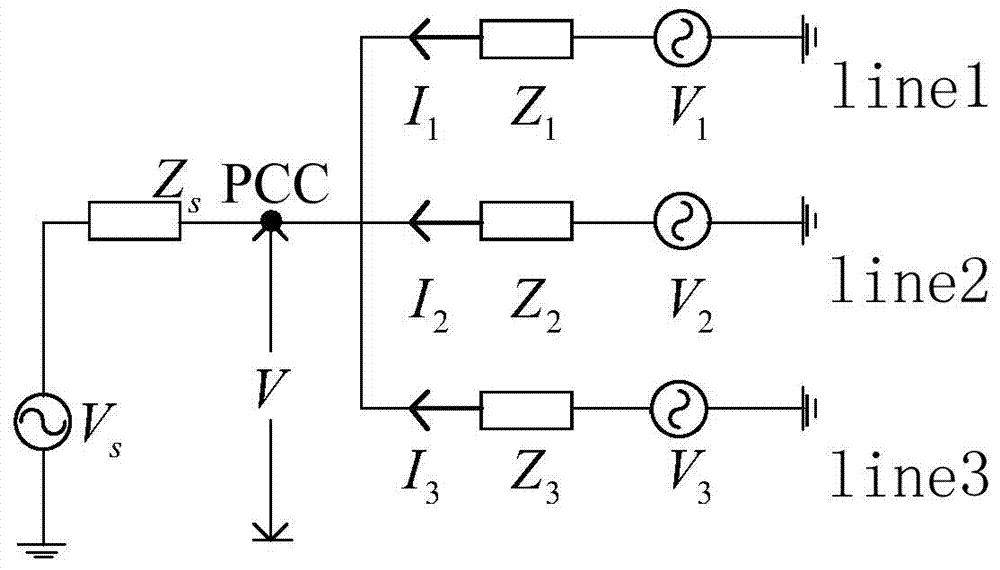
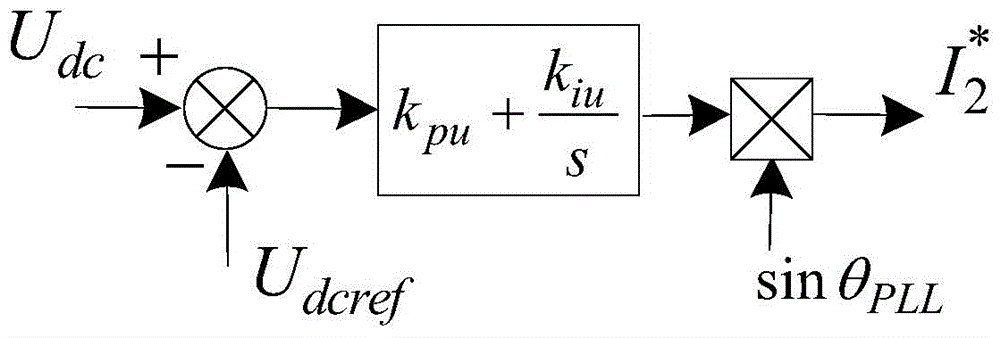
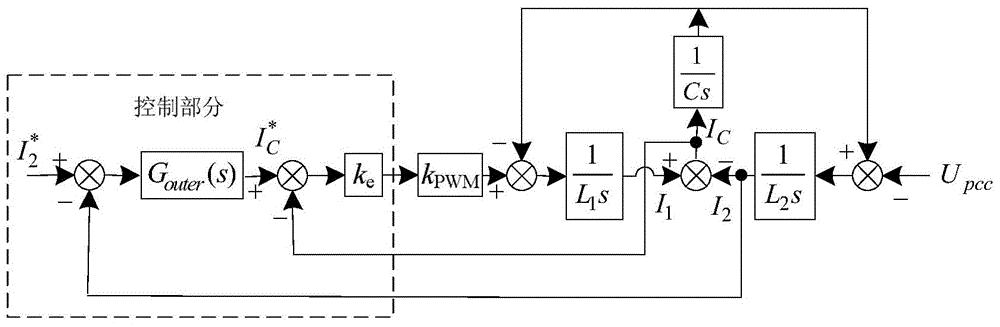
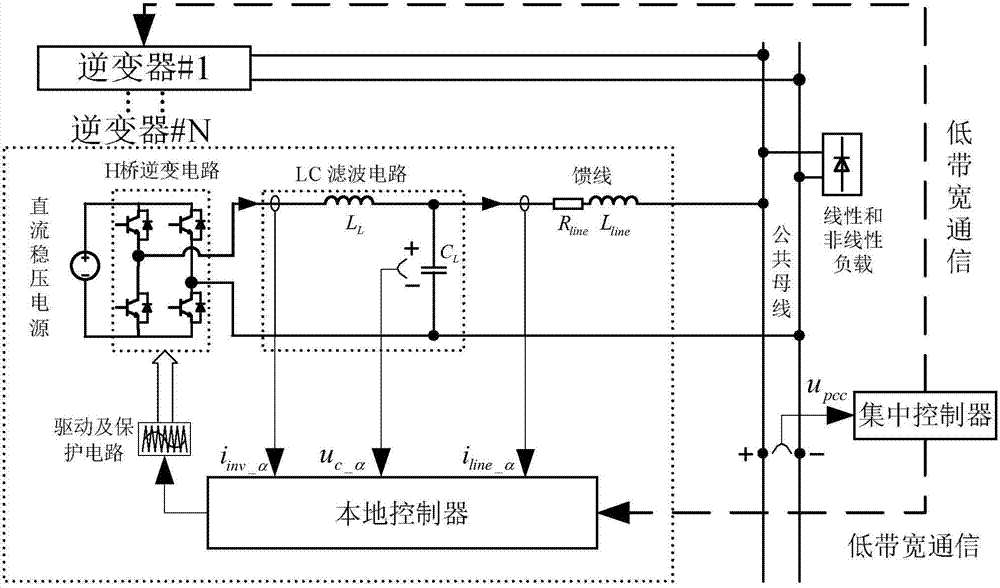
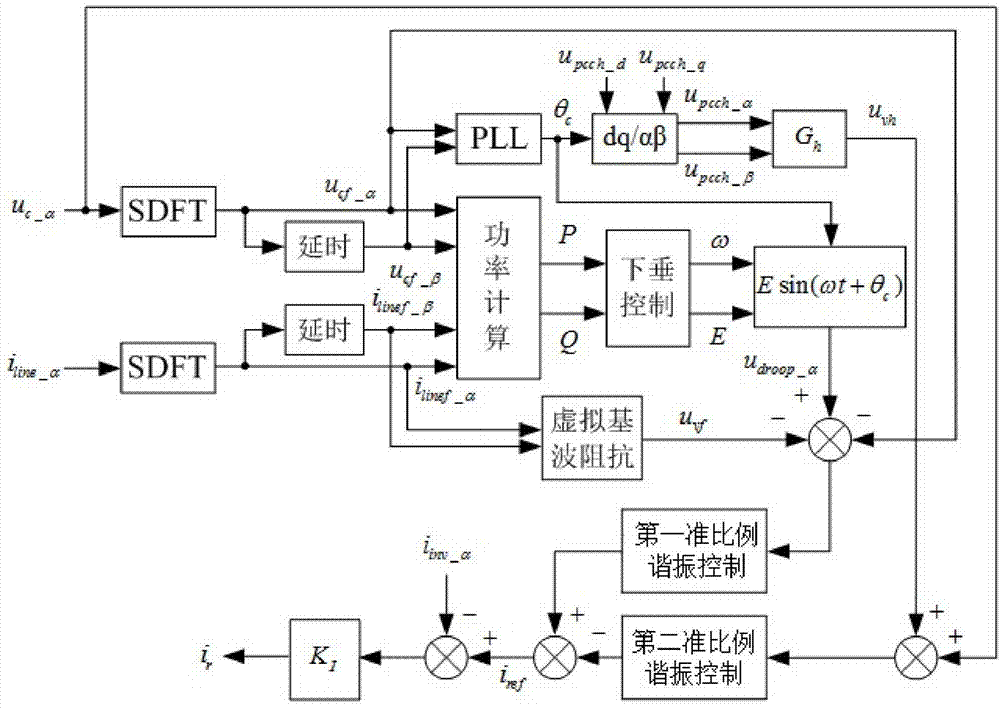
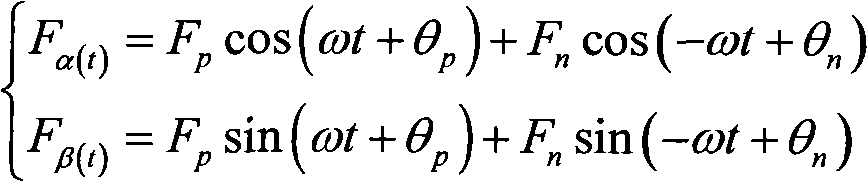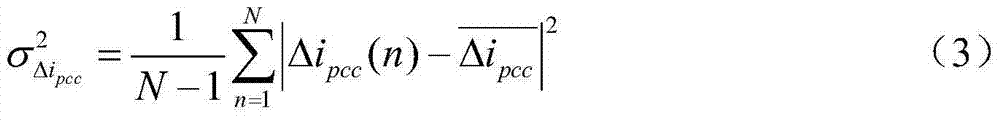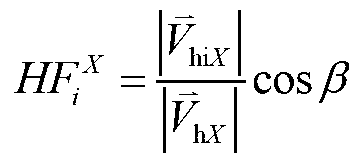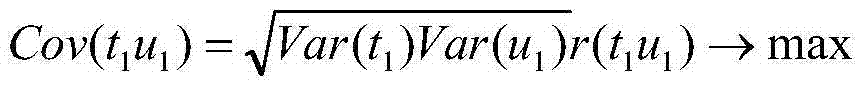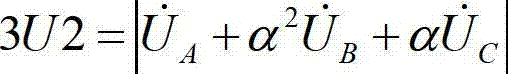Patents
Literature
883 results about "Harmonic voltages" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
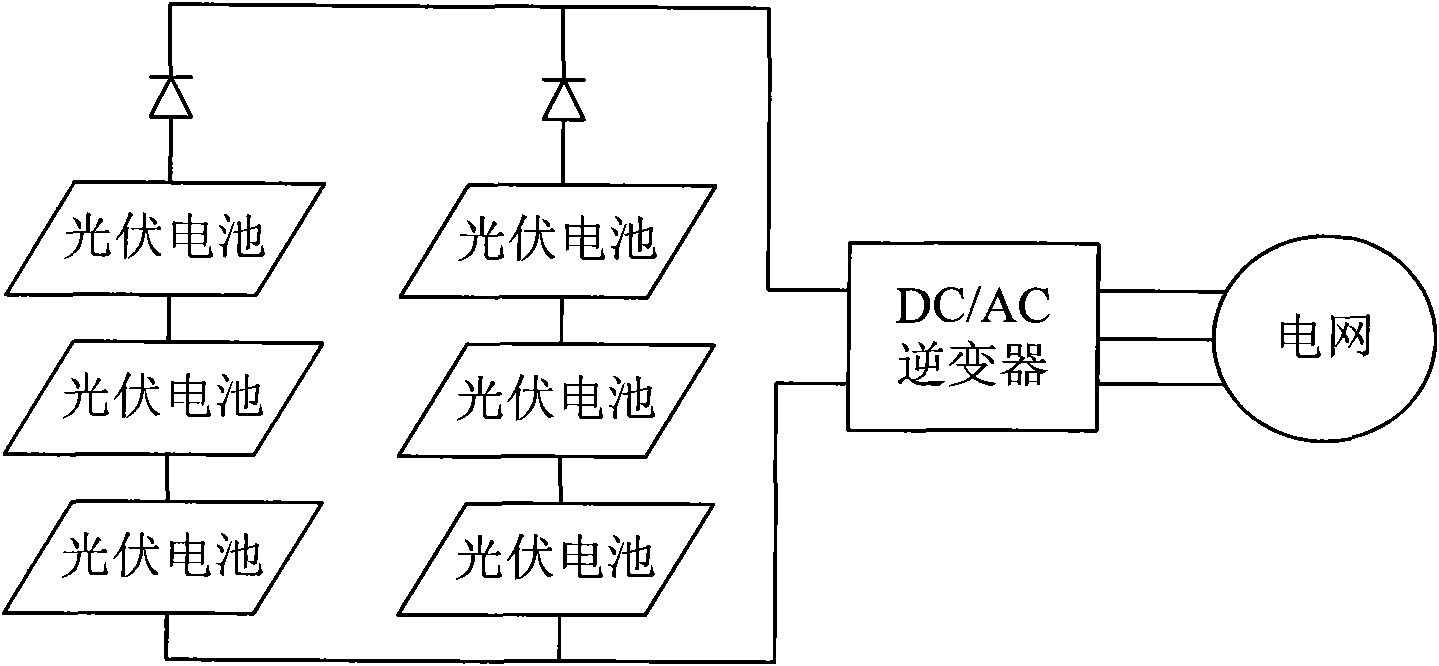
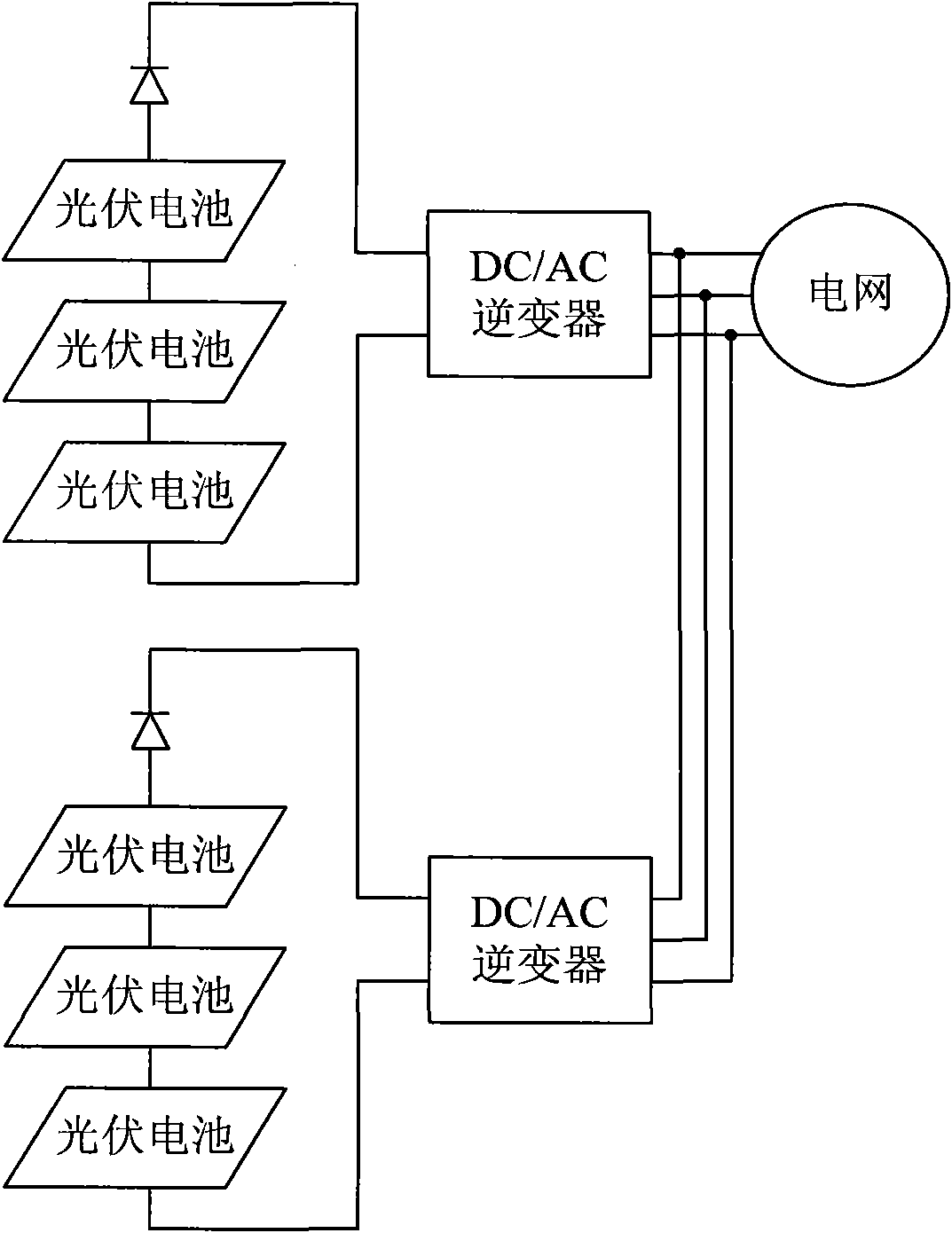
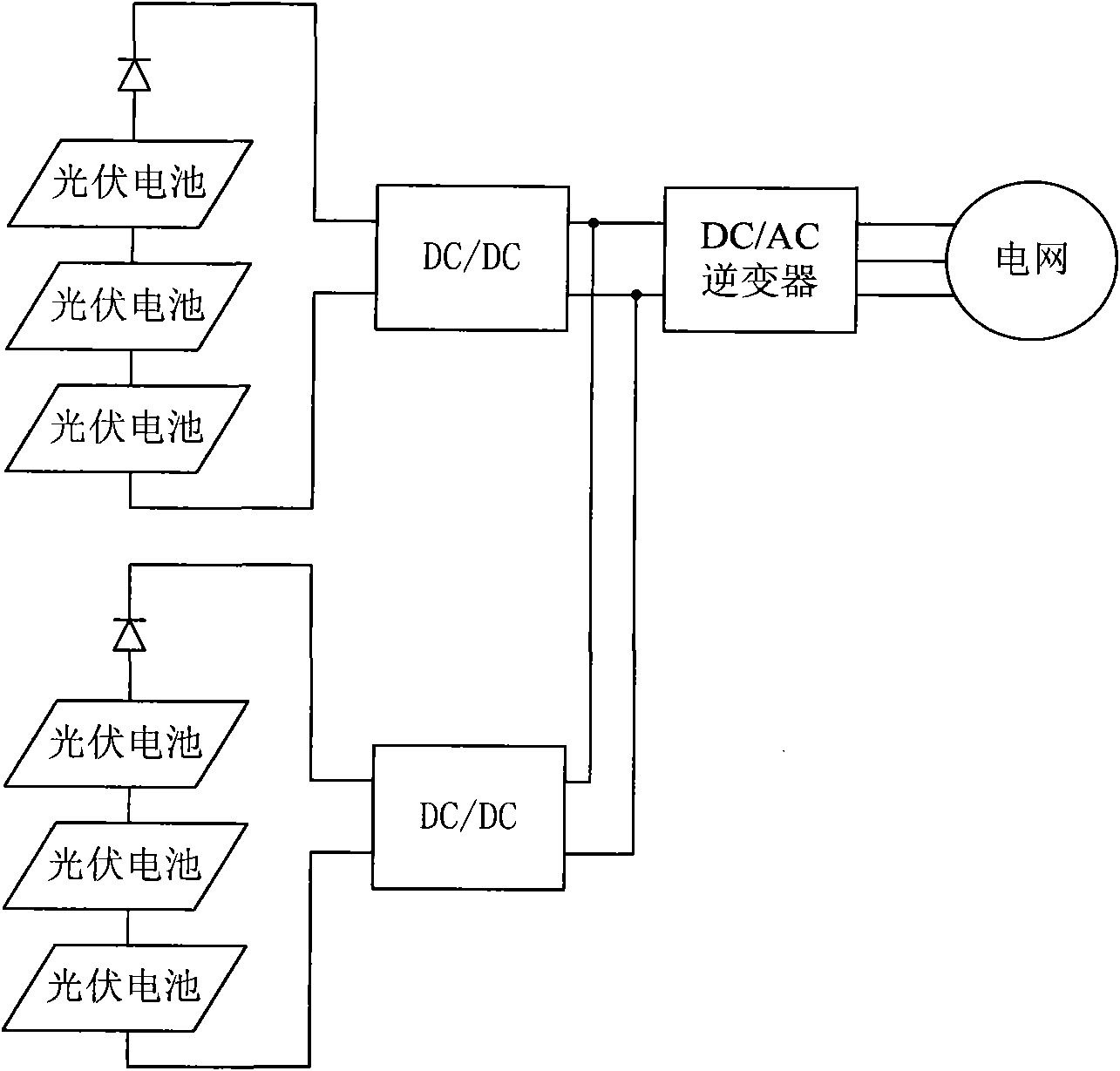
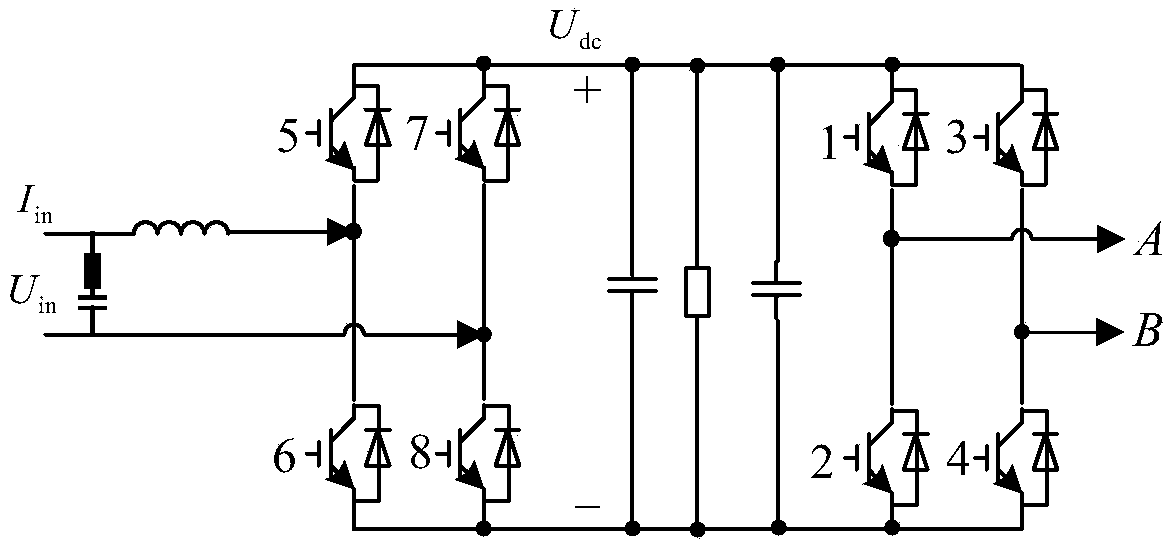
Energy-saving type cascade multilevel photovoltaic grid-connected generating control system
InactiveCN101917016AControl powerEliminate random fluctuationsActive power filteringSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHigh voltageHarmonic voltages
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
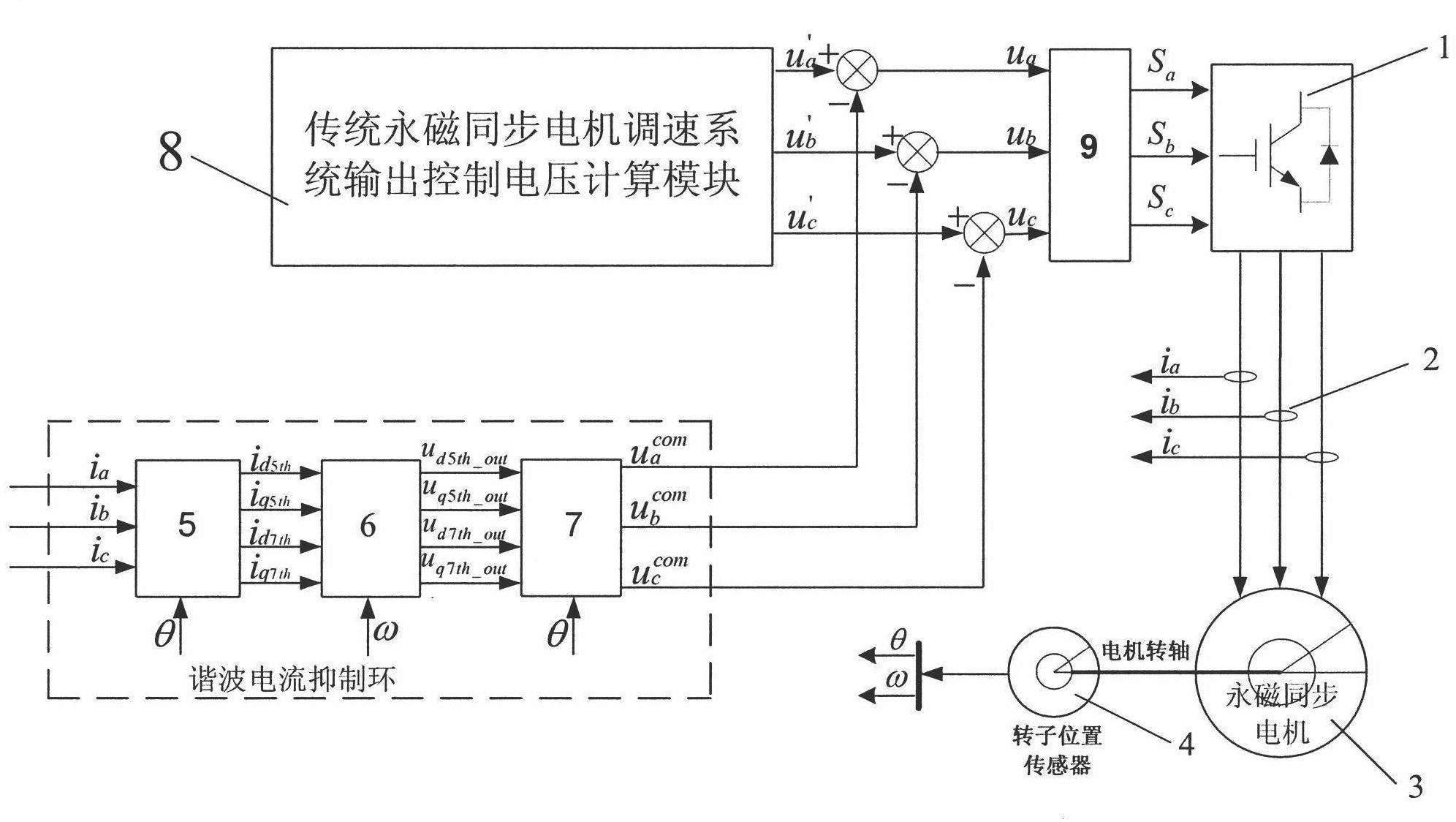
Method for injecting harmonic voltage to restrain harmonic current of PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor)
InactiveCN102201770AVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorClosed loop
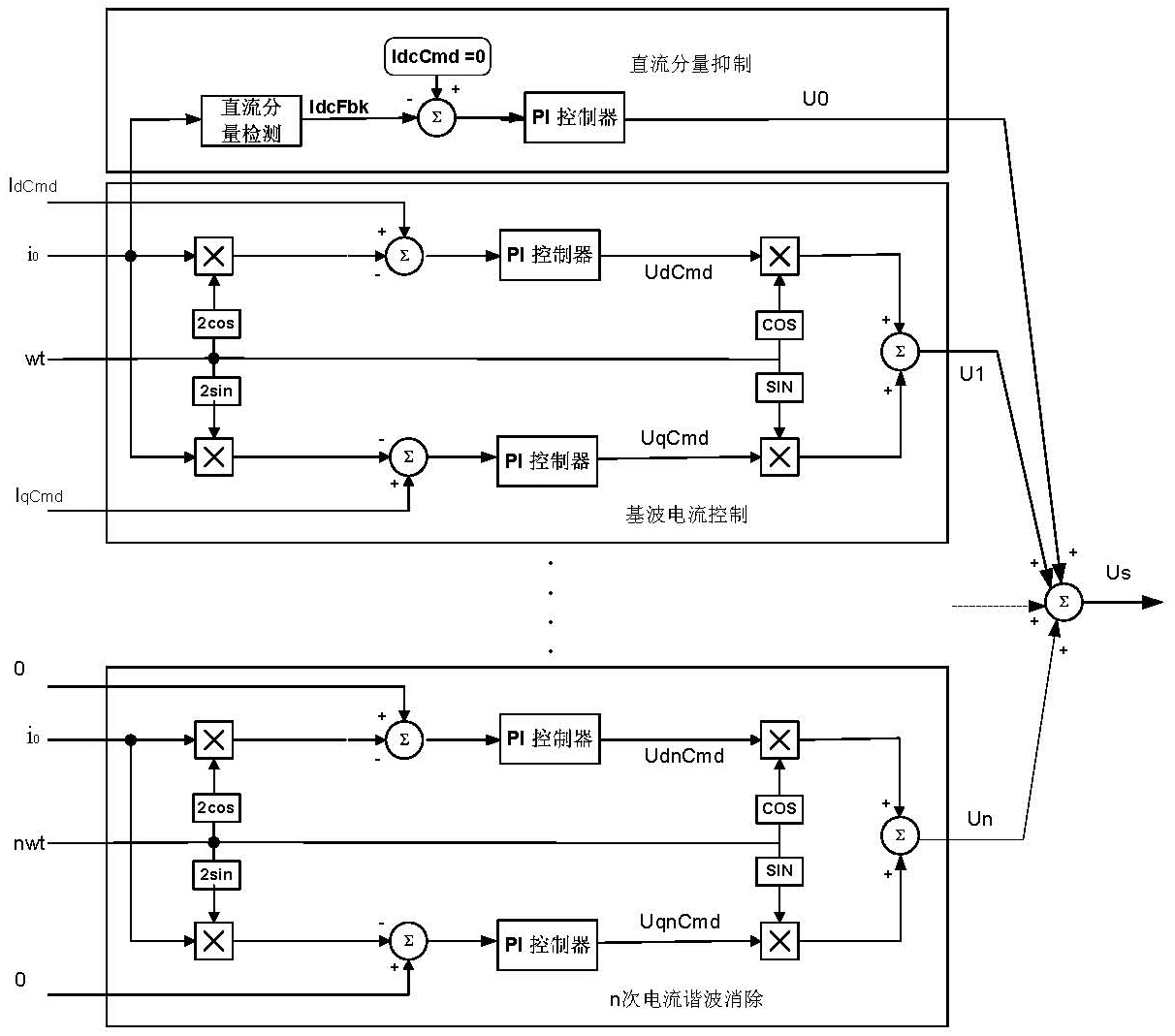
The invention provides a method for injecting a harmonic voltage to restrain a harmonic current of a PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor), which is characterized in that a ring to restrain the harmonic current is added to realize the closed-loop control for the harmonic current on the basis of extracting harmonic current components in the PMSM in real time, thus calculating to obtain harmonic voltage components which are required to be injected to restrain 5-order and 7-order harmonic currents of the PMSM; and then the obtained harmonic voltage components are injected into a three-phase control voltage in a speed control system of the PMSM so as to offset the 5-order and 7-order harmonic components in a motor current when the PMSM runs, thereby reaching the purpose of restraining the 5-order and 7-order harmonic currents. The method is used to solve the technical difficulty that current ZCP (zero crossing point) is required to detect accurately in a traditional mode to restrain the harmonic