Harmonic source responsibility division method based on cross-approximate entropy data screening
A technology of mutual approximate entropy and data screening, which is applied in spectral analysis/Fourier analysis, instruments, measuring devices, etc., and can solve problems such as large estimation error and poor fit.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
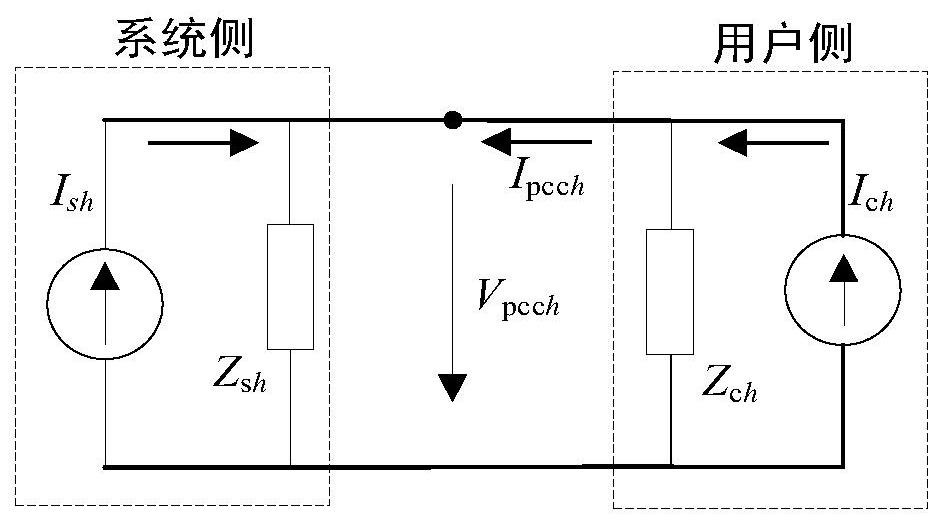
[0080] Embodiment 1: Basic explanation of the division of harmonic responsibilities; the division of harmonic responsibilities in power systems can be represented by Norton equivalent circuits, as follows figure 1 As shown in , the harmonic voltage and current values at the common connection point are simultaneously contributed by the harmonic sources on the system side and the user side. where I ch is the equivalent harmonic source on the user side, I sh is the equivalent harmonic source on the system side, Z ch is the user-side equivalent harmonic impedance, Z sh is the equivalent harmonic impedance of the system side, and h represents the harmonic order.
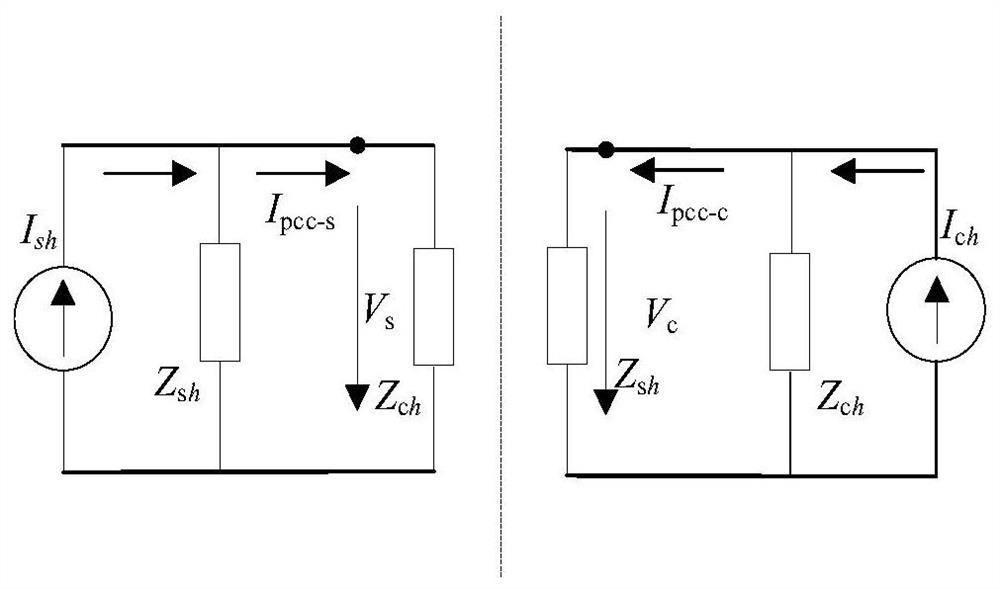
[0081] According to the superposition theorem, the figure 1 It is converted into two parts superimposed on the system side and the user side, such as figure 2 Shown:
[0082] In the picture I pcc-s is the equivalent harmonic source I on the system side s Contributing Harmonic Current, V s Contribute harmonic v...
