Threshold adaptive adjustment method based on statistical priority multiple access
An adaptive adjustment and threshold technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve the problems of making judgments on access conditions, low channel utilization, and inability to effectively guarantee service access channels, so as to reduce channel load jitter and improve channel utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
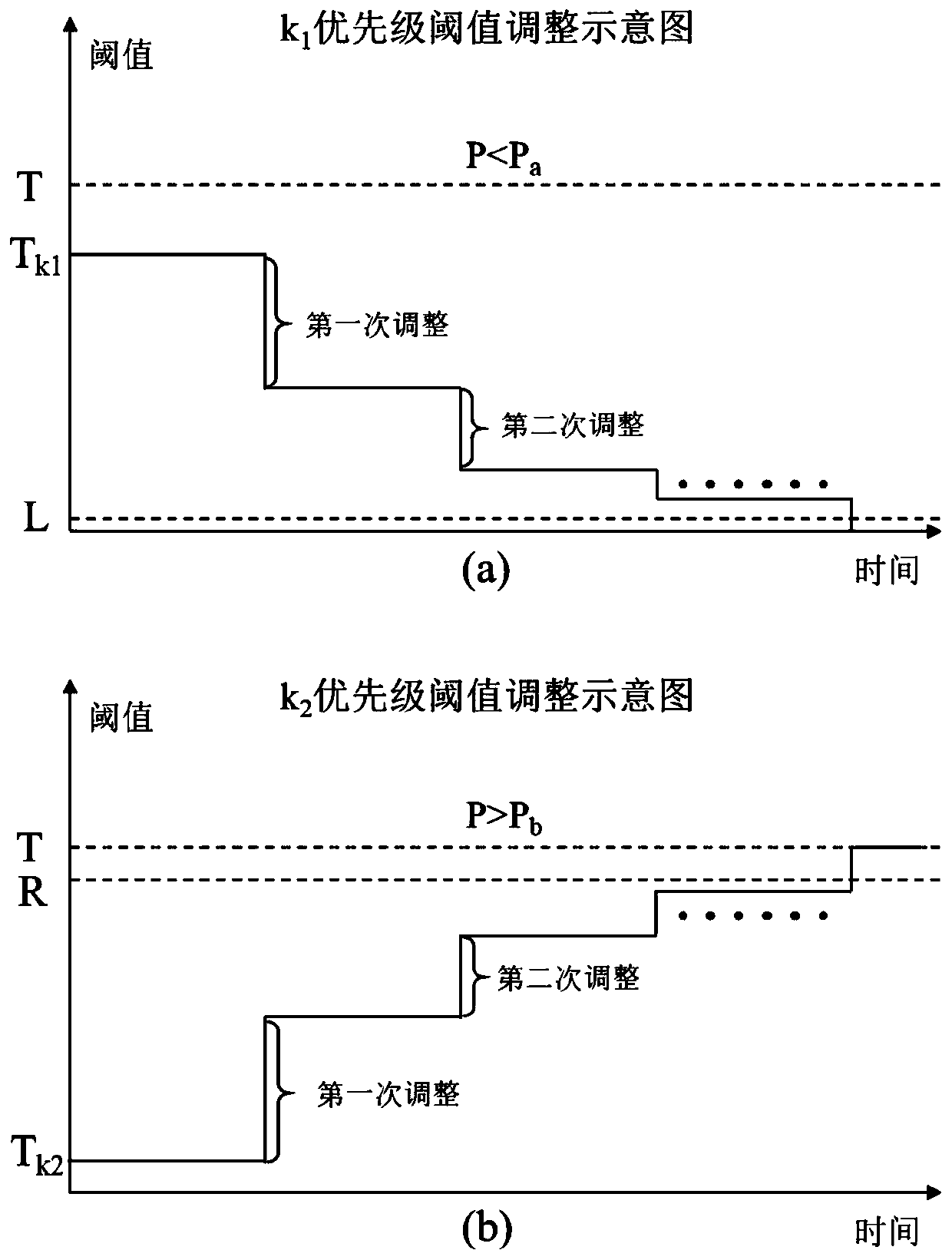
[0076] Example 1, in Figure 4 Threshold adjustment is performed in the adjustment scenario shown in (a).
[0077] Figure 4 (a) is a scenario where a certain priority has undergone multiple threshold adjustments, and the adjustment process is as follows:
[0078] First, the node detects that the probability of successful frame transmission P is less than P a Finally, according to step (5d), find a certain priority k whose threshold is greater than 0, and adjust its threshold to T k is the threshold before the adjustment of priority k;
[0079] Then, observe the value of P after the Δt time, and find that P is still less than P after the Δt time a , then adjust the threshold again to
[0080] Then, after a further time Δt, it is observed that P is greater than P b , then follow step (5e) to find the priority with the threshold less than T, the priority will still be the k priority, adjust the threshold
[0081] Finally, after multiple adjustments, P∈(P a ,P b ),...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Example 2, in Figure 4 Threshold adjustment is performed under the adjustment scenario shown in (b).
[0083] Figure 4 (b) is that the probability of successful frame transmission P is always less than P a In the scenario where two priorities are used for threshold adjustment, the adjustment process is as follows:
[0084] First, the node detects that the probability of successful frame transmission P is less than P a Finally, according to step (5d), find the priority k-1 whose threshold is greater than 0, and adjust where T k-1 is the threshold value before the adjustment of priority k-1;
[0085] Then, observe the value of P after every Δt time, and find that P is less than P a , then follow step (5d) to continuously lower the threshold of priority k-1 until T k-1 n =0, where T k-1 n is the threshold of k-1 priority adjusted n times;
[0086] Then, after a further time Δt, it is found that P is still less than P a , since the threshold of the current k-...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3, in Figure 4 Threshold adjustment is performed in the adjustment scenario shown in (c).
[0089] Figure 4 (c) is that the probability of successful frame transmission P is always greater than P b In the scenario where two priorities are used for threshold adjustment, the adjustment process is as follows:
[0090] First, the node detects that the frame transmission success probability P is greater than P b Finally, according to step (5e), find the priority k whose threshold value is less than T, and adjust where T k is the threshold size before priority k adjustment;
[0091] Then, observe the value of P after every Δt time, and find that P is greater than P b, at this time follow step (5e) to continuously increase the threshold of priority k until T k n = T, where T k n is the threshold value of k priority adjusted n times.
[0092] Then, after a further time Δt, it is found that P is still greater than P b , since the current k-priority thres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com