current, remarkably improves the current waveform of the motor, effectively restrains the 5-order and 7-order harmonic currents caused by the nonlinear characteristics of an inverter and the air-gap field distortion of the motor, effectively reduces the additional loss caused by the 5-order and 7-order harmonic current components, reduces the electromagnetic torque and the revolving speed pulse of the PMSM and improves the running efficiency and the running reliability of the PMSM.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
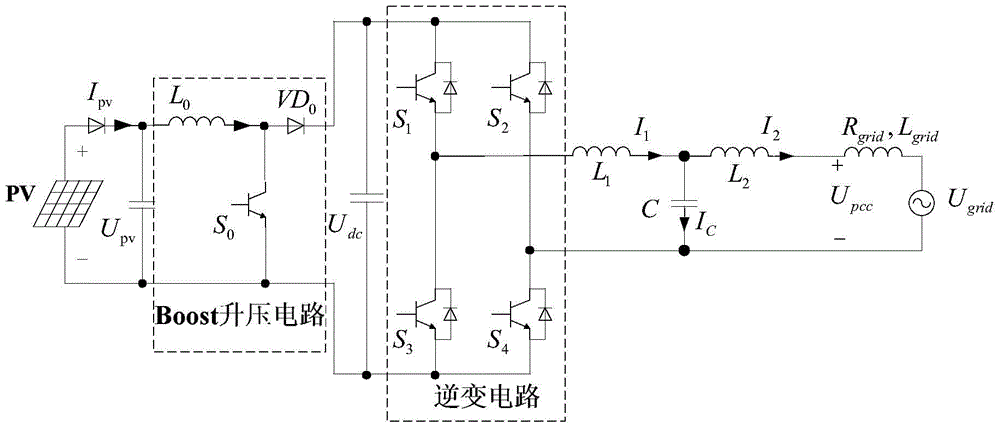
Method for suppressing output harmonic wave and direct current component of single-phase grid-combined photovoltaic inverter
InactiveCN101950985AImprove power qualitySuppresses the DC componentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationSingle phaseElectric energy
The invention relates to a method for suppressing an output harmonic wave and a direct current component of a single-phase grid-combined photovoltaic inverter. In the invention, an original voltage and current detection device and a digital controller in a photovoltaic grid-combined generation system are utilized, and the controls to the Boost circuit duty ratio and an inverter are increased on the basis of an original control algorithm. A phase current signal output by the inverter is subjected to single-phase conversion, actually output current is compared with a reference value, and a difference value is subjected to PI regulation to obtain a voltage control command of a fundamental wave and a harmonic wave; a direct current component detection value obtained by calculating the phase current signal and a given calibration currents difference value are processed to obtain a direct current component suppression voltage command; and after a control command of instantaneous fundamentalwave voltage, a control command of instantaneous harmonic wave voltage and the direct current component suppression voltage command are added and processed to obtain a control command used for the inverter. The invention realizes the control of the active and reactive current of the inverter, the elimination of the designated harmonic wave and the suppression of the direct current component and can effectively improve the electric energy quality of the grids.
