A preparation method of microenvironment-responsive immune regulation promoting nerve regeneration micro-nanofibers
A micro-nano fiber, immune regulation technology, applied in fiber treatment, tissue regeneration, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as low concentration and excessive drug loss, and achieve the goal of promoting angiogenesis, reducing inflammation, and reducing scar tissue formation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
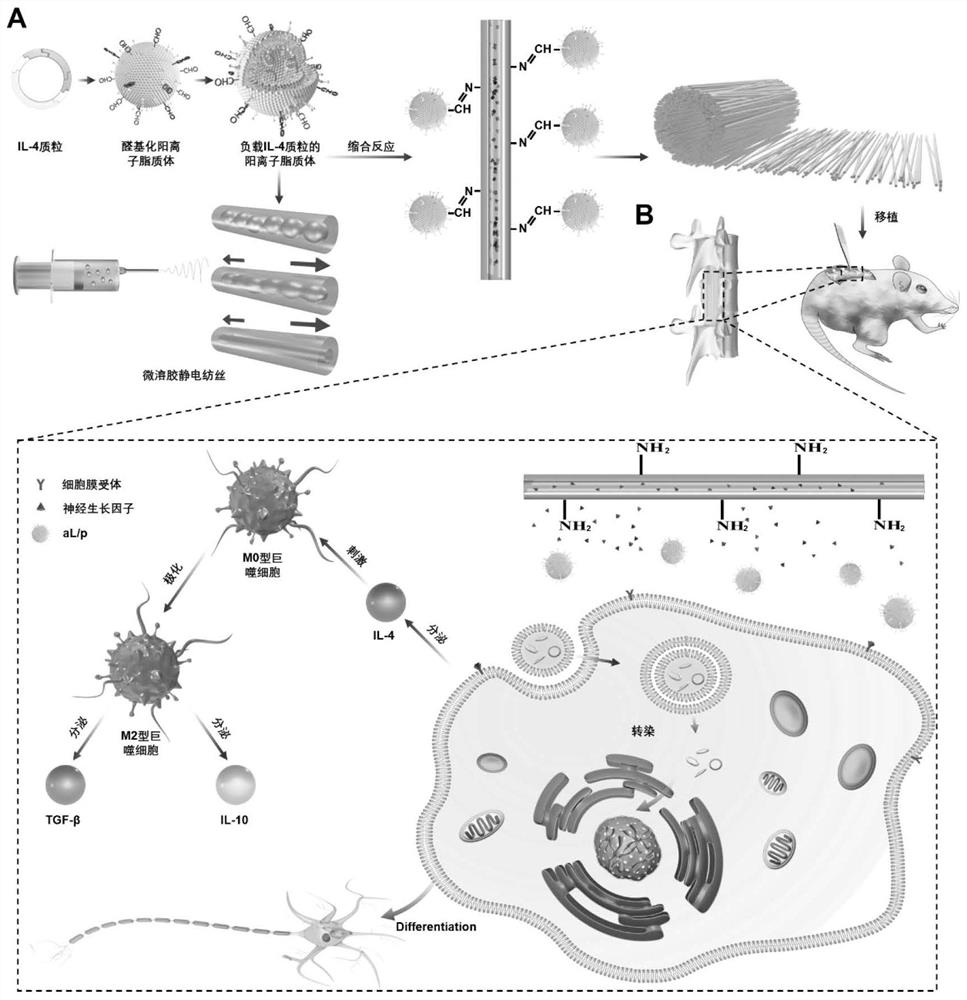
[0039] The preparation method of microenvironment-responsive immune regulation and promoting nerve regeneration comprises the following steps:
[0040] (1) Preparation of formylated cationic liposomes
[0041] The reverse evaporation method was used to prepare the aldylated cationic liposomes. First, 160 mg of soybean lecithin, 40 mg of cholesterol, and 4 mg of aldophospholipids were dissolved in 5 mL of chloroform, and 5 mg of octadecylamine was weighed and dissolved in 1 mL of chloroform. After mixing, carry out ultrasonication to obtain a uniform emulsion, then remove the organic solvent in a rotary evaporator to obtain a colloidal product, and finally add deionized water for hydration treatment to prepare a liposome emulsion. Filtrate to obtain formylated cationic liposomes.
[0042] (2) Preparation of liposomes loaded with eGFP-IL-4 plasmid
[0043] Prepare five 1mL centrifuge tubes, numbered A-E, add 100 μL Opti-MEM medium to each tube, and then add eGFP-IL-4 plasmid (...
