Battery cell modeling method
A modeling method and cell technology, which is applied in structured data retrieval, database design/maintenance, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient local accuracy, lack of equivalent mechanical models of cells, and simulation model safety issues that cannot be done More accurate reliability assessment and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
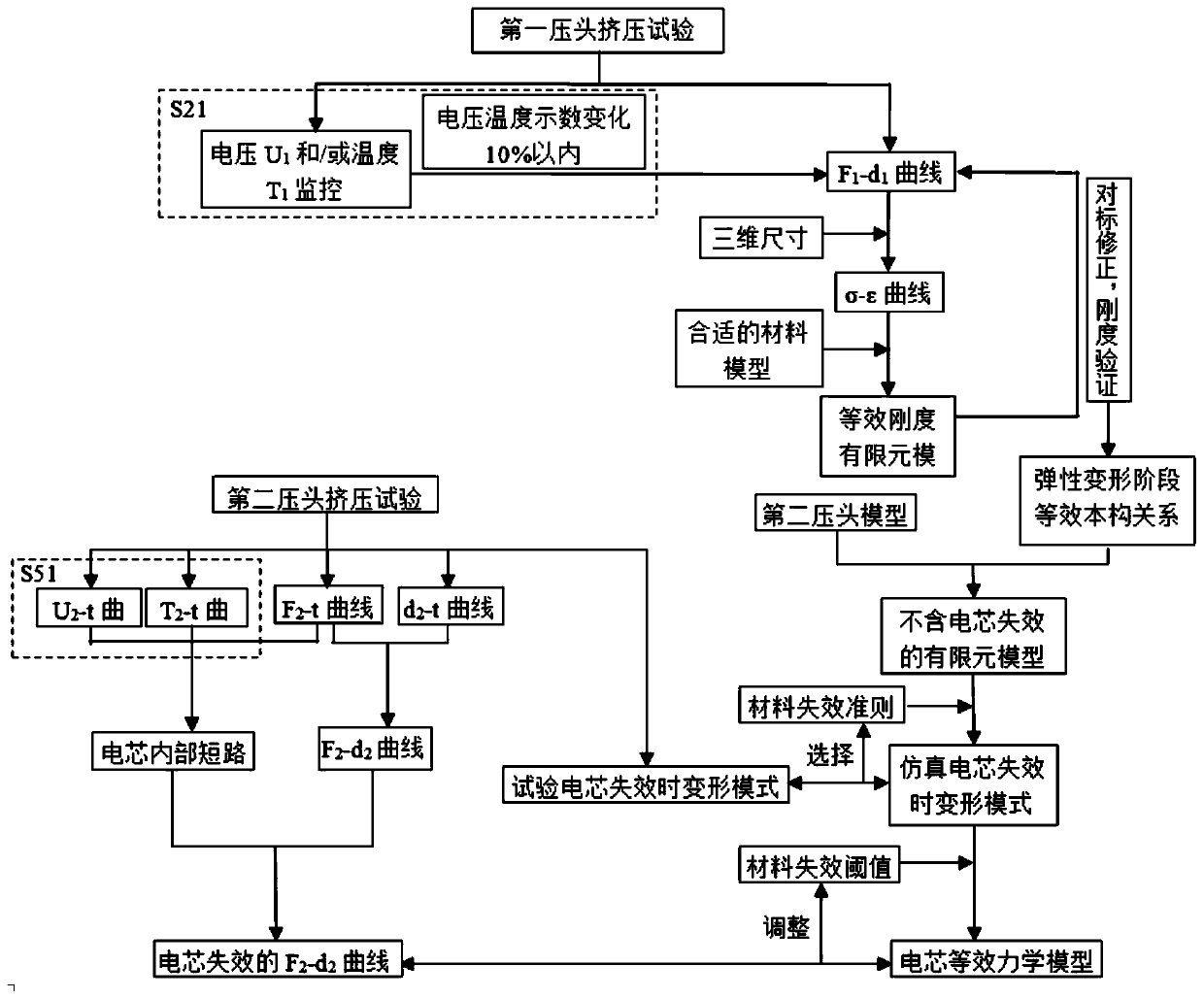
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown in the process content other than the dotted box, this embodiment provides a method for modeling the battery cell 10, including the following steps:
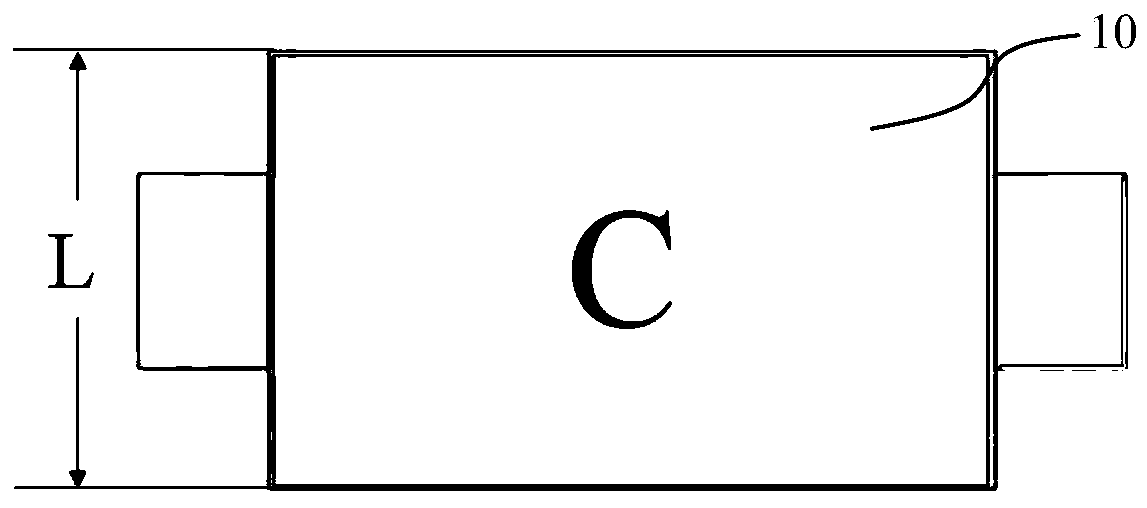
[0044] S1: Use a micrometer to measure the three-dimensional size of the battery core 10, including the thickness H of the battery core 10 and the area S of the C surface perpendicular to the thickness direction (such as figure 2 shown); the battery core 10 is a rectangular parallelepiped structure with a measured length of 59.50mm, a width of 34.00mm, and a thickness of 5.35mm. Therefore, the area S=59.5mm×34mm=202.3mm 2 , thickness H=5.35mm; the initial SOC of the battery cell 10 is 10%.