Owner:上海兆能电力电子技术有限公司
Control method of quality control system of micro source internetworking electric energy
ActiveCN102832642AImprove power qualityImprove power supply reliabilityActive power filteringEnergy industryCapacitanceQuality control system
The invention discloses a control method for a quality control system of micro source internetworking electric energy. A primary side of the coupling voltage transformer on a serial active power filter side of a UPQC (unified power quality controller) is connected with a larger current-limiting inductor in parallel, and a direct-current large-capacitance side of the UPQC is connected with a photovoltaic generating power supply in parallel. Due to effects of cooperative control, the photovoltaic power supply is internetworked for power generation during normal operation, active power is provided for a power grid by the parallel active power filter of the UPQC, and the harmonic current from a load side and the voltage fluctuation and harmonic voltage from the power grid side are governed and compensated by the UPQC. In the case of short-circuiting failure on the load side, the main circuit of the UPQC stops operating, a secondary side of the coupling voltage transformer is subjected to high impedance, and the current can be limited by the parallel current-limiting large inductor. By adopting the method, the functions of failure current limitation, harmonic treatment, voltage support, photovoltaic power generation and the like can be realized during micro grid internetworking operation, and the optimized protection and operation of the quality of electric energy in micro grid internetworking can also be realized.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
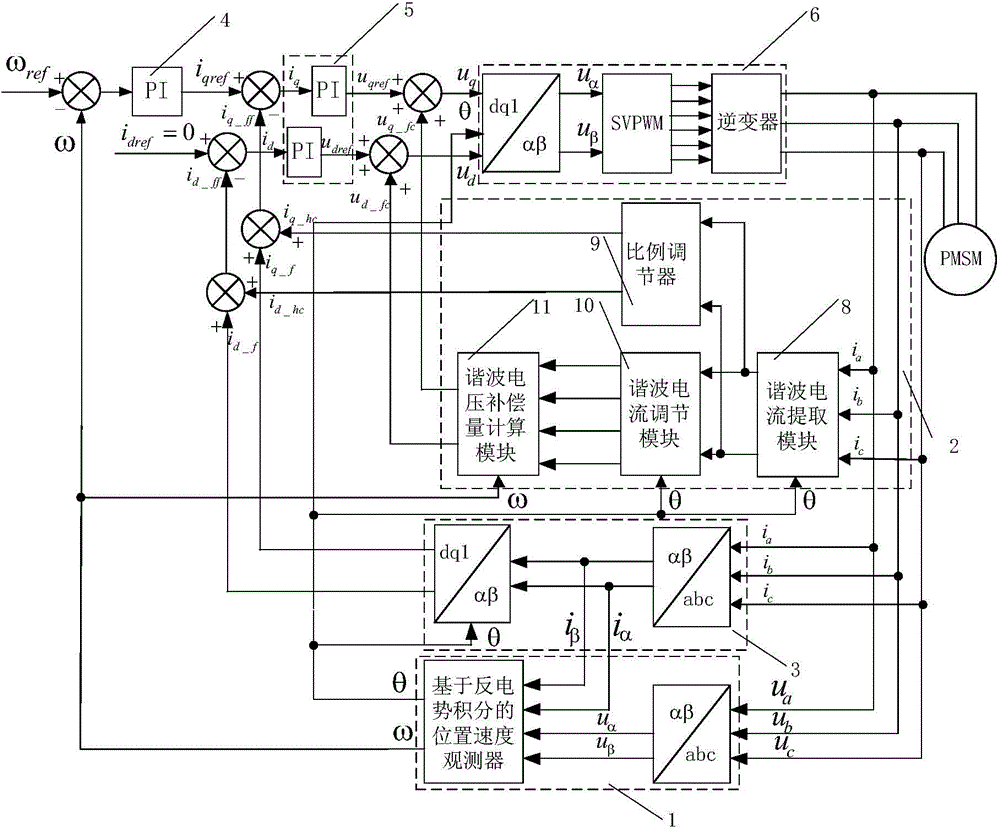
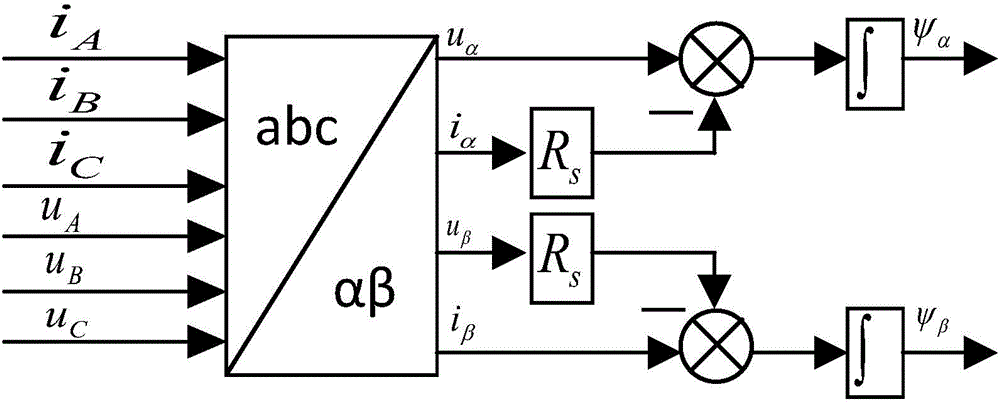
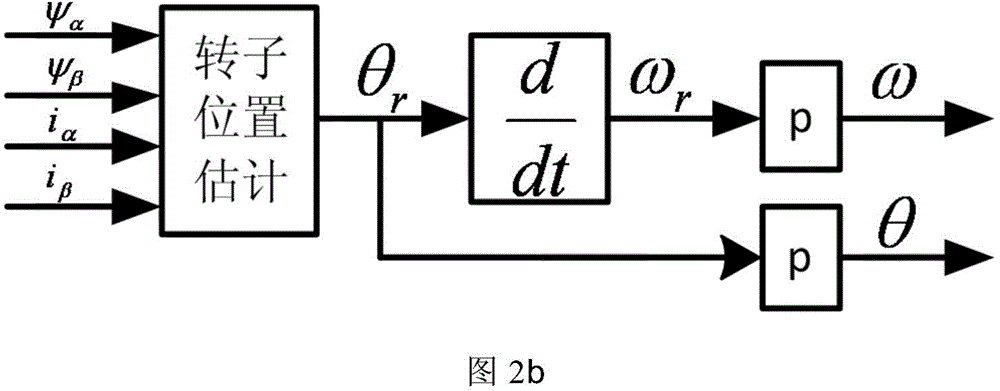
Space vector modulation based harmonic current compensation system for high-speed permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN104601077AAvoid installation and maintenance difficultiesSimple structureElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsMathematical model
The invention discloses a space vector modulation based harmonic current compensation system for a high-speed permanent magnet motor. The system comprises a rotor position and speed observation module, a stator phase current harmonic compensation module, a phase current feedback module, a rotation speed PI adjustment module, a current PI adjustment module and an SVPWM (space vector pulse width modulation) conversion output module. The stator phase current harmonic compensation module comprises a harmonic current extraction module, a proportional controller, a harmonic current adjustment module and a harmonic voltage compensation amount calculation module. The harmonic current extraction module extracts phase current harmonics of a permanent magnet synchronous motor in real time by the aid of an adaptive band-pass filter; the proportional controller adjusts the harmonic current and feeds the harmonic current to a current loop; the harmonic current adjustment module and the harmonic voltage compensation amount calculation module are used for calculating harmonic voltage compensation amount on the basis of a mathematical model of the high-speed permanent magnet motor and feeding back to the voltage loop. By the space vector modulation based harmonic current compensation system for the high-speed permanent magnet motor, voltage compensation amount can be calculated accurately, real-time compensation can be realized, phase current waveforms in operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor can be improved effectively, torques and rotation speed pulses can be reduced, and accordingly operation efficiency, stability and reliability of the motor can be improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Audible noise measuring circuit and method of power capacitor
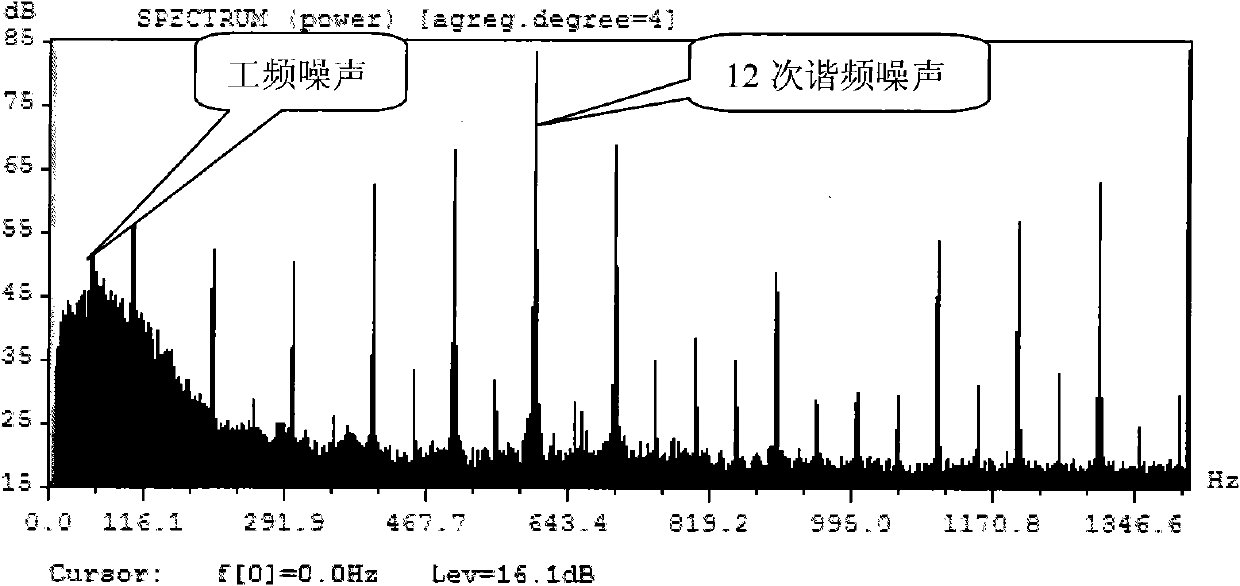
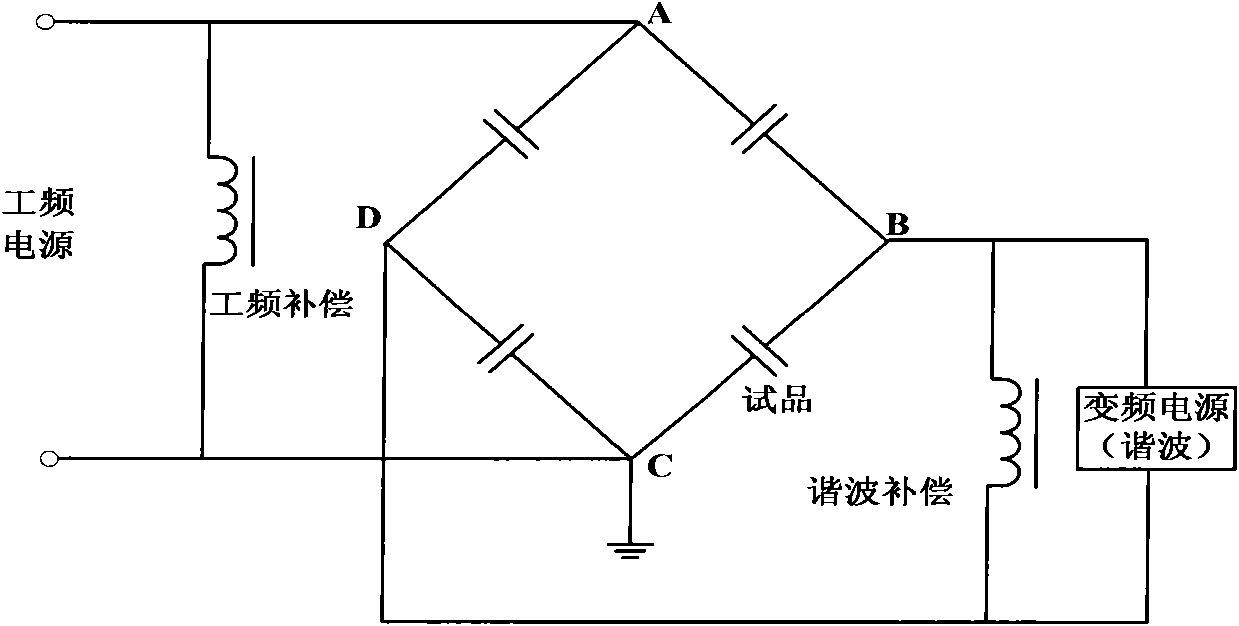
InactiveCN101793922AReduce randomnessComparableNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementHigh pressureMotor capacitor