Embodiment 2
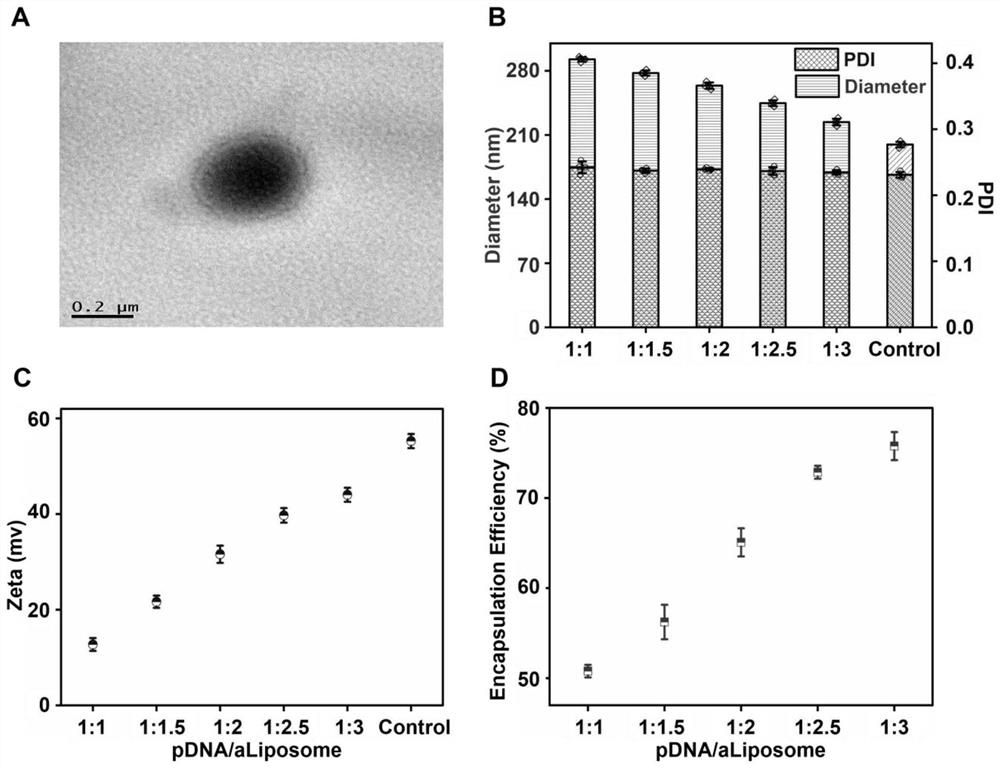
[0055] 1. Physicochemical properties characterization and screening of aldylated cationic liposomes
[0056] 1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
[0057] Take 2 μL of formylated cationic liposomes and drop them on the copper grid, and dry them at room temperature for 4 h. Apply a transmission electron microscope (TEM, Hitachi HT7700) to observe the surface morphology of the formylated cationic liposomes at a voltage of 120 kV.
[0058] 2. Detection of particle size and surface charge of aldehylated cationic liposomes
[0059] Take 2mL cationic liposome and plasmid composite solution of each ratio respectively, and use a dynamic light scattering particle size analyzer (DLS) to detect the size, polydispersity index, and kinetic potential.
[0060] 3. Encapsulation rate detection
[0061] Add 1mL cationic liposome and plasmid composite solution samples into ultrafiltration centrifuge tubes respectively, set the centrifuge speed to 5000rpm, and centrifuge for 5min. Then a...
Embodiment 3
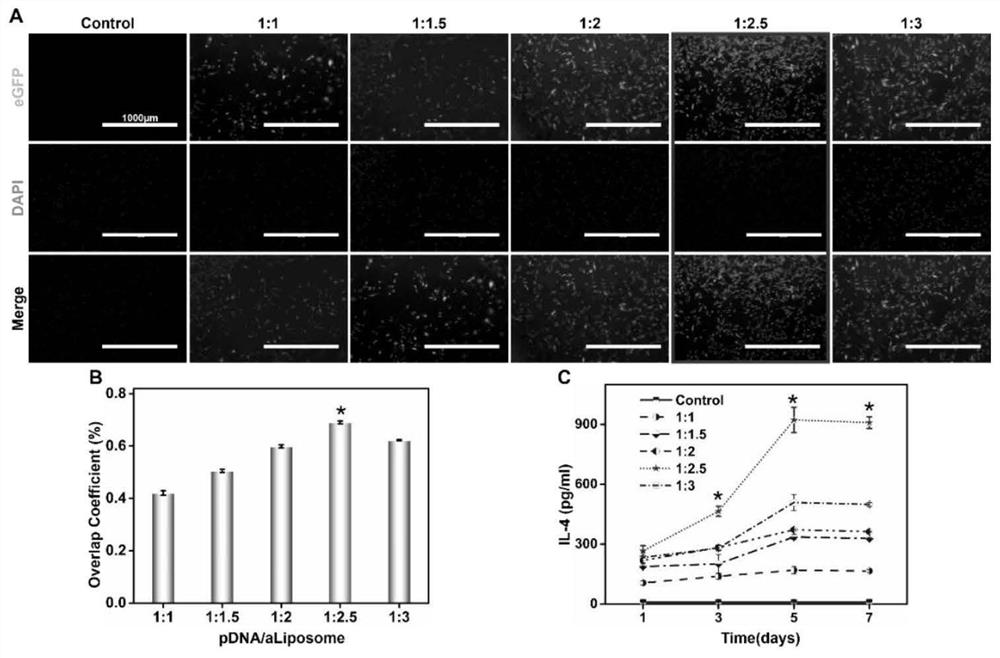
[0096] Example 3 Growth and differentiation of cells on the surface of micro-nano fibers
[0097] 1. Preparation of cells for research
[0098] Before cell research, fibrous scaffolds collected on coverslips with a diameter of 15 mm and a thickness of 100 μm were gently placed on the bottom of the Transwell plate and sterilized by irradiation, and then grafted with aldehylated cationic lipids loaded with pDNA as described above Plastids were placed in a 37°C cell culture incubator. According to the density of 1×10 4 SD rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) per hole were planted on the fiber scaffold, and the planting density of the upper chamber was 5×10 3 SD rat bone marrow macrophages (BMM) per well, put the Transwell plate at 37°C, relative humidity 95%, CO 2 Co-cultivation was performed in a partial pressure 5% incubator. The medium was changed every 2-3 days. The non-fibrous scaffold group (Control), traditional fibrous scaffold (aP), microsol fibrous scaffo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| encapsulation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com