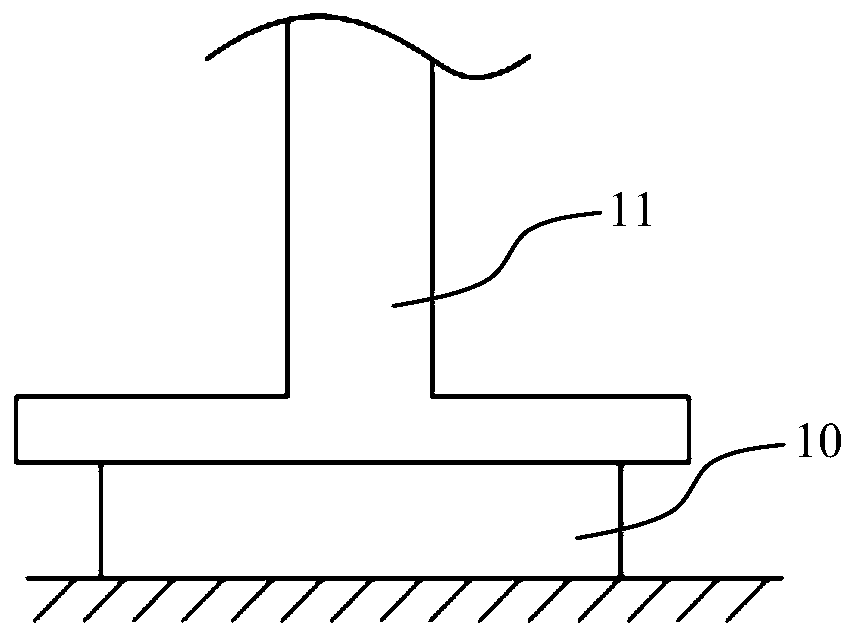
[0045] S2: Use the first indenter 11 to squeeze the battery core 10 at a rate of 1mm / min along the thickness direction (such as image 3 shown), the contact surface between the first indenter 11 and the C surface is a plane and the size is greater than or equal to the C surface, and the compressive deforma...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Same as Example 1, the difference is that the initial SOC of the battery cell 10 is 20%, and the step S2 also includes a step S21: monitoring the voltage U of the battery cell 10 during extrusion 1 and / or temperature T 1 As time changes, since the thickness of the tabs is smaller than the thickness of the cell 10, the two ends of the voltage sensor are connected to the two tabs of the cell 10 respectively, and the thermocouple is connected to any one of the tabs. When the voltage U 1 drop by more than 10% and / or temperature T 1 When the rise exceeds 10%, stop squeezing. When the voltage U 1 drop within 10% or temperature T 1 When the increase is within 10%, it is considered that the battery cell 10 has no internal short circuit or thermal runaway, that is, the internal structure and material of the battery cell 10 have not failed, and are in the elastic-plastic stage. Therefore, the battery cell 10 is in the elastic-plastic stage F 1 -d 1 The curve is the equivale...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the step S5 also includes a step S51: monitoring the voltage U of the battery cell 10 during the extrusion process 2 and / or temperature T 2 , when the voltage U 2 drops by more than 15% and / or the temperature T 2 When the rise exceeds 15%, stop squeezing. Since the second indenter 12 squeezes the cell 10, the cell 10 is in a local stress state, so a small extrusion force will cause the cell 10 to fail, and material failure will cause the nonlinearity of the structure and the bearing capacity. Decline. When an internal short circuit occurs in the cell 10, the voltage U of the cell 10 2 drop, temperature T 2 rise. Therefore, by monitoring the temperature T 2 , voltage U 2 and contact load F 2 At least one of the values in the value can determine the failure moment of the battery cell 10, and read the peak load F at the time of failure max , get with contact load F 2 F in descending segment 2 -d 2 curve, the F ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com