The invention discloses audible noise measuring circuit and method of a power capacitor. The audible noise measuring method comprises the following steps of: selecting a noise-eliminating test area; mounting a power capacitor to be measured in the noise-eliminating test area; setting a power capacitor to be measured in accompany; building the power capacitor to be measured and the power capacitorto be measured in accompany into a bridge-type power capacitor loading circuit; respectively loading an external high-voltage alternating current power source and an external harmonic power source attwo ends of the bridge-type power capacitor loading circuit, wherein the whole bridge-type circuit achieves resonance state under the common action of power frequency voltage generated by the high-voltage alternating current power source and various time harmonic voltage generated by the harmonic power source; and obtaining various noise values generated by the power capacitor to be measured in an actual work state according to data which are measured by a noise sensor arranged around the power capacitor to be measured and are related to the noise. The invention reduces the random of the noise measuring operation of the power capacitor, so that a measuring result has more comparability and a set of noise measuring method of the power capacitor with systematicness, completeness, science and reasonability is formed.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
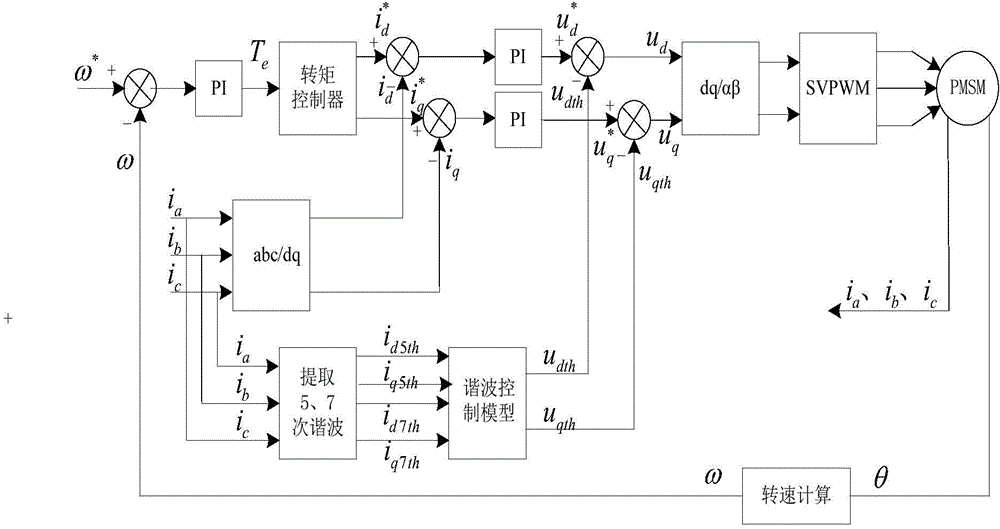
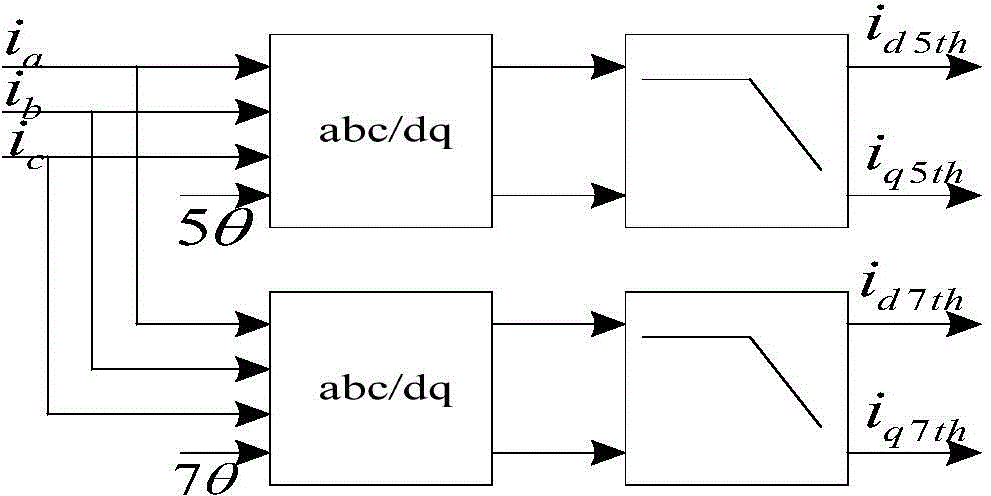
Torque pulsation inhibition method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN104579080AEliminate torque rippleEnhanced inhibitory effectElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPower flowHarmonic
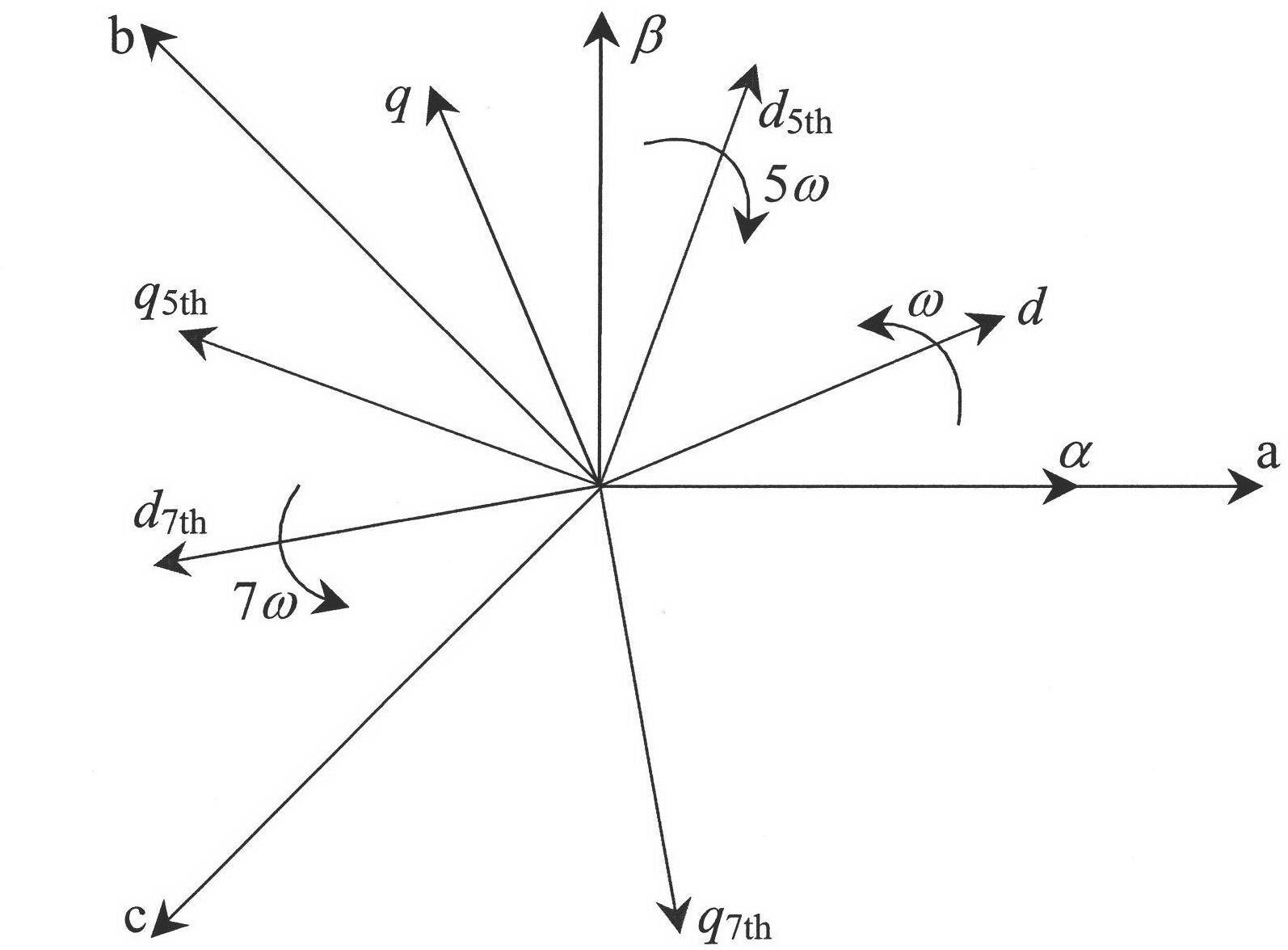
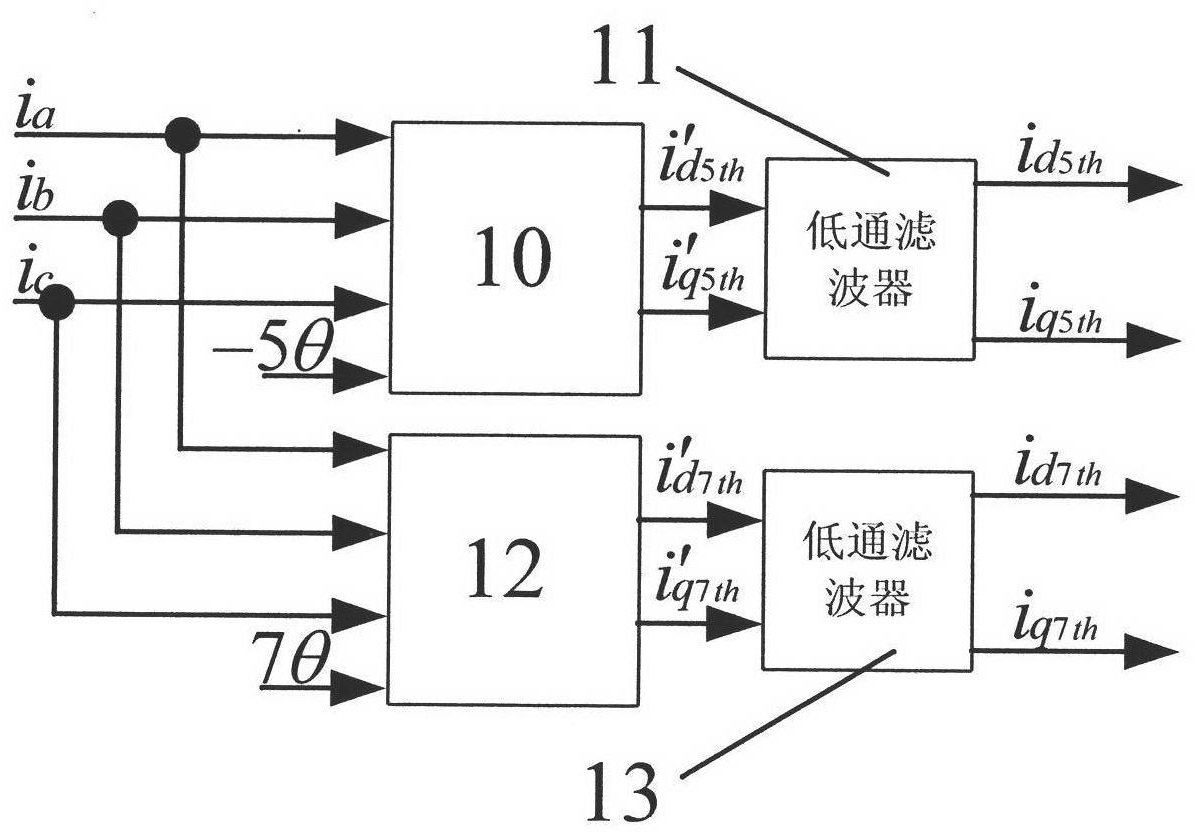
The invention discloses a torque pulsation inhibition method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring three-phase currents ia, ib and ic of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; acquiring the d-axis component id5th and the q-axis component iq5th of the fifth harmonic current in the corresponding synchronous rotation coordinate system by use of ia, ib and ic and acquiring the d-axis component id7th and the q-axis component iq7th of the seventh harmonic current in the corresponding synchronous rotation coordinate system by use of ia, ib and ic; acquiring the d-axis compensation quantity udth and the q-axis compensation quantity uqth of the harmonic voltage from id5th, iq5th, id7th and iq7th; feeding the udth back to the d-axis voltage ud of a control system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor and feeding the uqth back to the q-axis voltage uq of the control system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, eliminating the fifth harmonic current and the seventh harmonic current, and inhibiting the sixth torque pulsation and the twelfth torque pulsation. The method can effectively eliminate the harmonic current and can improve the effect of inhibiting the torque pulsation.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
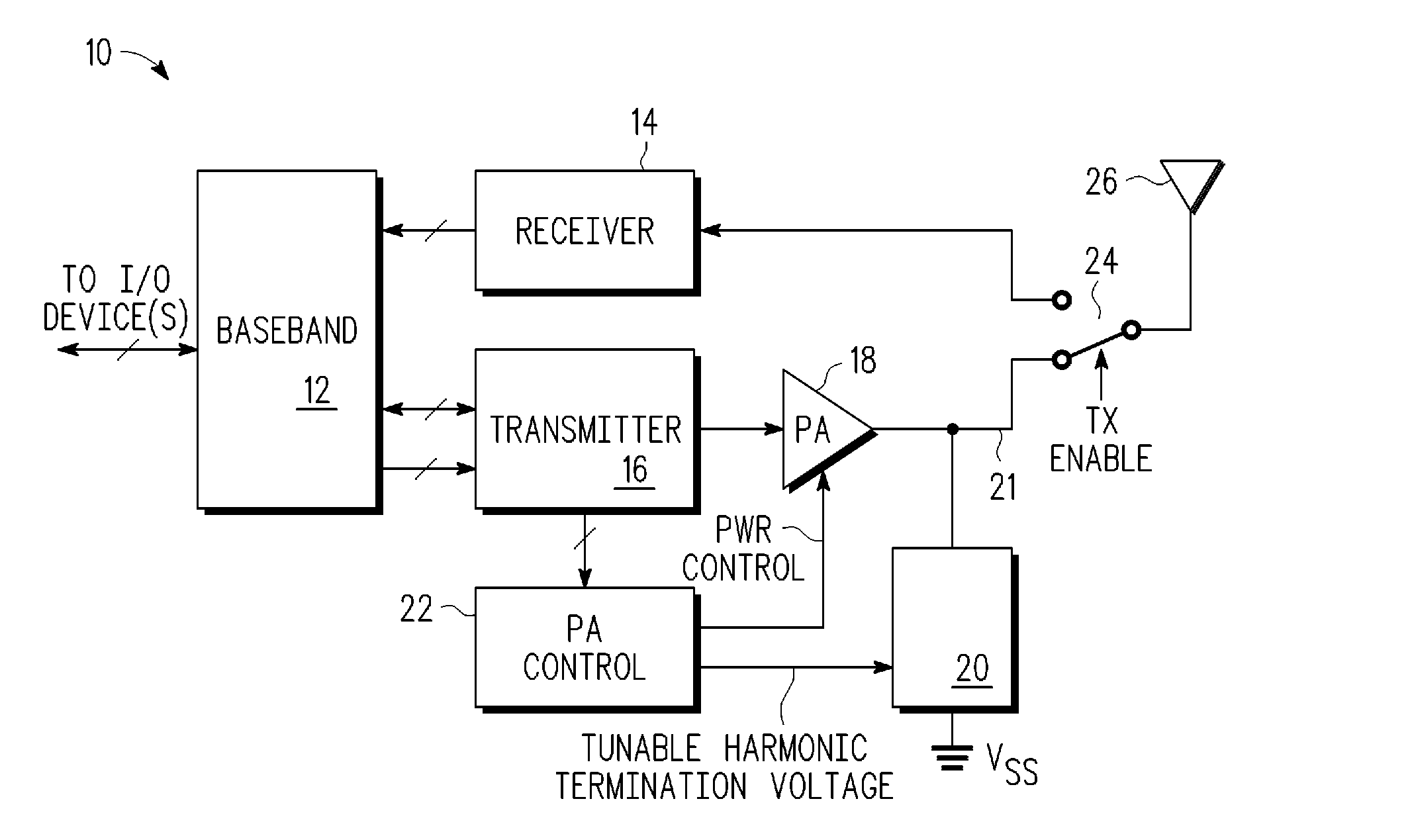
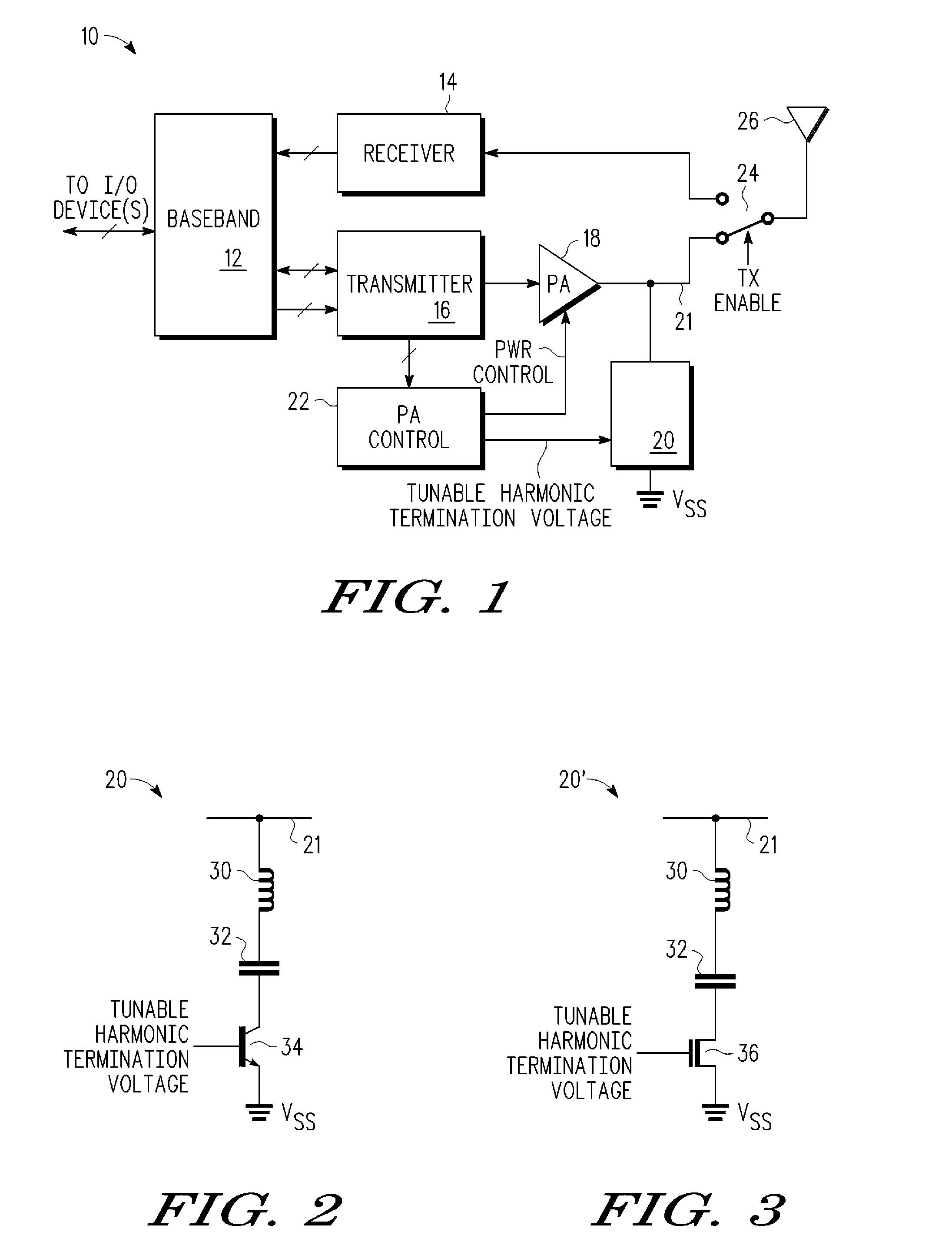
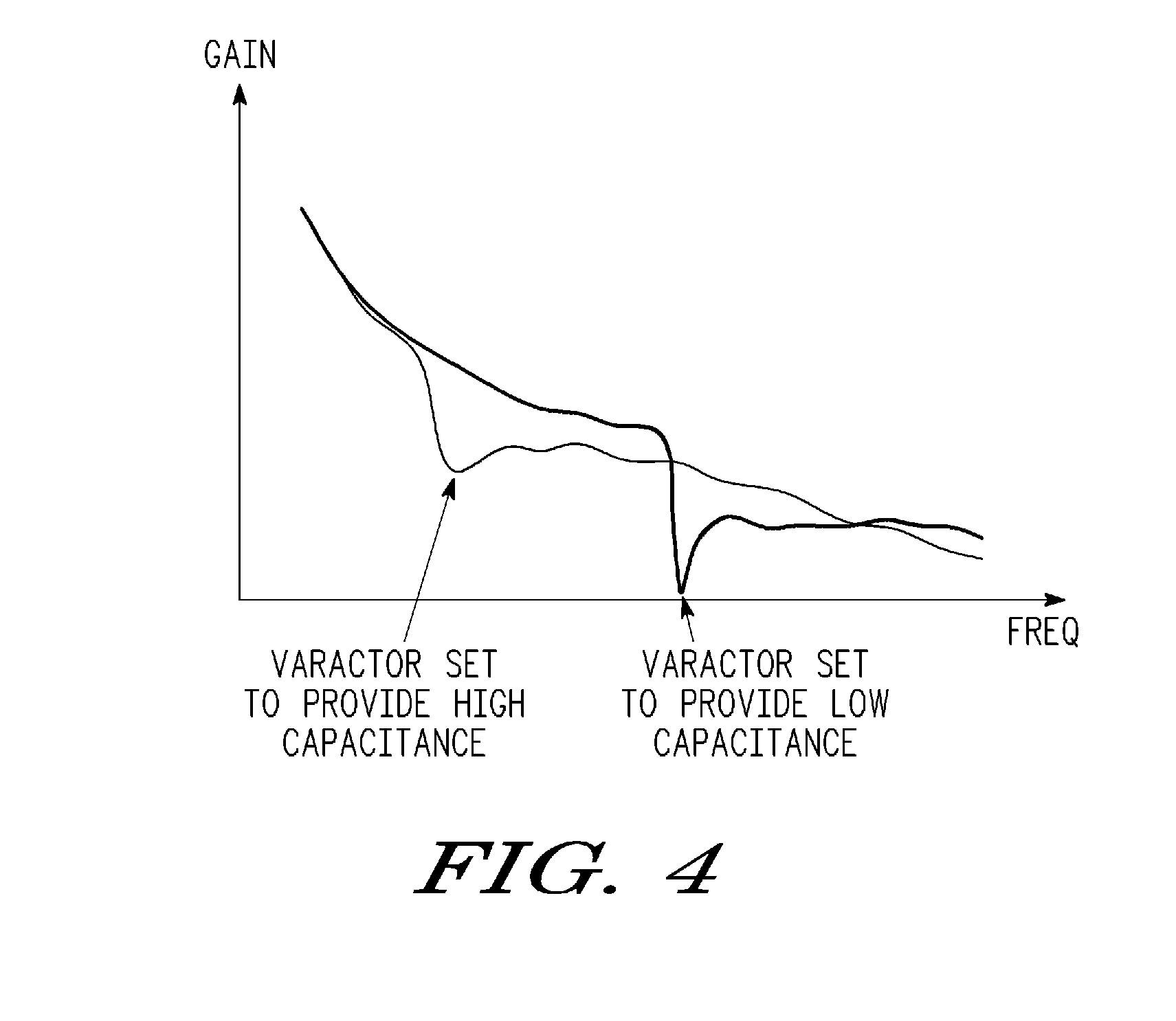
Multi-mode transceiver having tunable harmonic termination circuit and method therefor
ActiveUS20080039025A1Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCapacitanceTransceiver
A transceiver includes a harmonic termination circuit that receives a tunable harmonic voltage from a power amplifier control. The harmonic termination circuit includes a variable capacitor that is capable of adjusting its capacitance in response to the tunable harmonic termination voltage to achieve at least two modes of operation. The at least two modes of operation may be EDGE mode and GSM mode. In this embodiment, the harmonic termination circuit allows for linearity specifications of EDGE to be met, while not degrading the efficiency of the transceiver when operating in GSM mode. In one embodiment, the harmonic termination circuit further includes an inductive element in series with the variable capacitor.
Owner:NXP USA INC
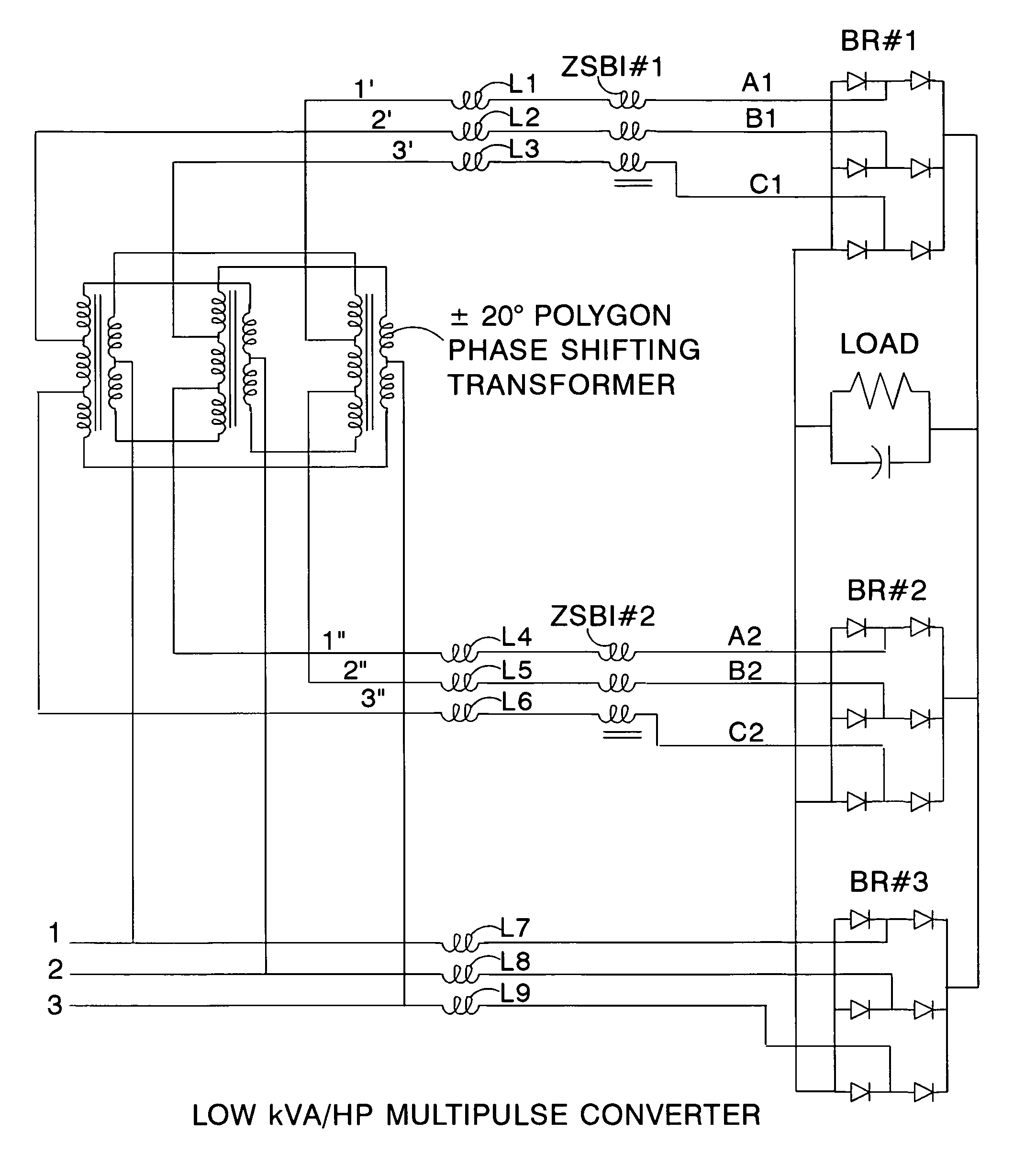
Low kVA/kW transformers for AC to DC multipulse converters
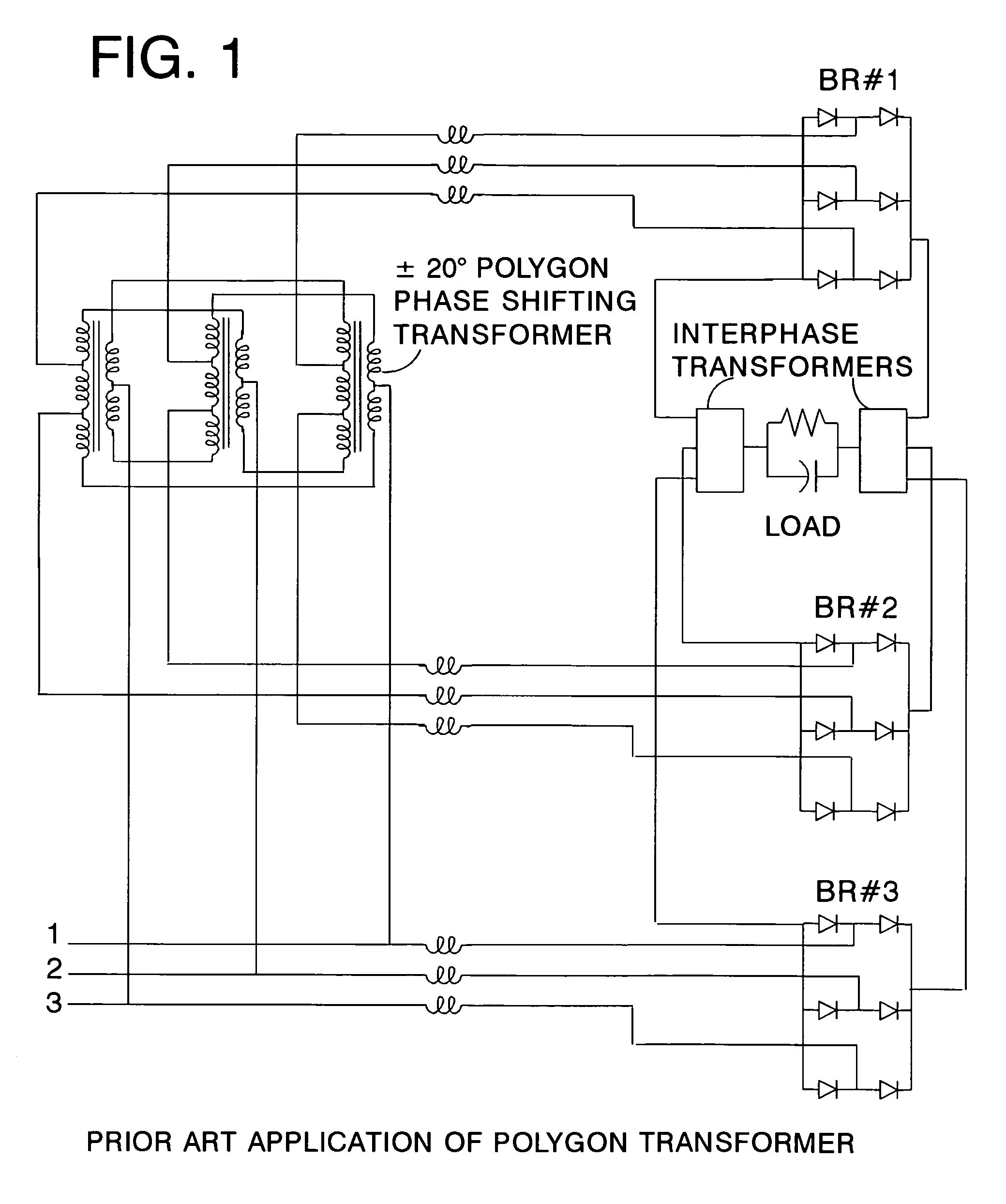
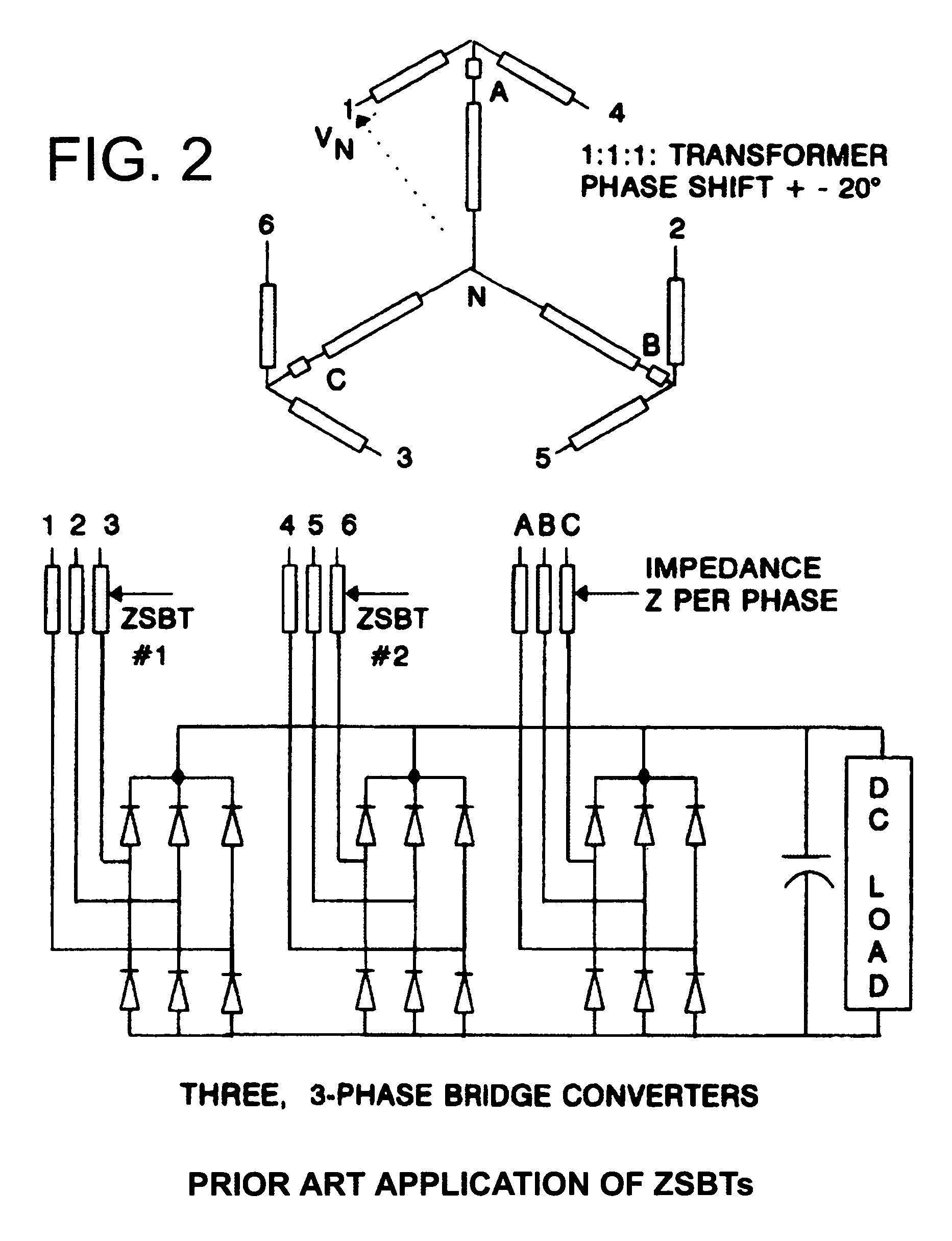
A polygon connected autotransformer in conjunction with zero sequence blocking inductor(s) enables multipulse AC to DC converters to use lower kVA parts rating by using appropriate phase-shifted voltage sets in conjunction with inductors that extend the conduction period and reduce rms current. Also, lower harmonic voltages in the transformer facilitate use of lower performance magnetic steel. Designs for 12, 18, and 24-pulse use the same conceptual approach. Very efficient high power ratings are feasible. Means are given to limit the maximum no-load DC output voltage. A technique is disclosed that reduces the size of polygon transformers supplying loads with substantial third harmonic.
