Temperature-sectioned efficient vitrification treatment method for sludge containing organic components
A disposal method, a technology of organic components, applied in sludge treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of fast ablation speed of refractory materials, high glass transition temperature, and unfavorable long-term stability of melting furnaces Operation and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
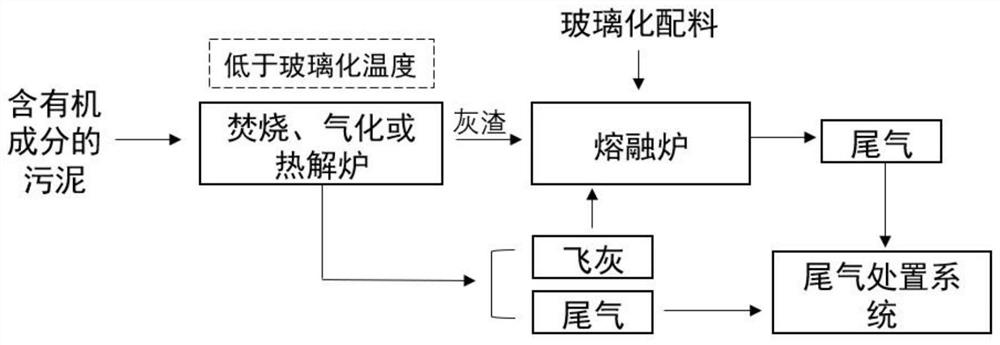
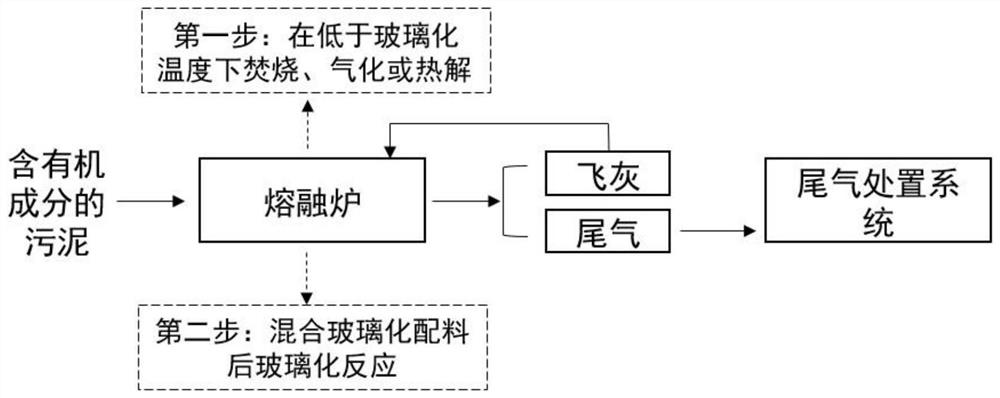
[0025] Experimental conditions: with figure 1 The method is to weigh 200g of excess sludge with a moisture content of 70%, dry it to a moisture content of 40%, first burn it in an incinerator at 900°C for 30min, add 15g of 100-mesh quartz sand, and cosolvent B 2 o 3 2 g, mixed evenly, placed in a high-temperature melting furnace, kept at 1500°C for 15 minutes, and cooled with water to obtain a glass body. The fixation rates of heavy metals Zn, As and Ni in the sludge in the glass body reached 80%, 82% and 84%. In the vitreous leaching toxicity test, none of the inorganic elements involved in the GB 5085.3-2007 standard in the leaching solution exceeded the limit value in GB 5085.3-2007. Compared with the fixation rate of heavy metals in Comparative Example 1, the fixation rates of Zn, As and Ni elements were increased by 79.5%, 81.9% and 52%, respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Experimental conditions: with figure 1 The method is to weigh 150g of oil sludge, first incinerate in an incinerator at 900°C for 45min, then add 15g of 100 mesh quartz sand, 3g of CaO, B 2 o 3 4 g, mixed evenly, placed in a high-temperature melting furnace, kept at 1500 ° C for 20 minutes, and cooled with water to obtain a glass body. The fixation rates of heavy metals Ti, V and Mn in the sludge in the glass body reached 98%, 96% and 93% respectively. %. In the vitreous leaching toxicity test, none of the inorganic elements involved in the GB 5085.3-2007 standard in the leaching solution exceeded the limit value in GB5085.3-2007. Compared with the fixation rate of heavy metals in Comparative Example 2, the fixation rates of Ti, V and Mn elements were increased by 13%, 9% and 8%, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Experimental conditions: with figure 1 The method is to weigh 200g of excess sludge with a moisture content of 70%, dry it to a moisture content of 20%, first incinerate at 900°C for 20min in an incinerator, and then add 15g of 100-mesh quartz sand, 4g of CaO, and B 2 o 38 g, mixed evenly, placed in a high-temperature melting furnace, kept at 1200°C for 10 minutes, and cooled with water to obtain a glass body. The fixation rates of heavy metals Zn, As and Ni in the sludge in the glass body reached 81%, 83% and 88%. In the vitreous leaching toxicity test, none of the inorganic elements involved in the GB 5085.3-2007 standard in the leaching solution exceeded the limit value in GB 5085.3-2007. Compared with the heavy metal fixation rate in Comparative Example 3, the fixation rates of Zn, As and Ni elements were increased by 80%, 82.4% and 48%, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com