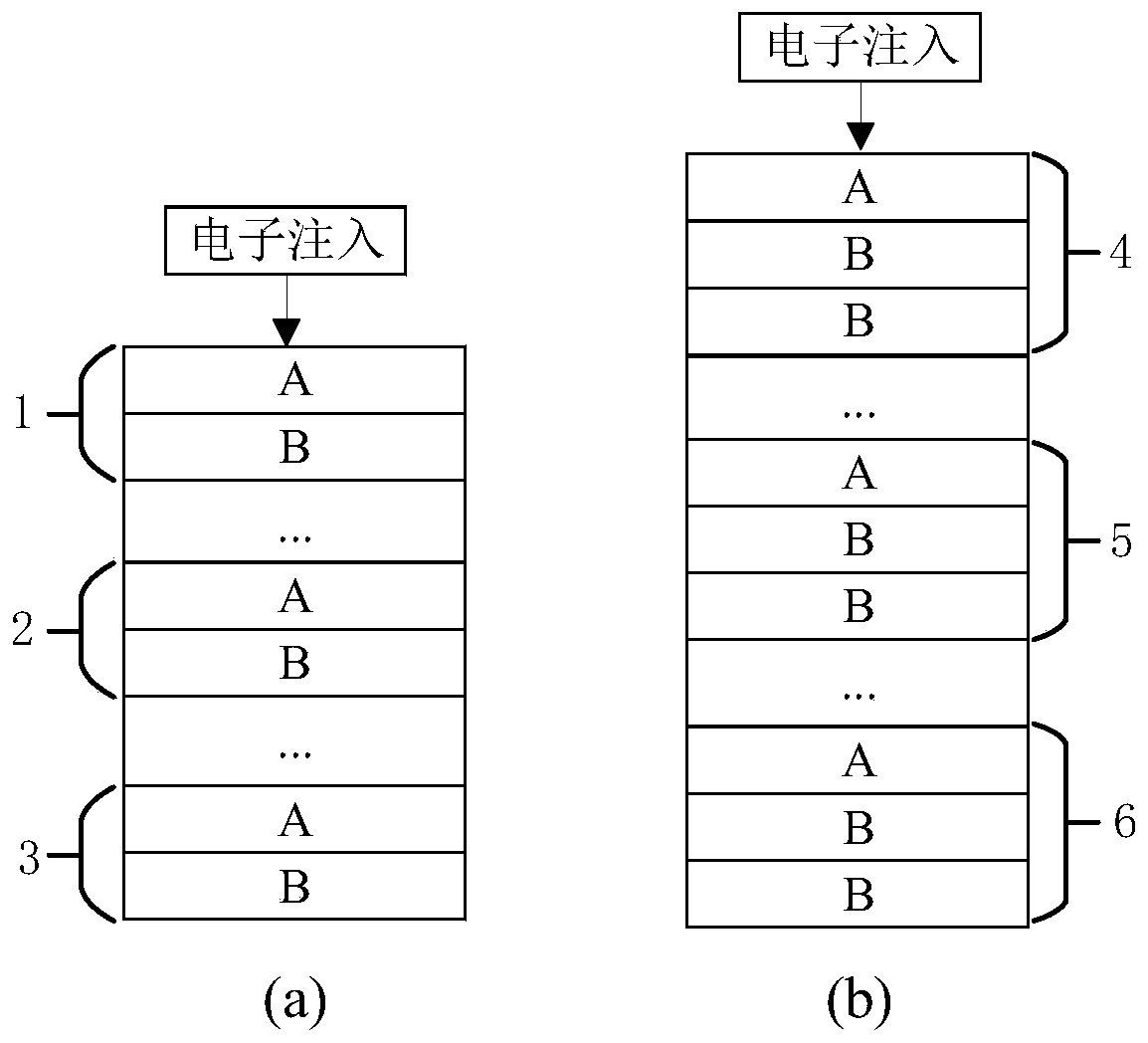
[0069] Such as figure 1 As shown, the schematic diagrams of two arrangement structures of the quantum cascade structure layer 9 in this embodiment, wherein, figure 1 The QCL stack units in (a) are all AB stacks, including the first QCL stack unit AB1, the i-th QCL stack unit AB2; the Nth QCL stack unit AB3, the quantum cascade structure layer 9 consists of N aforementioned QCL stacks Units are stacked to form an AB / … / AB / … / AB stack structure. figure 1 The QCL stack units in (b) are all ABB stacks, including the first QCL stack unit ABB4, the i-th QCL stack unit ABB5, and the N-th QCL stack unit ABB6. The quantum cascade structure layer 9 consists of N aforementioned QCL stacks Units are stacked to form an ABB / … / ABB / … / ABB stack structure.
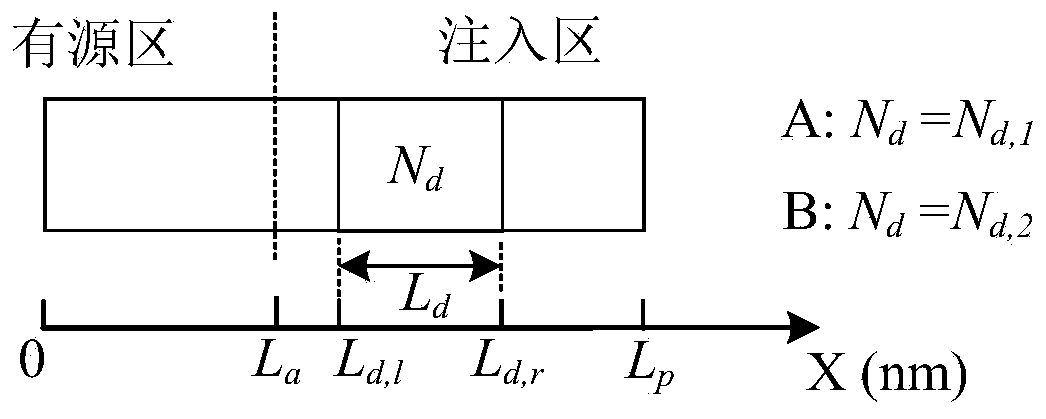
[0070] figure 1 (a), figure 1 Each QCL stack unit in (b) only contains two types of QCL subunits, A and B, and the two types of QCL subunits are composed of active regions and implanted regions, and the implanted regions only contain a se...