Owner:SCHAFFNER MTC LLC
Electric energy quality harmonic disturbance source platform
ActiveCN104034982AAmplitude adjustableLarge current rangeElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingOutput transformerPower quality
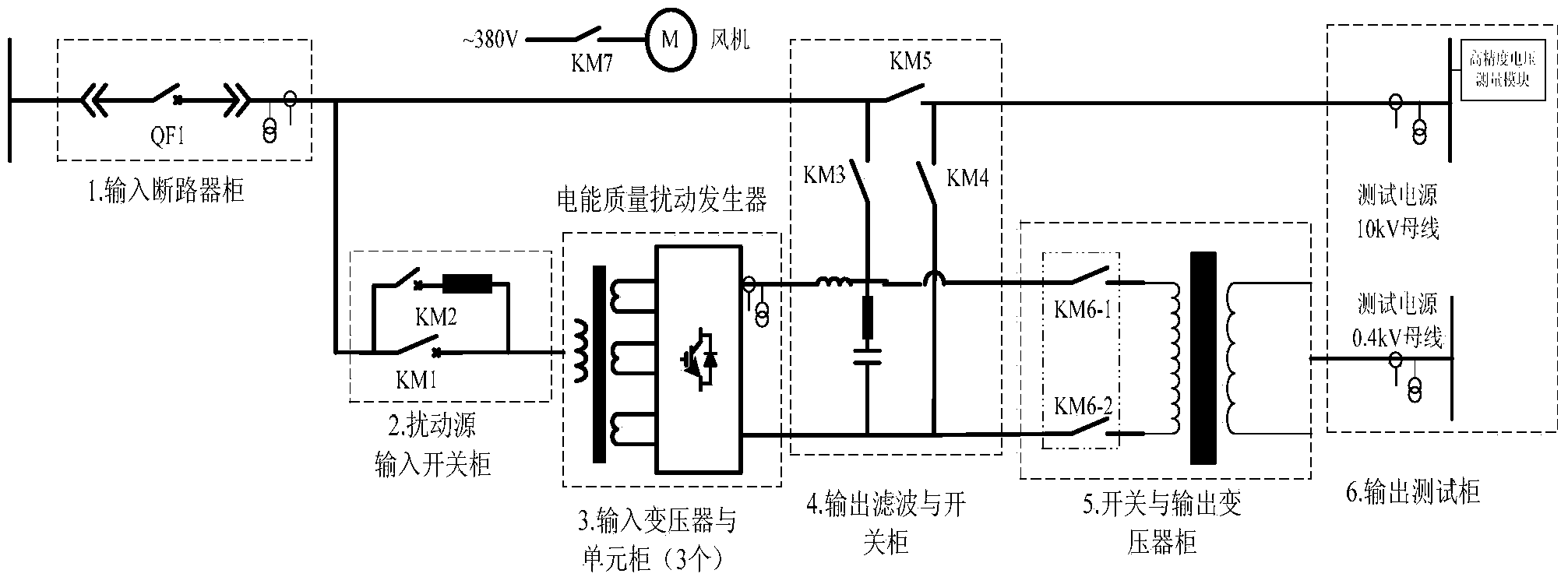
The invention relates to an electric energy quality harmonic disturbance source platform. In the disturbance source platform, an input circuit breaker cabinet, a disturbance source input switch cabinet, an output filter and switch cabinet and an output test cabinet are all connected to a 10kV bus; the disturbance source input switch cabinet, an input transformer and unit cabinet, the output filter and switch cabinet, a switch and output transformer cabinet and the output test cabinet are sequentially connected; the output test cabinet, the input transformer and unit cabinet are connected with the input control cabinet; the electric energy quality harmonic disturbance source outputs 0-50 times or stacking folds of standard harmonic voltage current source with adjustable amplitude and phase under the conditions of 10kV and 0.38kV fundamental voltages, and the maximal total harmonic distortion THDu is less than 20%. The platform can be used as a standard electric energy quality harmonic output source and a power grid equipment assessment platform for testing operation stability of a power grid and performance of power grid equipment under the harmonic output condition; electric energy quality problems about sag, fluctuation and three-phase imbalance of the power grid are simulated, and a platform is built for test, analysis and assessment of electric energy quality improvement.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
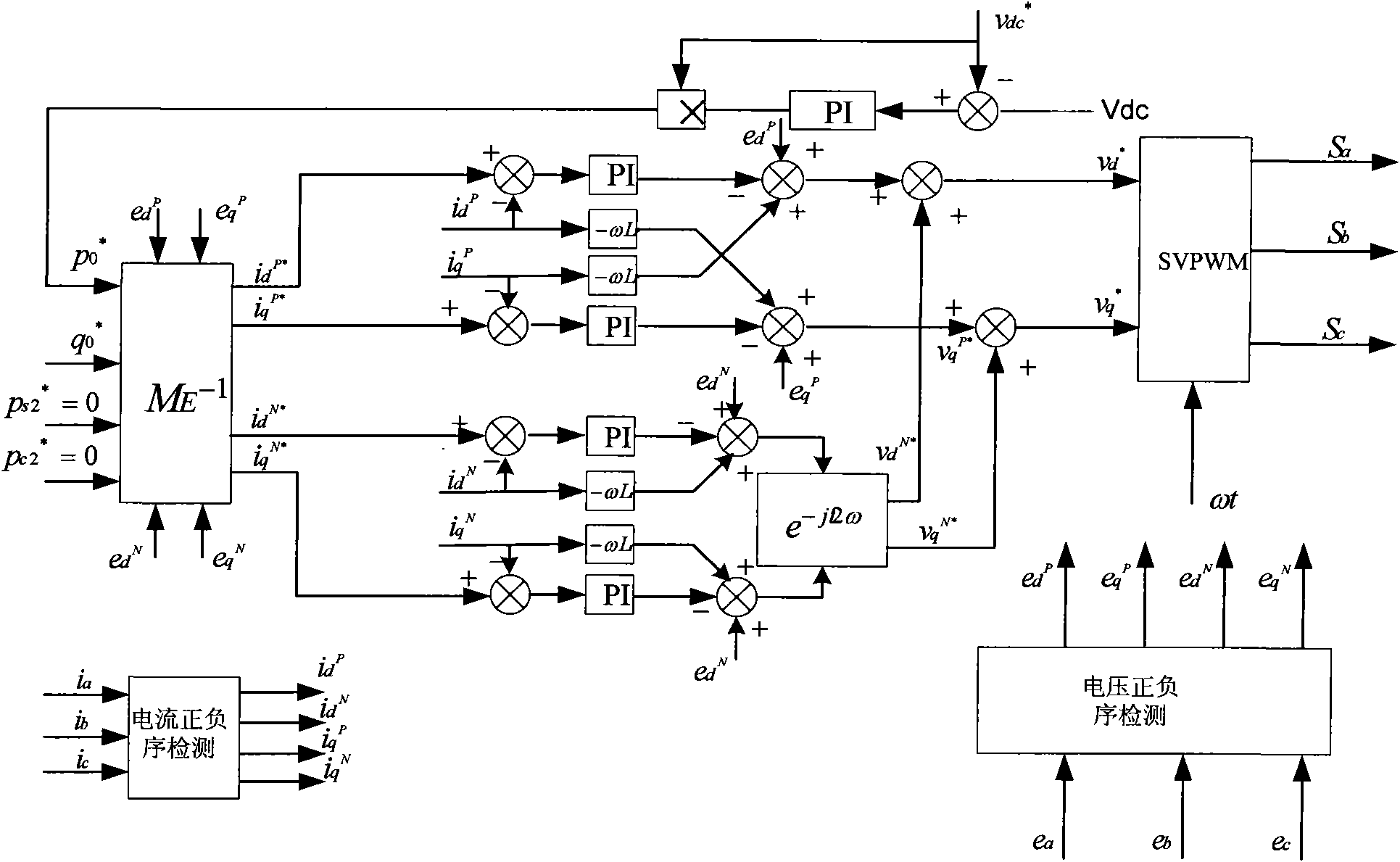
Control method for eliminating DC harmonic voltage for grid-side converter of double-fed wind power generator
ActiveCN101944840ASmall fluctuationImprove job stabilityPower conversion systemsEngineeringHarmonic voltages
The invention discloses a method for eliminating DC harmonic voltage for the grid-side converter of a double-fed wind power generator in the case of asymmetric power grid. The method adopts a phase-shift T / 4 delay negative sequence fast separation method, which performs positive-negative sequence separation on the voltage and current of the three-phase power grid, wherein the positive-negative sequence separation method has simple calculation which only includes addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, fast response that the positive-negative sequence component can be worked out only in 5 m and small delay which facilitates the design of PI parameters. In order to obtain good control effect, the positive-negative double-dq current control with completely symmetric structure is adopted. Therefore, the positive-negative sequence current instructions are both DC components and the PI regulator can realize floating control.
Owner:四方蒙华电(北京)自动化技术有限公司
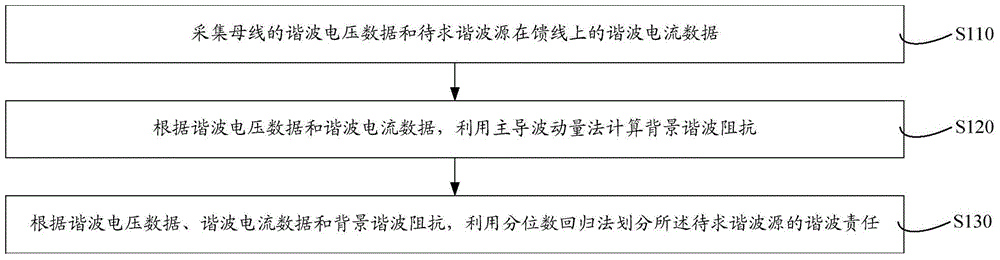
Harmonic contribution calculating method applicable to background harmonic voltage change
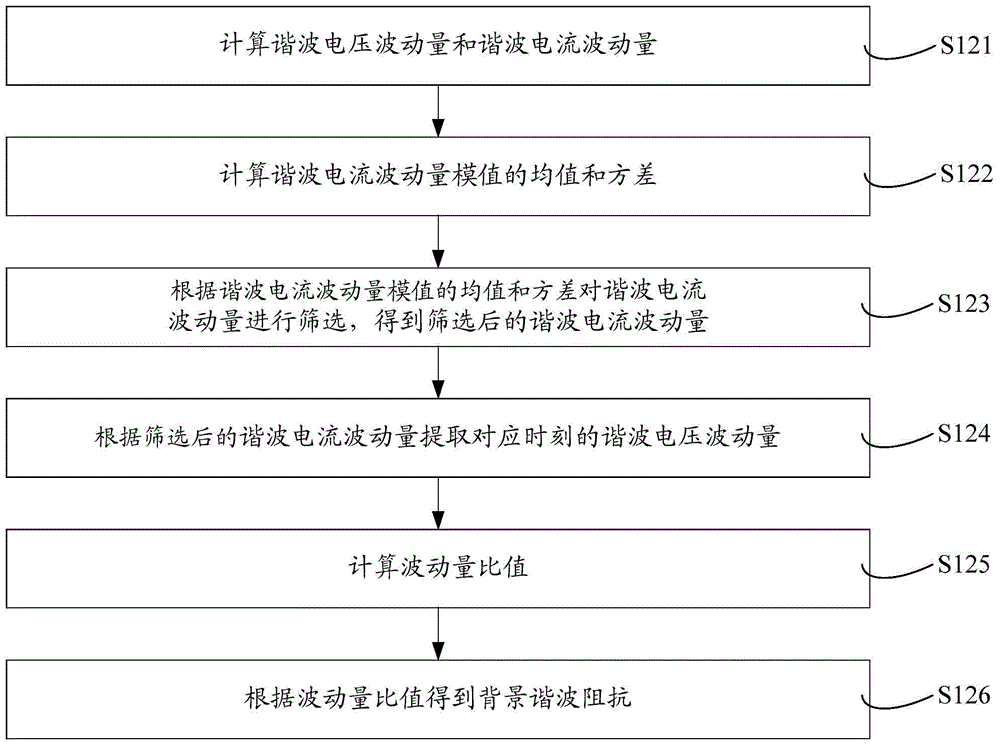
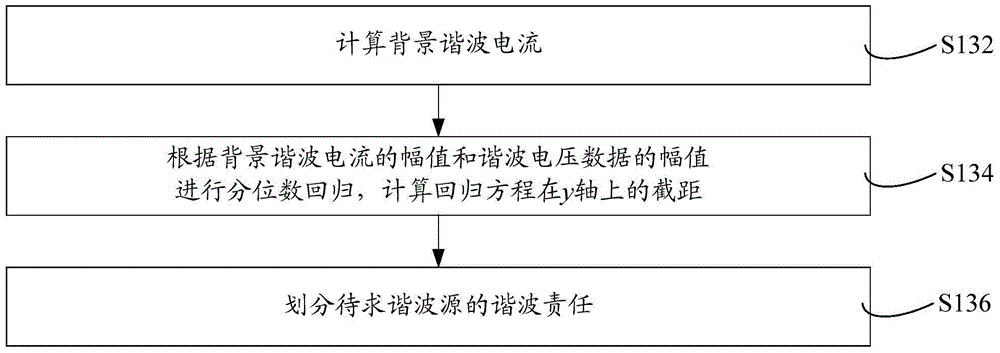
ActiveCN104502704AInhibition effectImprove accuracySpectral/fourier analysisSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumData segment
The invention discloses a harmonic contribution calculating method applicable to a background harmonic voltage change. The harmonic contribution calculating method comprises the steps that under the condition of a plurality of harmonic sources, the system harmonic impedance is estimated through a leading fluctuation quantity method; clustering processing is conducted on background harmonic voltage data through a mean shift algorithm according to the change conditions of the background harmonic voltage, and the background harmonic voltage data are divided into different data segments according to background harmonic voltage values; harmonic contributions of the data segments are calculated through a partial least square method, weighted summation is conducted, and therefore the harmonic contribution in a focused time period can be obtained. The harmonic contribution calculating method improves accuracy of harmonic contribution calculation, and can effectively eliminate the influence of the background harmonic voltage change on harmonic contribution calculation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for computing harmonic impedance of system based on maximum likelihood estimation theory
InactiveCN102998535AImprove quality management levelAccurate calculationResistance/reactance/impedencePower qualityComplex normal distribution
The invention discloses a method for computing harmonic impedance of a system based on maximum likelihood estimation theory. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: collecting bus voltage instantaneous value of common coupling point and current instantaneous value of user access system, and establishing a relation between harmonic voltage phasor and harmonic current phasor; on the basis of defining a complex covariance, deriving to obtain a probability density function of unary complex normal distribution so as to obtain a maximum likelihood estimation function; establishing the maximum likelihood estimation theory of complex field estimated by the harmonic impedance of system; utilizing an extreme value theory to solve the maximum likelihood estimation function so as to obtain the estimated value of harmonic impedance of the system finally. The method has the beneficial effects that the method for computing harmonic impedance of the system based on maximum likelihood estimation theory is capable of relatively accurately computing equivalent harmonic impedance of the system and has important meanings for further solving the problem of harmonic pollution and improving the management level of electric energy quality.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
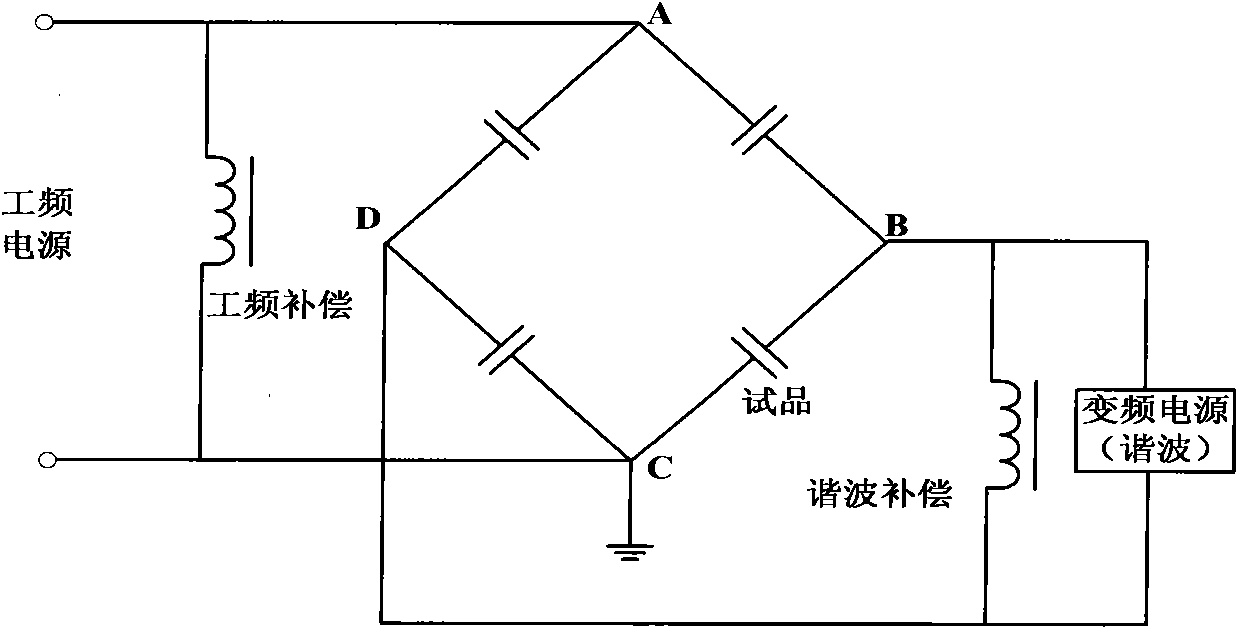
Superposition principle based programmable harmonic voltage source for large power test
InactiveCN101064479AReduce sizeIncrease system capacityConversion with intermediate conversion to dcAc-dc conversionTransformerControl manner
