Profiling three-dimensional fabric
A technology of three-dimensional fabrics and frames, applied in non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of reduced continuous fiber content in special-shaped cross-sections, complex parts, low continuous fiber content, etc., to achieve good profiling continuity, Strong, structurally enhanced effects can be designed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
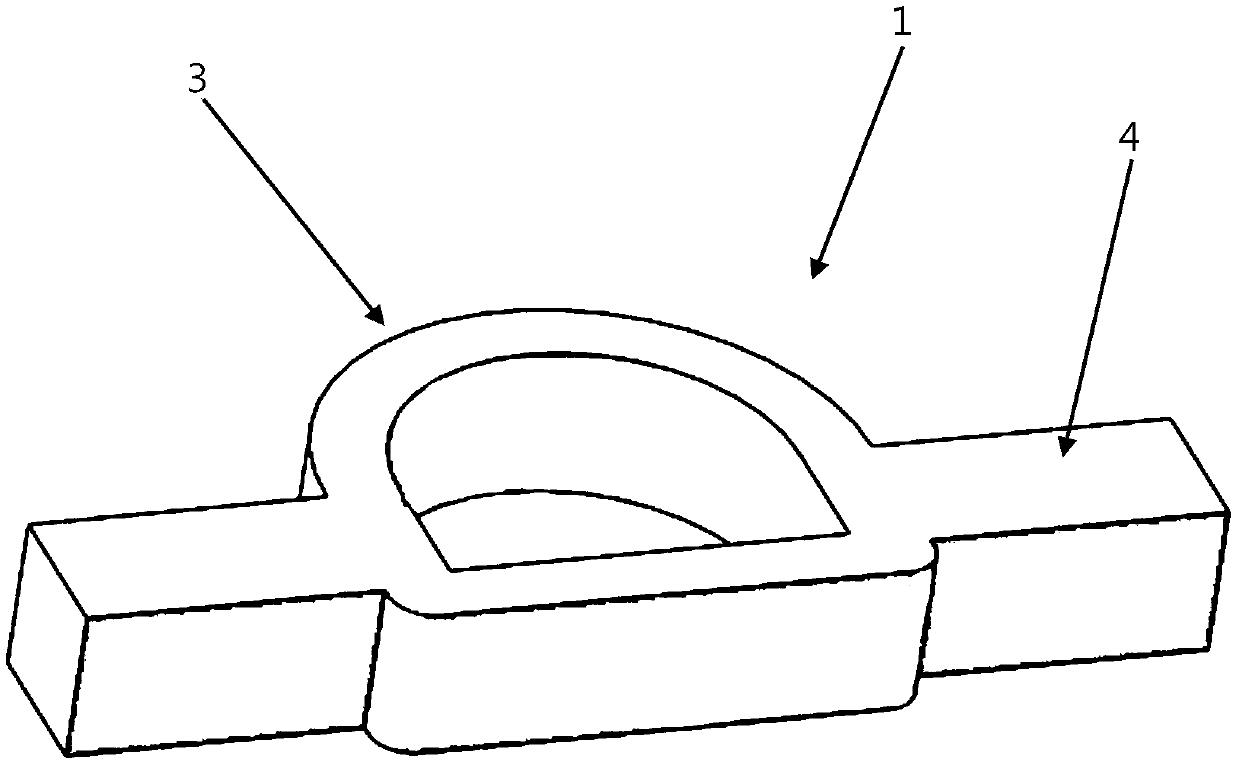
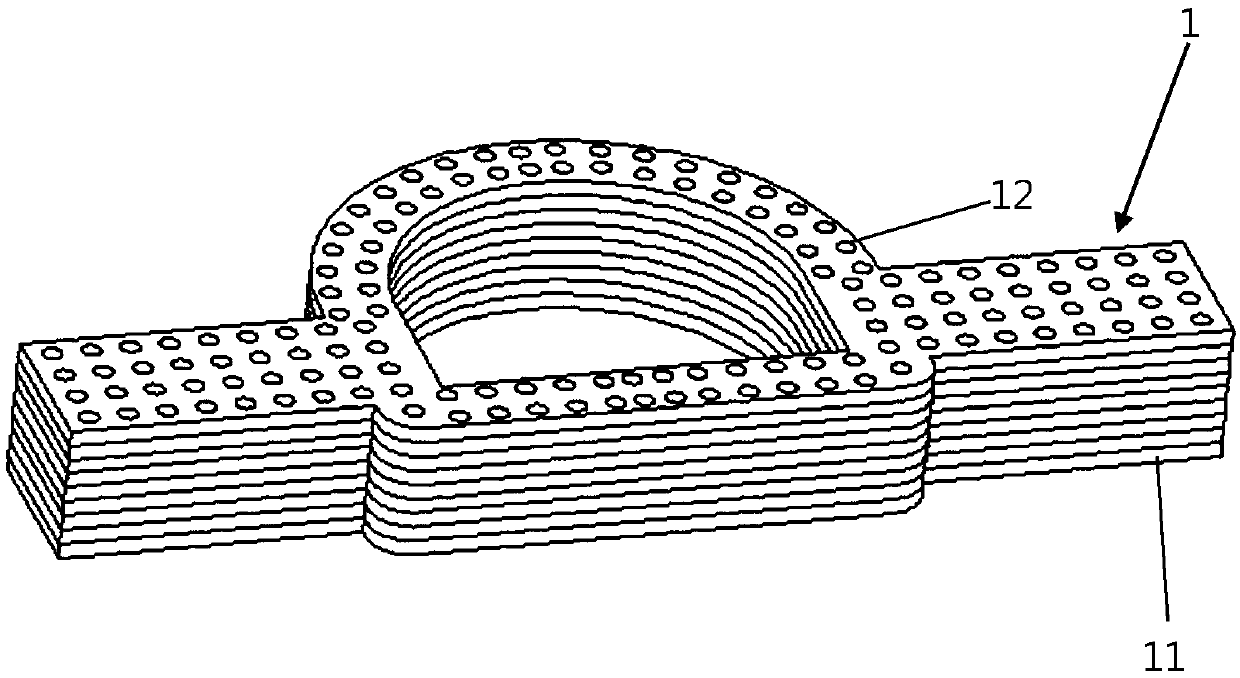
[0043] A profiled three-dimensional fabric 1, see 1 and figure 2 , including a frame body 3 located in the middle and side wings 4 located on both sides of the frame body 3 in the length direction. In this embodiment, the side wings 4 are arranged on opposite sides of the frame body 3, and the side wings 4 on both sides are symmetrical set up. Both the frame body 3 and the side wings 4 are composed of 225 layers of X-Y plane contoured unit layers 11 laminated, and the frame body 3 and side wings 4 are respectively provided with Z-direction fiber bundles 12 penetrating through the X-Y plane contoured unit layers 11 .