Embodiment 2
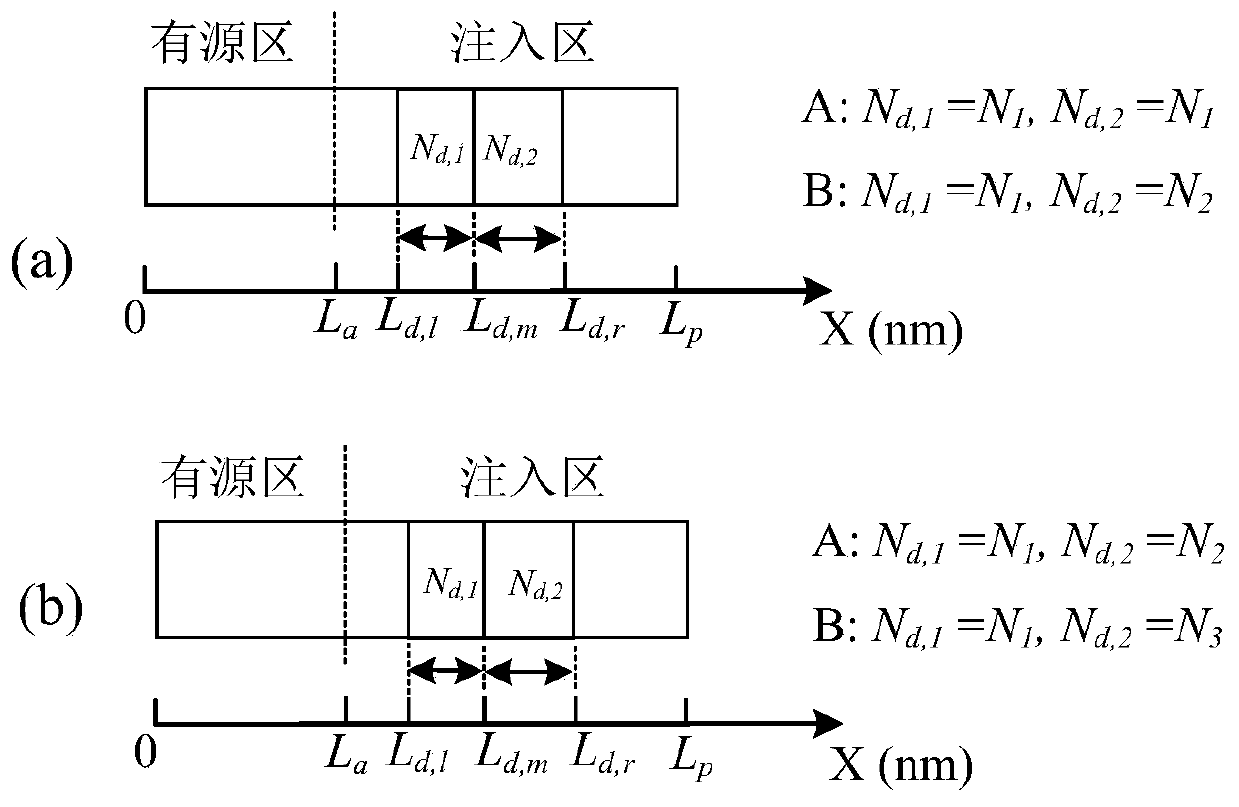
[0077] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the QCL subunits of the quantum cascade structure layer 9 all have two doped regions. image 3 In (a), the doping concentration parameters of the two doped regions of the type A QCL subunit are the same, both being N 1 . The doping concentration parameters of the two doped regions of the B-type QCL subunit are N 1 and N 2 (N 1 ≠N 2 ).
[0078] image 3 In (b), there are two sections of doping regions in the type A QCL subunit, and the doping concentration parameters of the two sections of doping regions are respectively N 1 and N 2 (N 1 ≠N 2 ). Type B QCL subunits have two sections of doping regions, and the doping concentration parameters of the two sections of doping regions are respectively N 1 and N 3 (N 3 ≠N 2 ).
[0079] same, image 3 Among them, the A and B QCL subunits are the same in other parameters except the doping concentration parameter, where other parameters include: the layer thickness seq...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Such as Figure 5 As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of the multipolar quantum cascade ring laser of the present invention, the substrate 7, the collector electrode 8, and the quantum cascade structure layer 9 are sequentially arranged along the z direction in the multipolar quantum cascade ring laser. , a quantum level matching layer 10, a base 11 and an emitter 12, and the emitter 12 is etched into a strip-shaped straight waveguide 18 and a ring waveguide 19 structure. The base 11 and the emitter 12 are arranged in steps, and the collector 8 and the quantum cascade structure layer 9 are also arranged in steps. Further, the collector electrode 8 may include a lower cladding layer, and the emitter electrode 12 may include an upper cladding layer. Specifically, the layer sequence of the device along the z direction from bottom to top is a heavy n-doped substrate 7, an n-doped collector 8, a quantum cascade structure layer 9, a quantum energy level matching l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com