The invention discloses a big-power test programmable resonance wave voltage source which is based on superposition principle, the resonance wave voltage source includes three phase commutating bridge, dc-to-ac converter, transformer in series, three phase resistance-capacitance loop and current track control circuit, the three phase commutating bridge is connected with the electricity net via inlet inductance and three switch; the structure of the dc-to-ac converter is three single-phase H bridges, each of which composes four switching tubes IGBT, the big-power test programmable resonance wave voltage source which is based on superposition principle adopts principle of separating base wave and resonance wave, the electricity provides the voltage of base wave, voltage of resonance wave is provided by the resonance wave voltage source, they are combined to make tested equipment get required voltage wave, the resonance wave is generated by controlling the dc-to-ac converter, the control mode can decreases the current in the dc-to-ac converter, and increases the capability of system, it can replace the programmable power source under most conditions.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Generator stator single phase grounding protection method
InactiveCN1411116AHigh sensitivityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric power systemHarmonic
This invention put forward two single phase earth protection methods for generator stator based on zero-sequence voltage fault component, both utilizing that of its terminal and neutral point, in which the first method is to utilize triple-frequency harmonic voltage fault component vector composition to make up the decision basis; the second method is to directly take the sum and difference of random value of the zero-sequence voltage fault component at both sides of its terminal and neutral point as the protect signal and brake signal to detect the stator single phase earth fault by comparing spectrum energy in the data window.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Motor control apparatus and motor control method
InactiveUS6861813B2Reduced responseImprove responseDC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersOrthogonal coordinatesEngineering
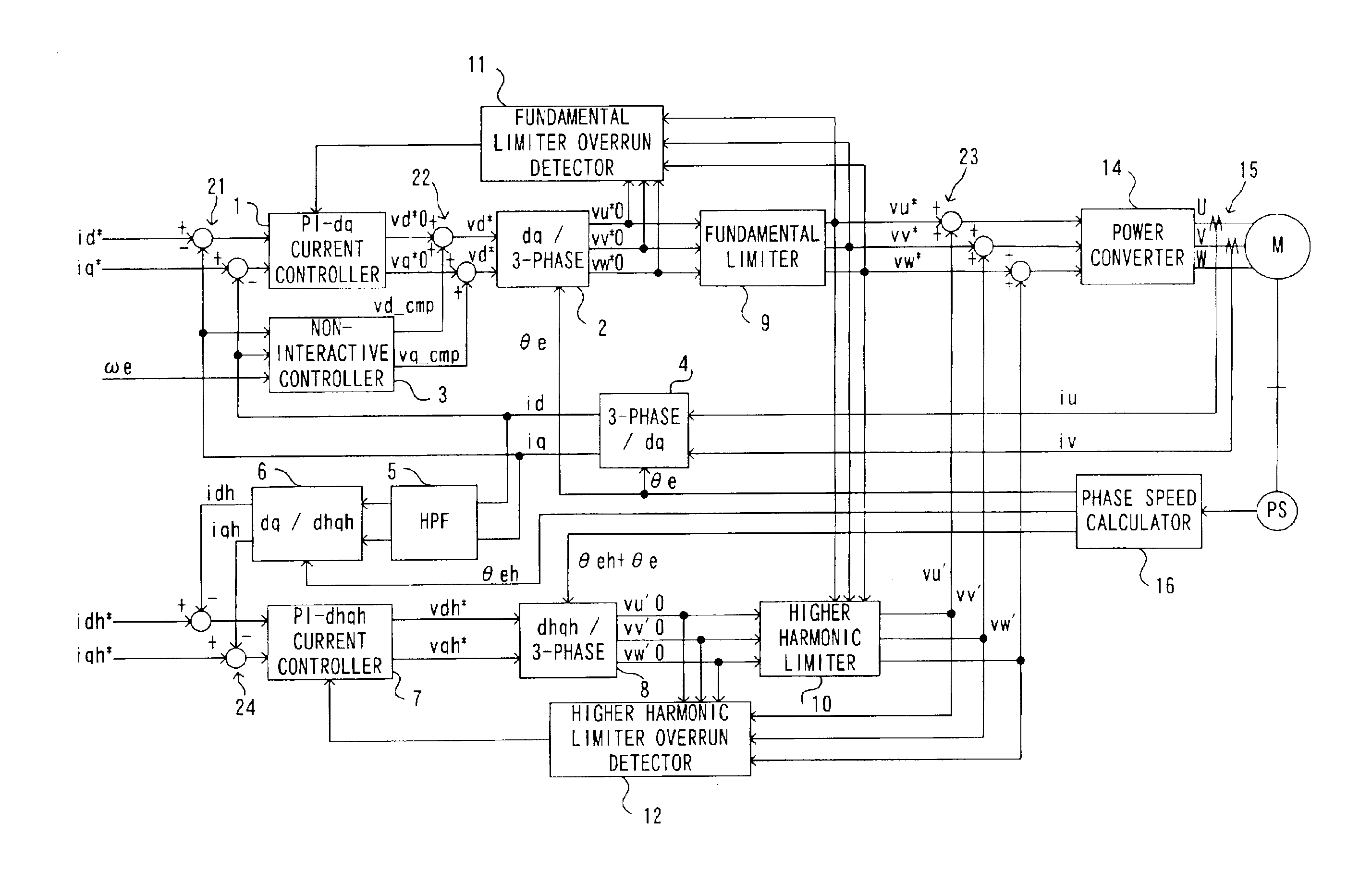
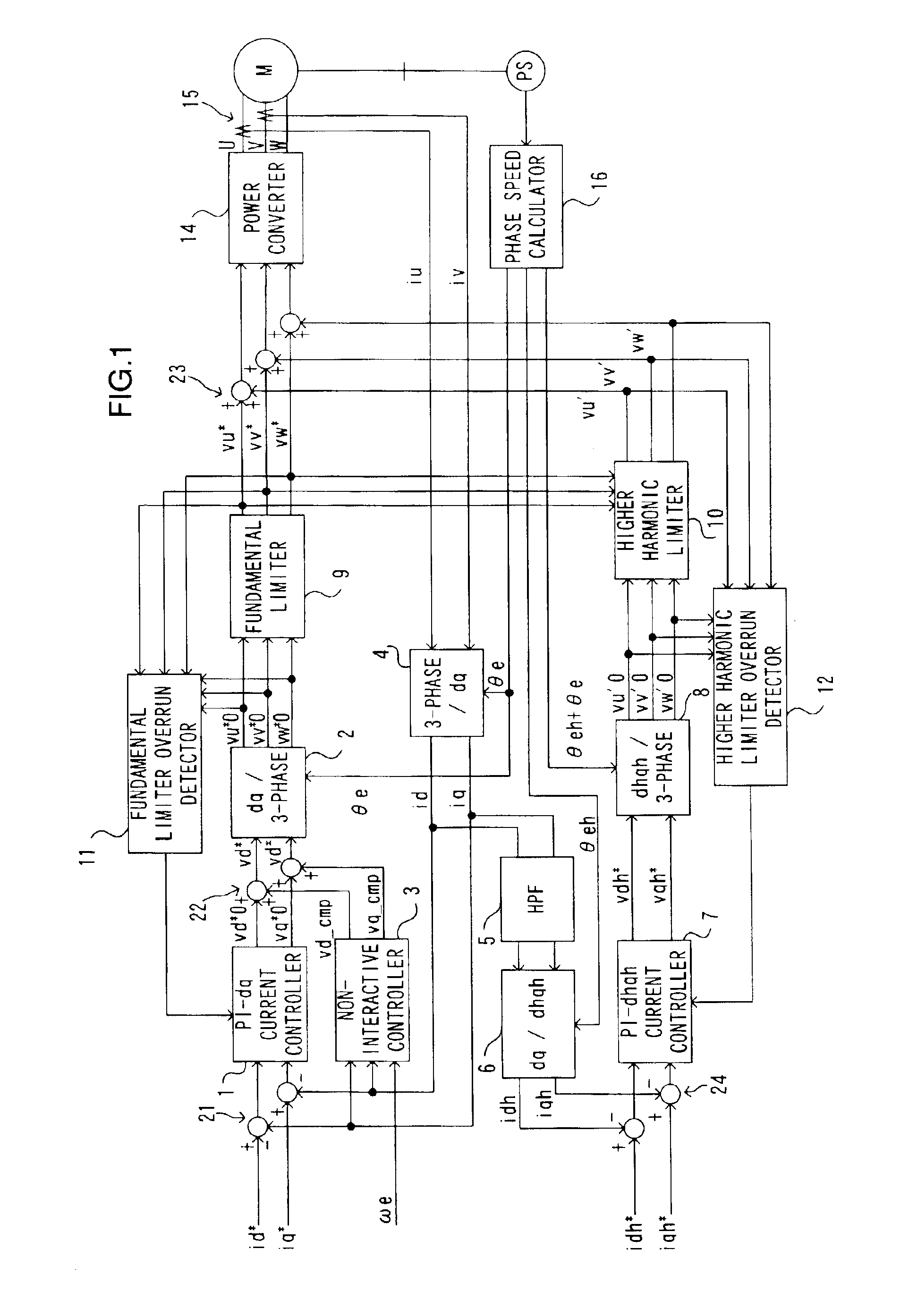
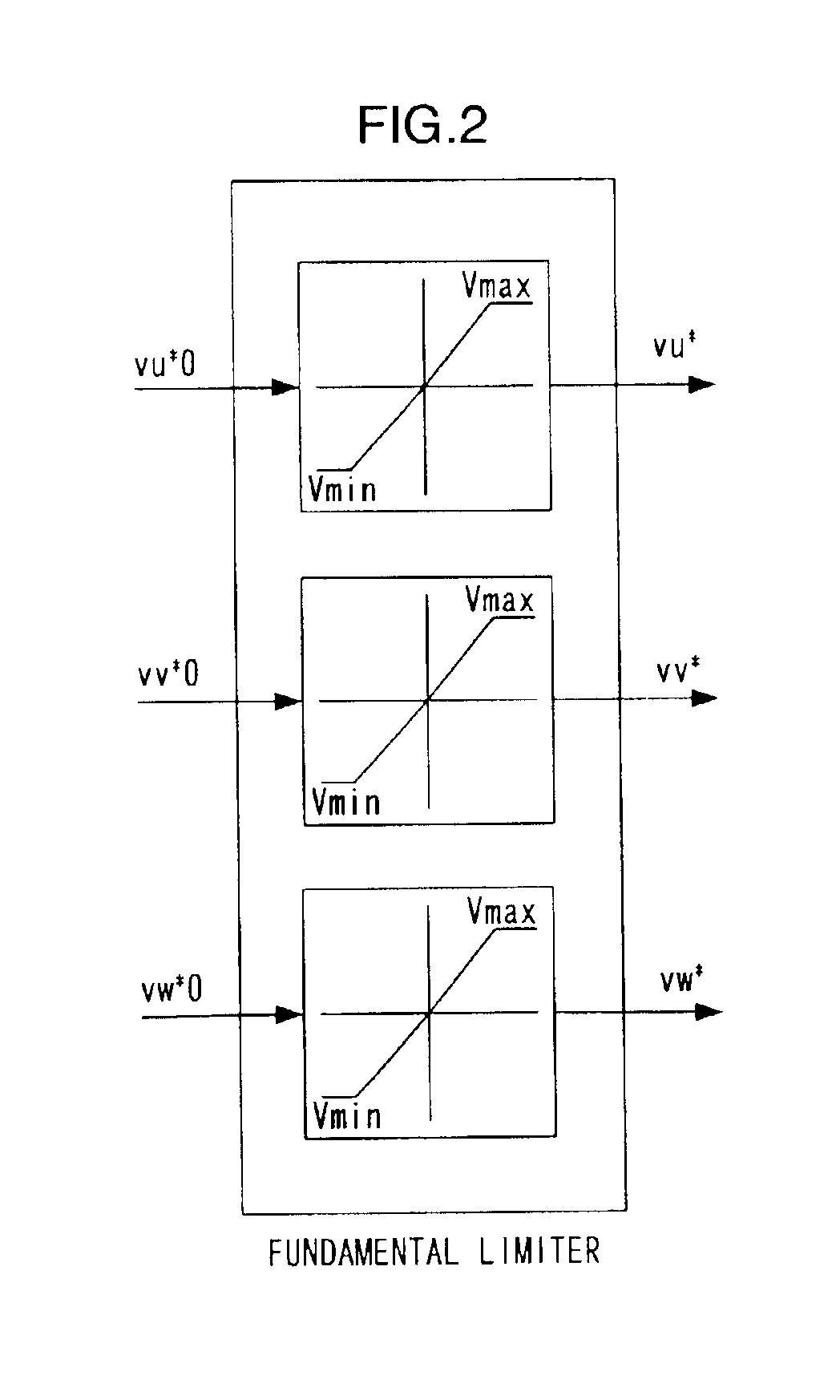
Limits are imposed on a fundamental voltage command value calculated at a fundamental current control circuit that controls a fundamental component of a 3-phase AC motor current in a dq-axis coordinate system rotating in synchronization with the rotation of the 3-phase AC motor by using predetermined limit values and limits are imposed on a higher harmonic voltage command value calculated in an orthogonal coordinate system (a higher harmonic coordinate system) rotating at a frequency set to an integral multiple of the frequency of the fundamental component in the 3-phase AC motor current by using a predetermined limit values. The voltage command values resulting from the limit processing are added together and a voltage corresponding to the sum is applied to the AC motor for drive control.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Harmonic duty quantitative allocation method based on statistical data correlation analysis
The invention discloses a harmonic duty quantitative allocation method based on statistical data correlation analysis. The method comprises the following steps of 1, acquiring and pre-processing data, mounting an electric energy quality monitoring instrument at a main harmonic source load point, and acquiring the voltage signal and the current signal of each feeder line; 2, selecting the data on the basis of a time sequence segmentation method; 3, determining h-time harmonic duty indexes of a harmonic source load i to the X position; and 4, obtaining the harmonic duty indexes. According to the method, the correlation analysis method based on the statistical law is adopted, historical measured data of harmonic voltage and harmonic current is directly used, the data required by the method is easy to acquire, and all the data can be acquired by the ordinary electric energy quality monitoring instrument. The method can lay a theoretical foundation for harmonic duty quantitative allocation, harmonic government, harmonic reward and punishment implementation and the like in a multi-harmonic source system and has wide application prospect and good social and economic benefit.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Harmonic contribution division method and harmonic contribution division system
ActiveCN104698273AAccurate calculationInhibition effectSpectral/fourier analysisQuantile regressionMomentum
The invention relates to a harmonic contribution division method and a harmonic contribution division system. The harmonic contribution division method comprises the following steps of acquiring harmonic voltage data of a bus and harmonic current data of a harmonic source to be calculated on a feeder line; calculating background harmonic impedance by using a leading fluctuation quantity method according to the harmonic voltage data and the harmonic current data; and dividing harmonic contributions of the harmonic source to be calculated by using a quantile regression method according to the harmonic voltage data, the harmonic current data and the background harmonic impedance. The background harmonic impedance is estimated by the leading fluctuation quantity method, fluctuation quantity with a leading function is screened out to calculate the background harmonic impedance, influences of background harmonic and measurement noise fluctuation on a background harmonic impedance estimation result are restrained effectively, and the background harmonic impedance is calculated accurately; and the background harmonic current is calculated according to the background harmonic impedance, and quantile regression is performed to obtain the harmonic contributions of the harmonic source. Calculation deviation caused by background harmonic fluctuation can be reduced, division accuracy is improved, and the stability and the data utilization rate are high.