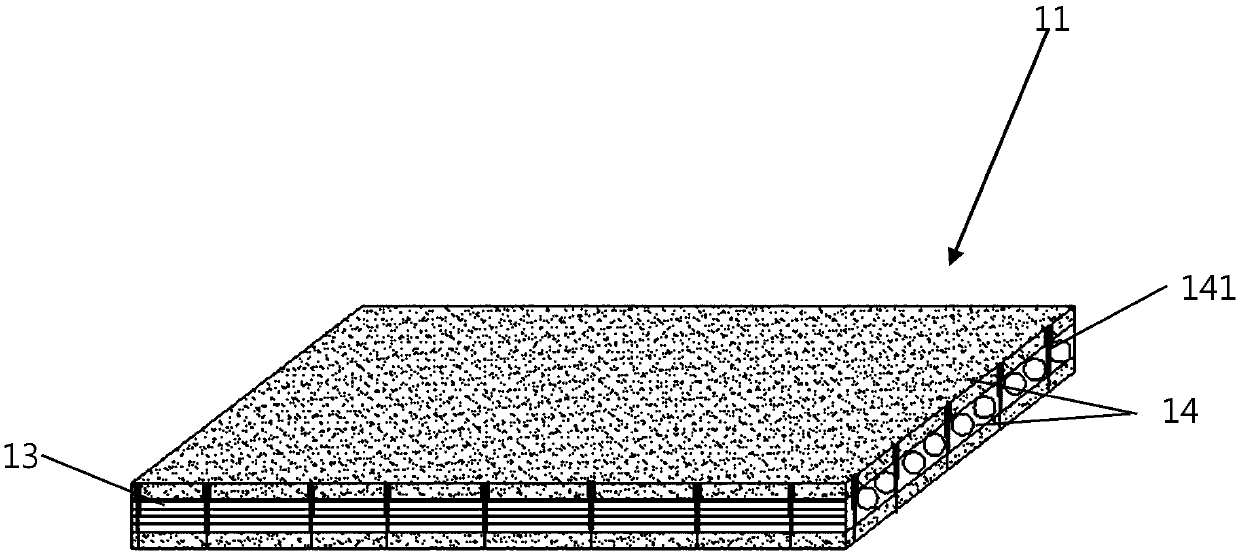
[0044] In this embodiment, the X-Y plane profiling unit layer 11 is composed of two layers of continuous fiber profiling layers 13 and three layers of fiber mat layers 14, and the two layers of continuous fiber profiling layers 13 are respectively arranged as circumferentially arranged Continuous fibers and continuous fibers pointing towards the center. In thi...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The profiling three-dimensional fabric 1 in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, the difference is that in this embodiment, the frame body 3 and the side wings 4 are formed by stacking 375 layers of X-Y plane profiling unit layers 11 , wherein, the X-Y plane profiling unit layer 11 is formed by one continuous fiber profiling layer 13 and two fiber mat layers 14.
[0051] In this embodiment, please refer to 5, the continuous fiber profiling layer 13 is arranged in the circumferential direction, and the dominant continuous fiber arranged in the circumferential direction is the frame area 131 arranged on the outer periphery of the frame body 3, and the frame area 131 is at the end of the wing 4 The ends are closed one by one from the inside to the outside, and the continuous fiber also includes a side wing middle area 133 arranged on the side wing 4, and the frame area 131 surrounds the side wing middle area 133 inside it and is profiled side by si...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The profiling three-dimensional fabric 1 in this embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, the difference is that in this embodiment, the frame body 3 and the side wings 4 are formed by 192 layers of X-Y plane profiling unit layers 11 Wherein, the X-Y plane profiling unit layer 11 includes two continuous fiber profiling layers 13 and three fiber mat layers 14.
[0058] The two layers of continuous fiber profiling layers 13 are continuous fibers arranged circumferentially and directed to the center respectively. In this embodiment, the continuous fibers directed to the center are the same as in Example 1; please refer to 6. The continuous fibers arranged in the direction include a frame area 131 closed one by one from the inside to the outside at the end of the side wing 4 and a side wing middle area 133 located on the side wing 4, and the frame area 131 is included in the outer periphery of the side wing middle area. In this embodiment, the circ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com