Embodiment 2
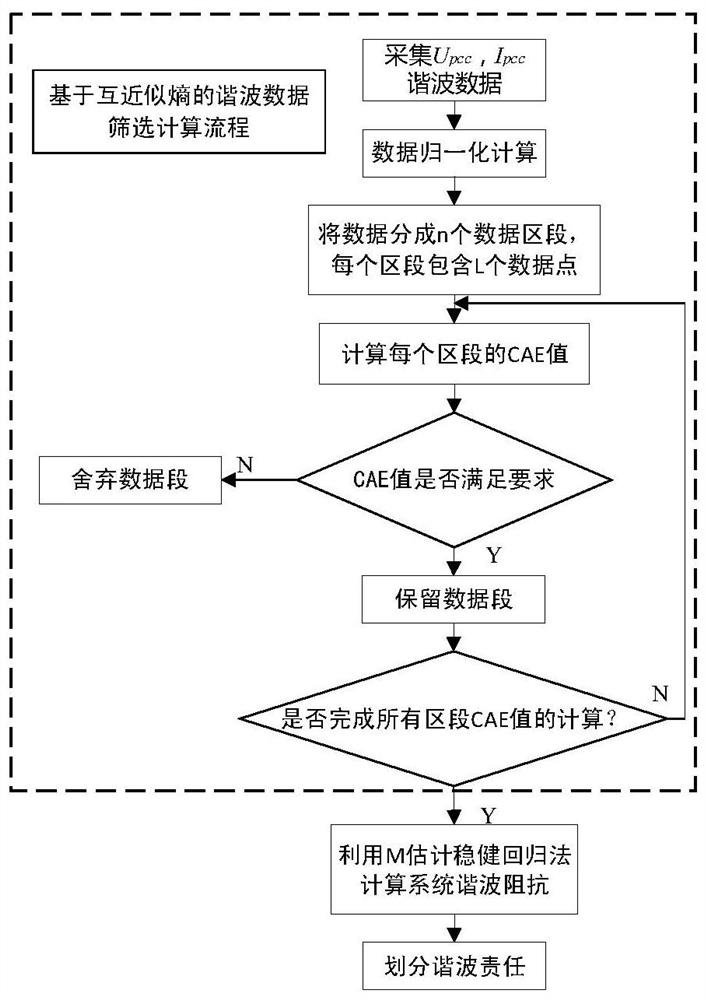
[0099] Embodiment 2: The principle of mutual approximation entropy is explained; From the above-mentioned principle, if the influence of background harmonics is excluded, V pcc with I pcc The waveform pattern is consistent. The accuracy of the system harmonic impedance calculated from this will be higher. Therefore, in order to filter out V pcc with I pcc For data segments with similar waveform trends, this paper introduces the concept of mutual approximation entropy, and uses the method of waveform segment matching to convert V pcc with I pcc Similar waveform data segments are retained, and dissimilar data segments are eliminated to achieve the purpose of eliminating background harmonic interference.
[0100] Aiming at the problems that traditional entropy requires a large amount of sampled data, is sensitive to noise, and is not easy to converge, Steven M. Pincus proposed Approximate Entropy (ApEn) in the 1990s from the perspective of measuring the complexity of time se...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Example 3: Principle of M-estimation robust regression method; the traditional linear regression method uses the least squares method for calculation, and its principle is to minimize the sum of squares of residual errors. When there are outliers in the original data, the calculation of the least squares method will accommodate the remote data, which increases the calculation error, so the traditional linear regression method lacks robustness. In this paper, M-estimated robust regression is used to eliminate the influence of outliers on the method [18]. The following is an example of linear regression calculation. Known measured data (x i ,y i )(i=1,2,...,n), if the linear relationship is y=ax+b, the coefficients a and b of the equation can be calculated by the least square method.
[0117] From the above description, we can see that the residual e i The objective function of can be expressed as:
[0118]
[0119] The traditional least squares method is to estim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com