Owner:GUANGZHOU POWER SUPPLY CO LTD +1
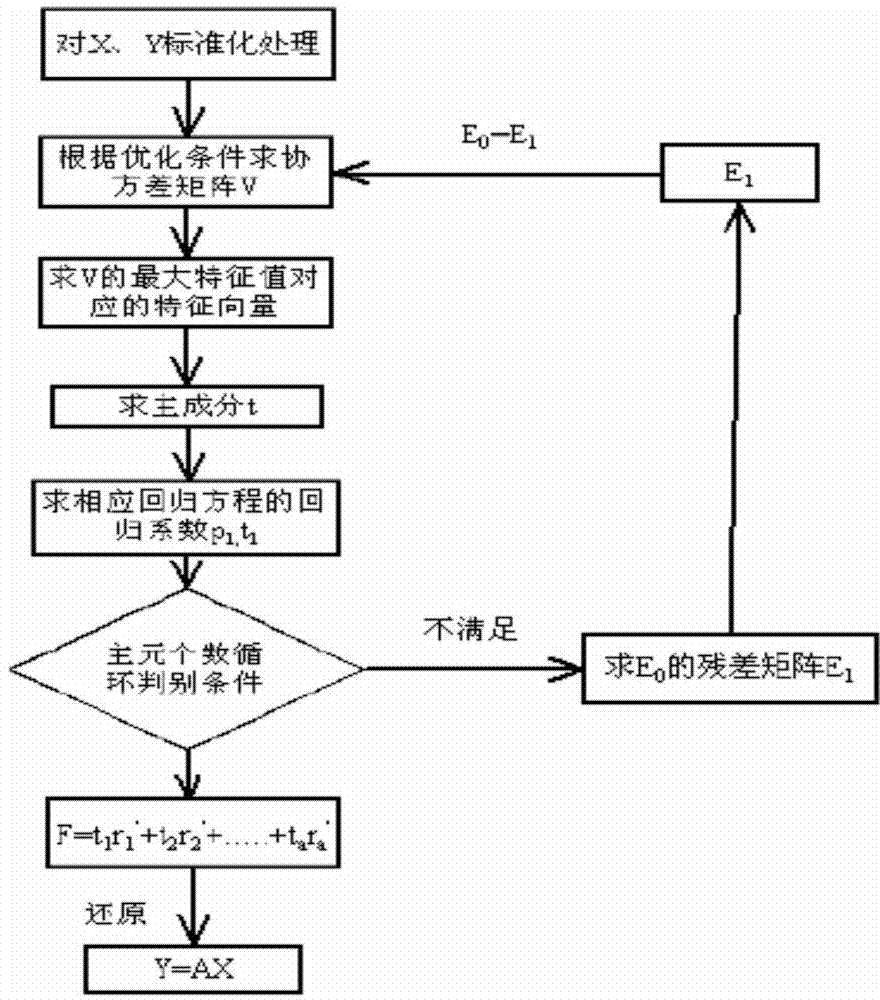
Method for applying partial least squares regression to power distribution network harmonic source positioning and detecting
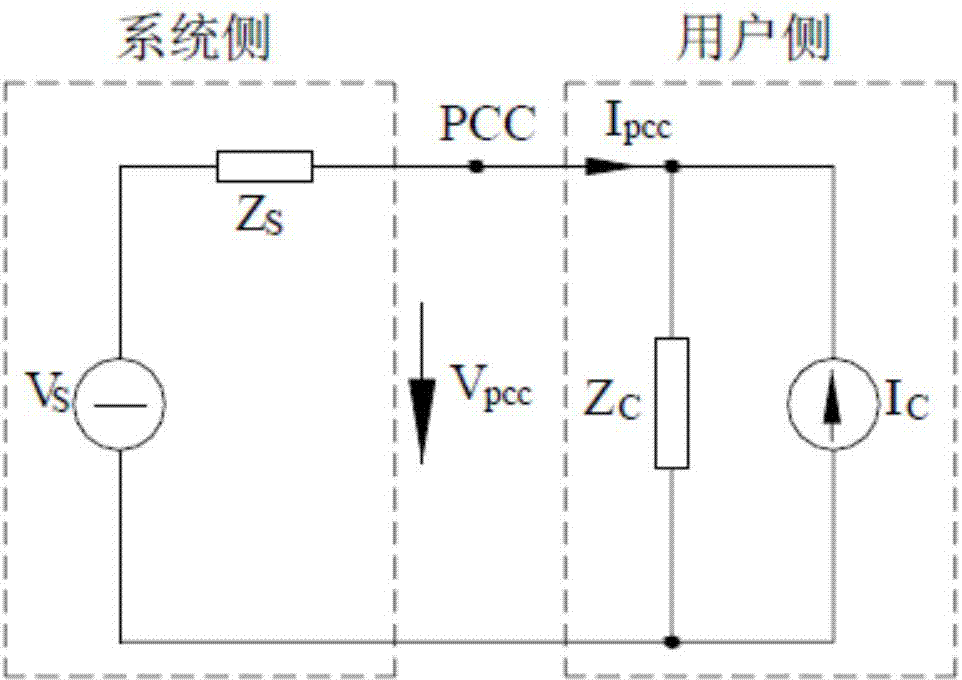
InactiveCN103838959AImplement regression modelingSimplify the data structureSpecial data processing applicationsPower qualityElectric power system
The invention belongs to the field of power quality managing, and discloses a method for applying the partial least squares regression to power distribution network harmonic source positioning and detecting. According to a model for carrying out equivalent transformation on the electrical power system side and the distortion user side and a harmonic voltage and a harmonic current signal which are obtained through synchronous measurement at the common coupling joint, a regression coefficient is dissolved through the partial least squares regression algorithm, an aggregative variable with the best explanatory capability for a dependent variable is extracted in the manner of decomposing and screening data information in the system, and information and noise in the system are identified. The method integrates the basic functions of multiple linear regression, the canonical correlation analysis and the principal component analysis, the modeling predicting type data analysis method and non-model type data recognition are organically combined, regression modeling, data structure simplifying and variable correlation analyzing can be achieved at the same time, and the method can be widely applied to power quality analyzing, monitoring, evaluating and controlling fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Grid-tied testing device for wind electricity and photovoltaic energy and testing method thereof
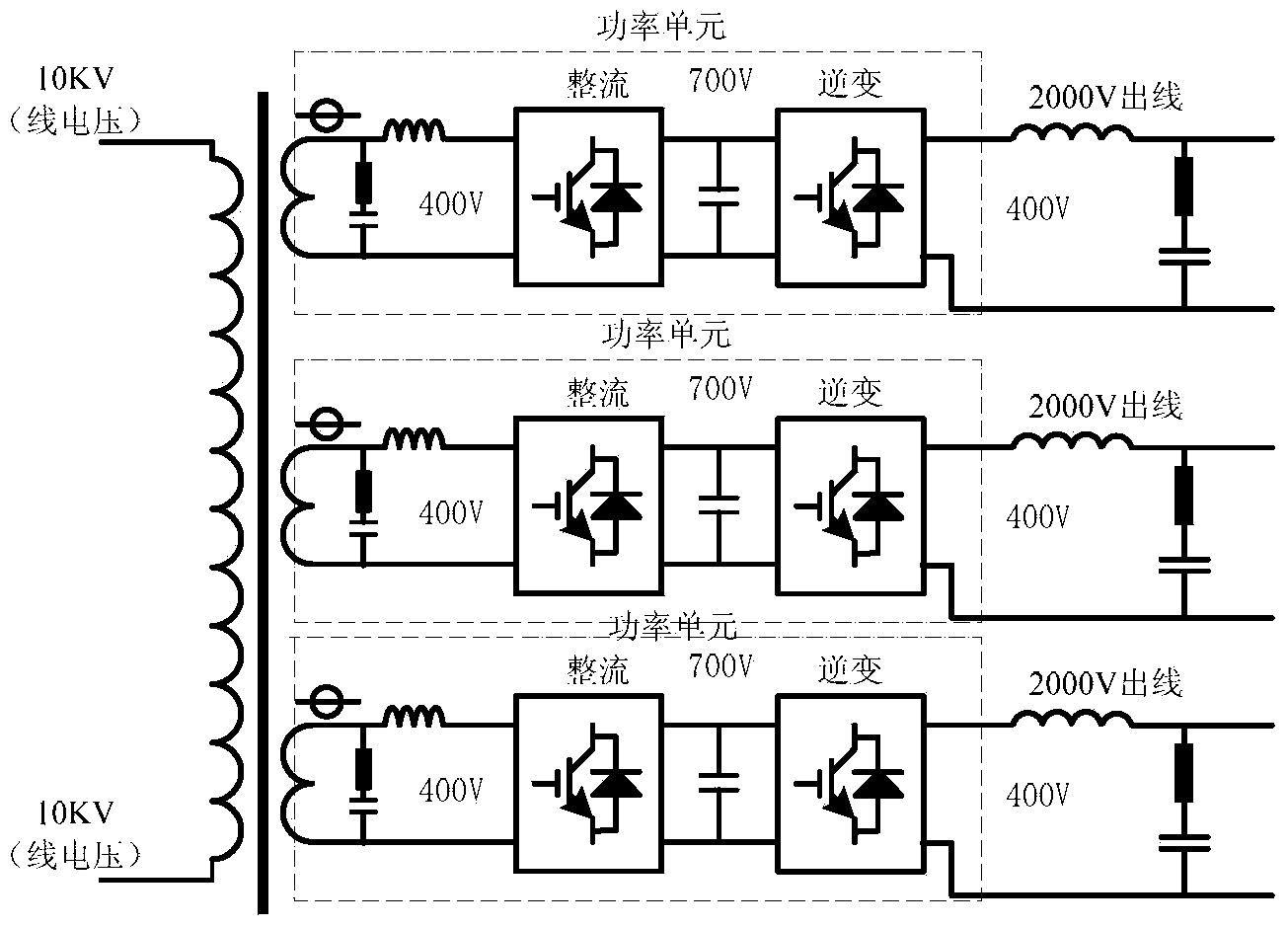
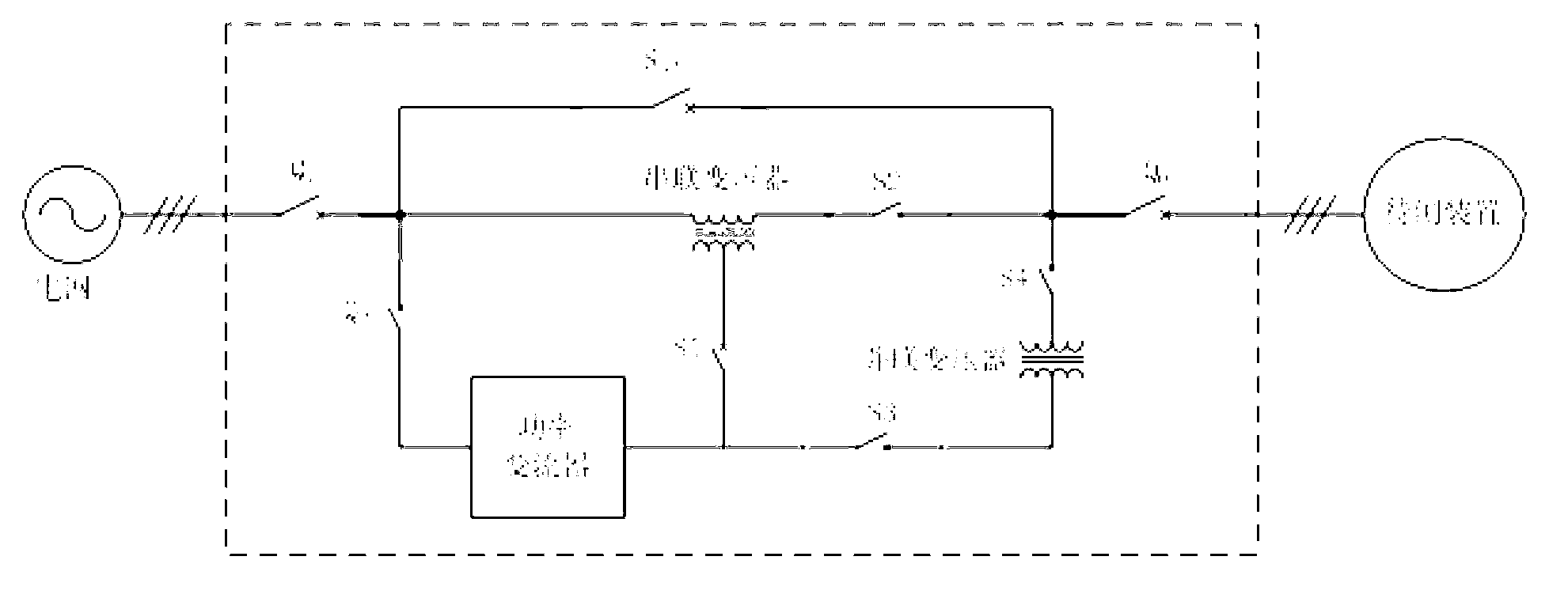
ActiveCN103064023AReduce capacityLow costDynamo-electric machine testingNameplate capacityTransformer
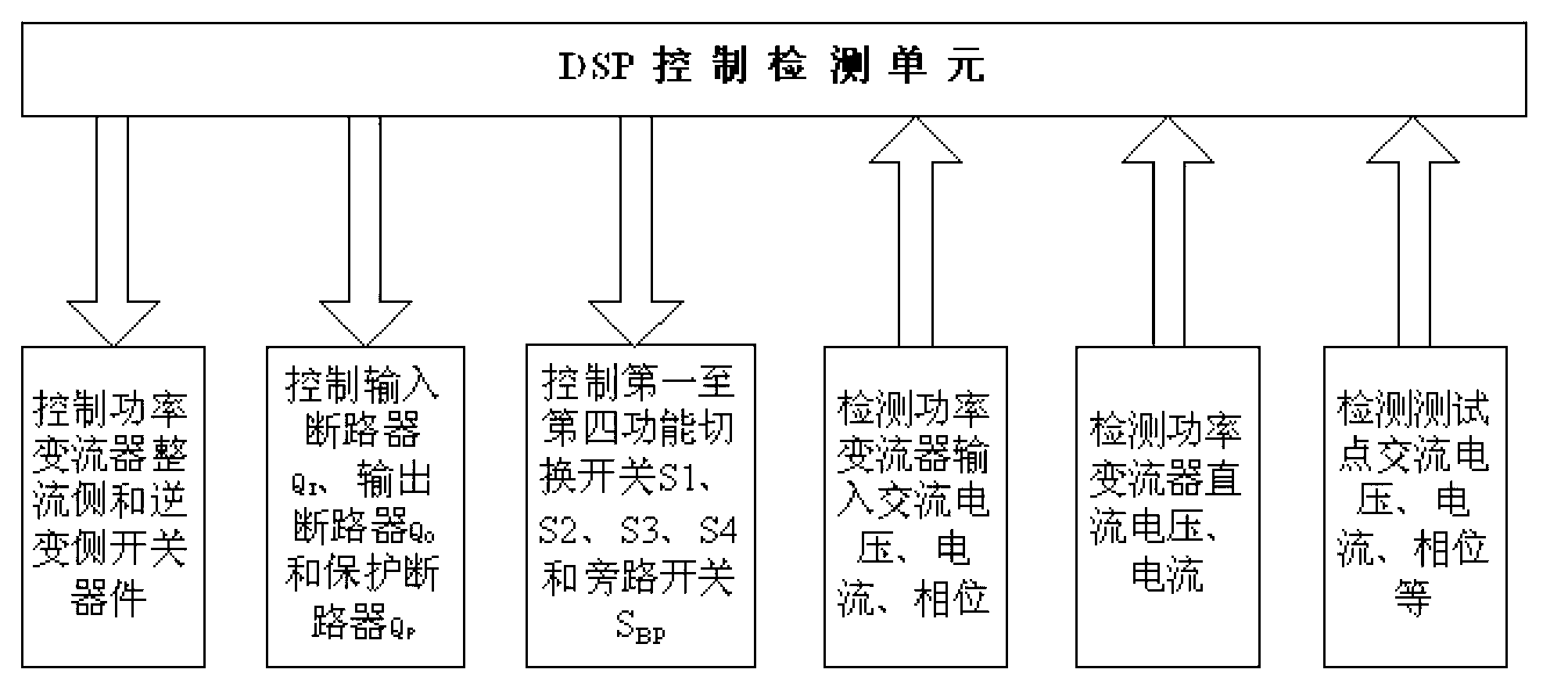
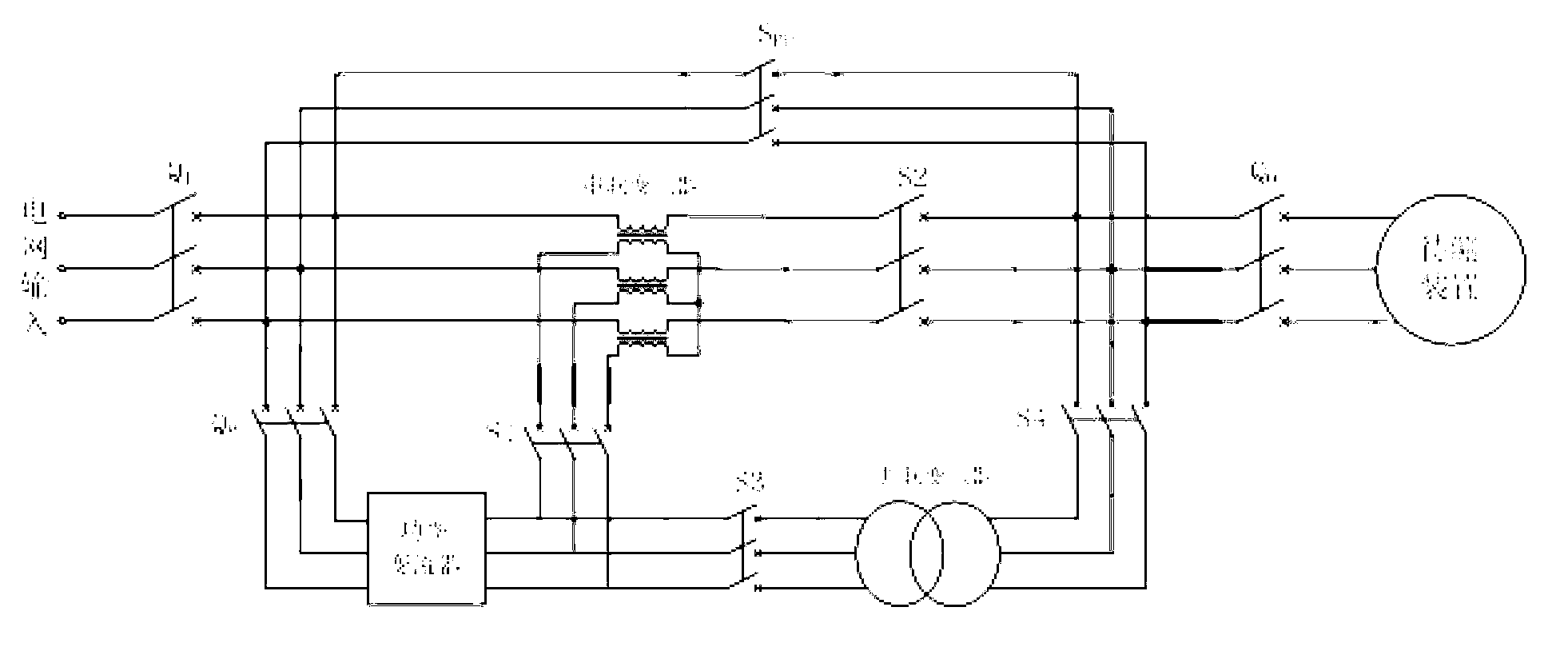
The invention provides a grid-tied testing device for wind electricity and photovoltaic energy and a testing method thereof. The testing device comprises a power converter, a series connection transformer, a shunt transformer, an input breaker, an output breaker, a protective breaker, a first function change-over switch, a second function change-over switch, a third function change-over switch, a fourth function change-over switch, a by-pass switch and a digital signal processor (DSP) control and detection unit. An input end of the testing device is connected with a power grid, and an output end of the testing device is connected with a wind generating set or a photovoltaic generating station as a device to be tested. Deviation voltage or harmonic voltage output by the power converter and nominal voltage or fundamental voltage of the power grid are overlaid for achieving power grid adaptability requirements, and therefore the capacity of the power converter is far smaller than the rated capacity of the device to be tested. Due to the fact that the capacity of the power converter is reduced, the purposes that a system is low in cost, small in size, light in weight, small in heating value, high in reliability and the like can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING RONGHUA HENGXIN SWITCH TECH +2
Ac voltage output apparatus and hybrid vehicle including the same
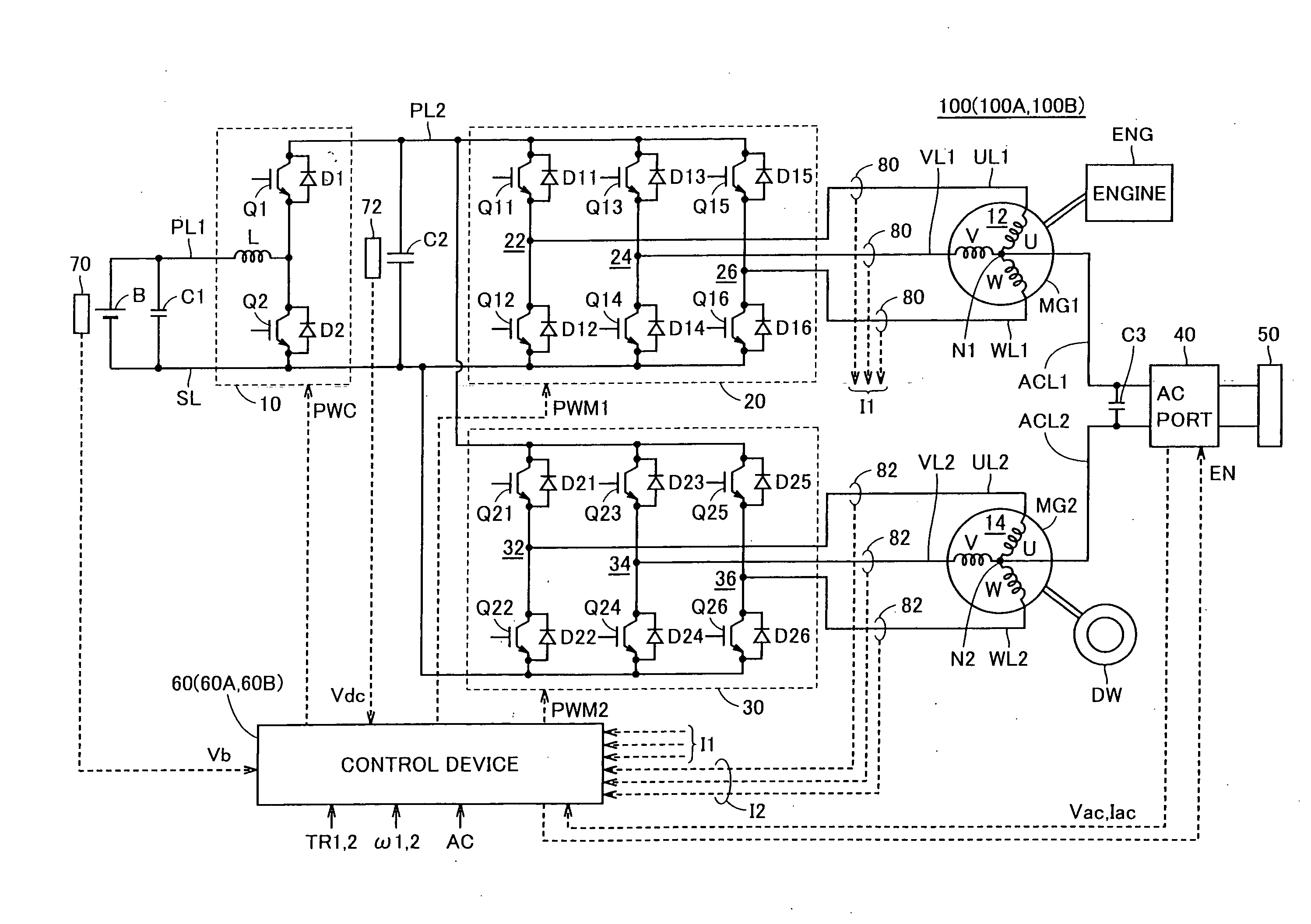
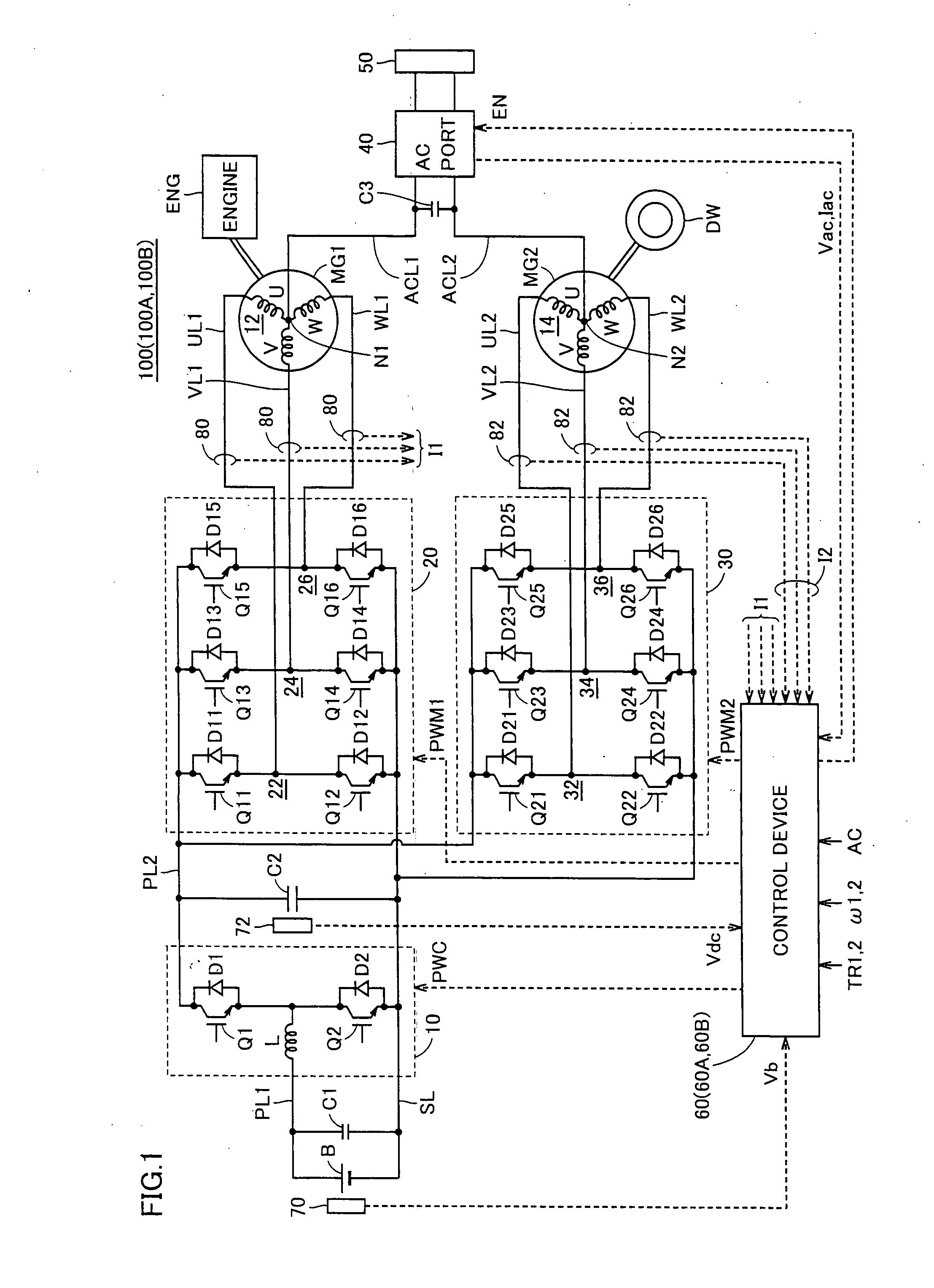
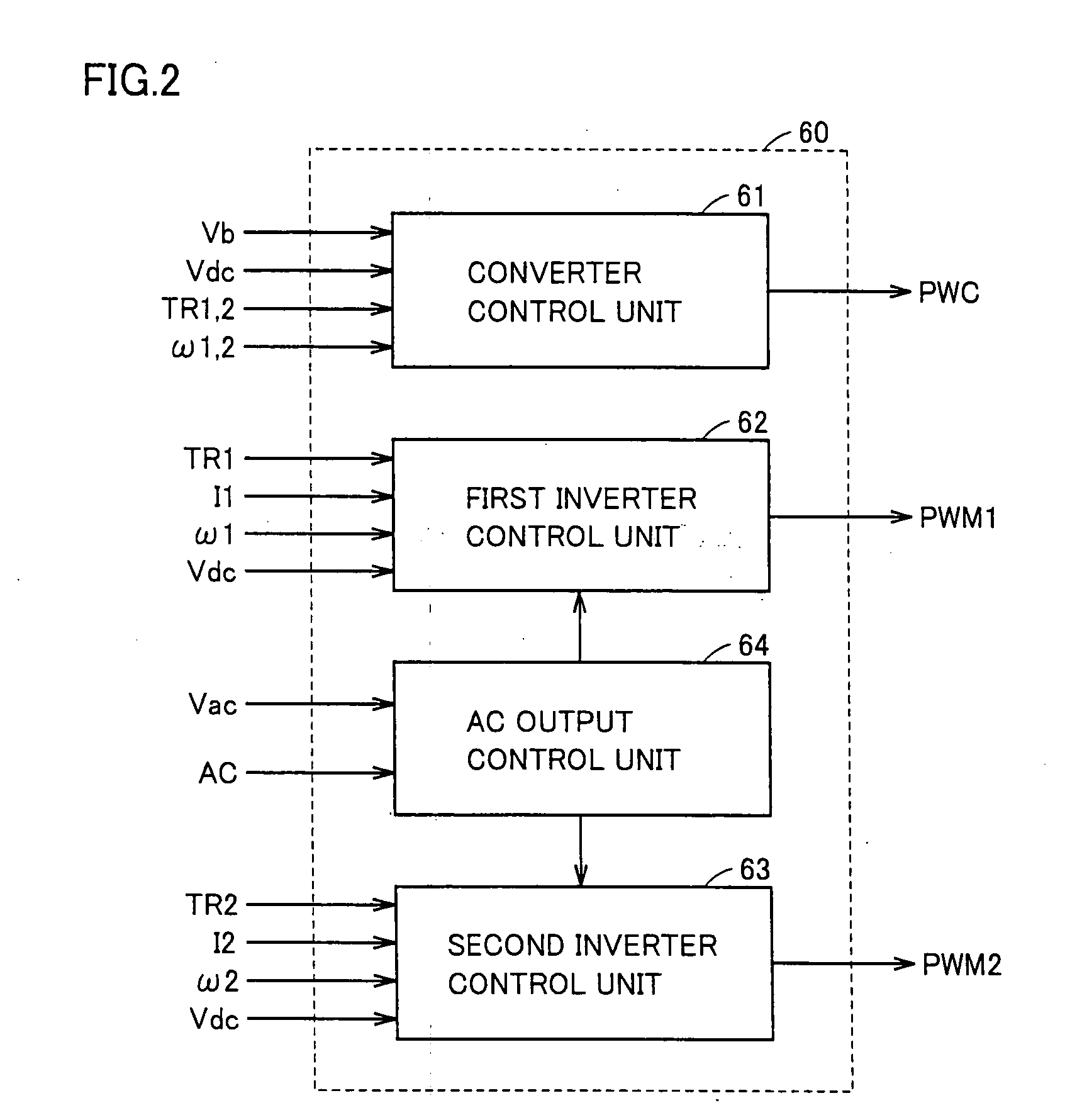
ActiveUS20090224720A1Small sizeLow costAC motor controlMultiple dynamo-motor startersHarmonicEngineering
A first inverter control unit includes a harmonic generation unit. The harmonic generation unit generates a harmonic voltage instruction having a phase opposite to a harmonic generated at a neutral point of a motor-generator when the motor-generator revolves, based on motor revolution number of the motor-generator. A PWM signal generation unit generates a signal based on a voltage instruction obtained by superimposing an AC voltage instruction from an AC output control unit and the harmonic voltage instruction from the harmonic generation unit onto each voltage instruction of U-phase, V-phase and W-phase from a conversion unit.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Discriminated method of generator terminal voltage mutual inductor once-off-line
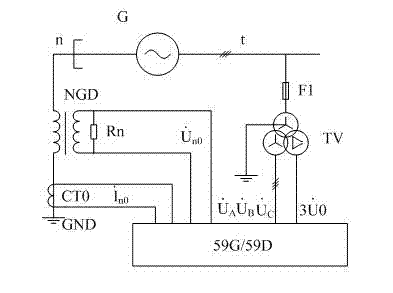
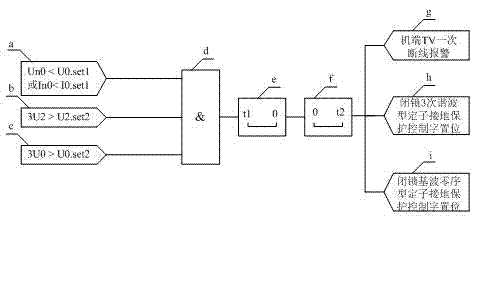
ActiveCN103091595ASolve the problem of reliable judgment of a disconnectionAvoid false protectionElectrical testingElectricityTerminal voltage
Disclosed is a discriminated method of generator terminal voltage mutual inductor once-off-line. A protector detects negative sequence voltage of a generator terminal voltage mutual inductor, open-mouth triangle fundamental wave zero sequence voltage and zero sequence voltage or a zero sequence current of a neutral point of a generator. According to the following formula, the detectable quantities are respectively compared with corresponding constant values, namely, when the conditions that the terminal voltage (TV) negative sequence voltage is larger than a constant value or the TV open-mouth triangle fundamental wave zero sequence voltage is larger than a constant value, and meanwhile the zero sequence voltage or the zero sequence current of the neutral point of the generator is smaller than a constant value are satisfied, once-off-line of the TV appears and alarm signals are sent, third harmonic voltage-type stator grounding protection and harmonic voltage-type stator grounding protection of a generator are locked, and protection mal-operations are avoided.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
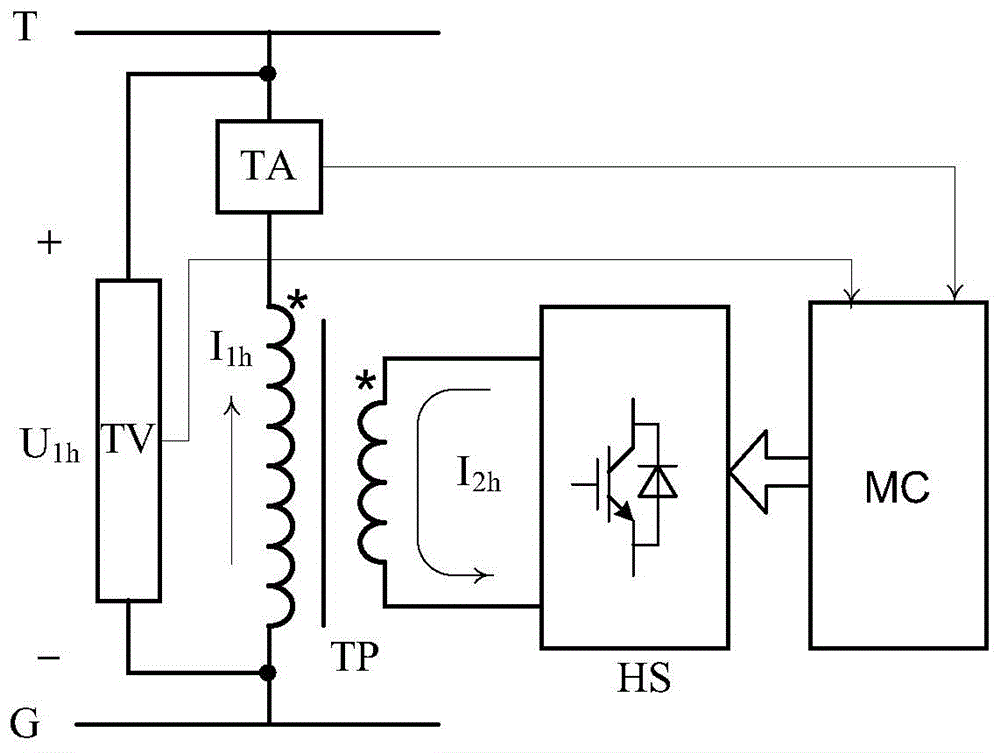
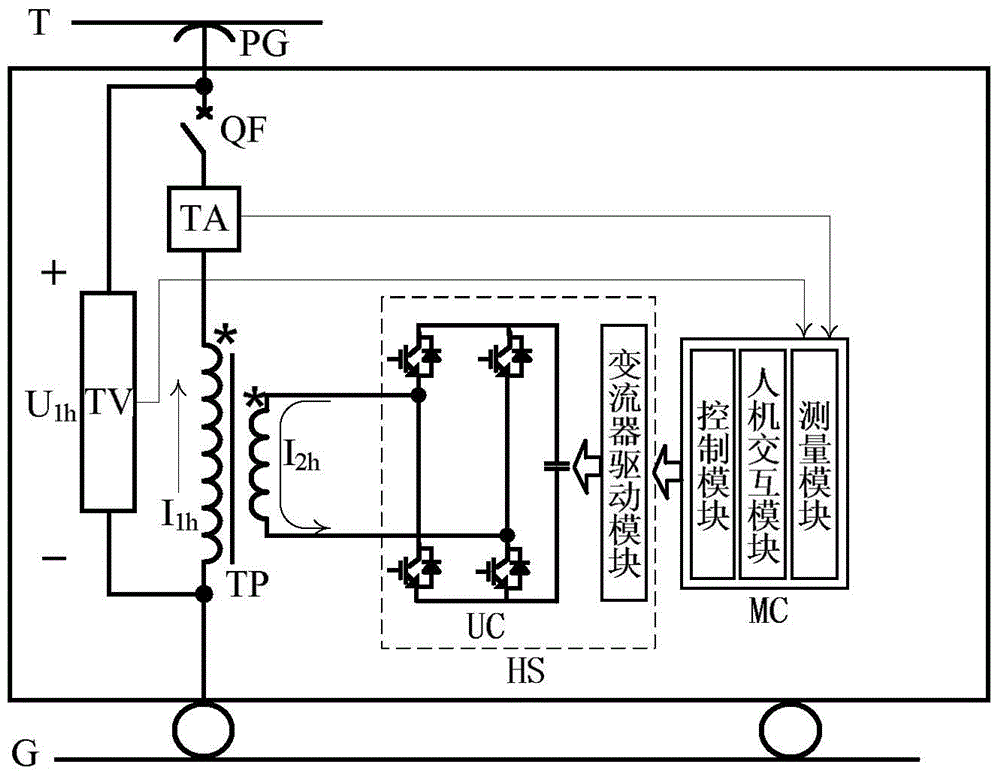
Alternating current electrified railway traction network impedance frequency characteristic testing device
An alternating current electrified railway traction network impedance frequency characteristic testing device is composed of a step-down transformer TP, a harmonic source HS, a monitoring device MC, a voltage transducer TV and a current transducer TA. The monitoring device MC controls that the harmonic source HS sends harmonic current and injects a primary side winding of the step-down transformer TP into a traction network. The voltage transducer TV and the current transducer TA respectively detects harmonic voltage between a contact network T and a steel rail G and the harmonic current injected into the traction network, and the monitoring device MC receives output signals of the voltage transducer TV and the current transducer TA and finishes harmonic impedance calculation. Under the situation that the contact network is electrified, an impedance frequency characteristic of the traction network can be obtained by adjusting the frequency and amplitude of the current sent by the harmonic source, and further the harmonic frequency is obtained. The alternating current electrified railway traction network impedance frequency characteristic testing device can be used for newly-constructed electrified railway joint debugging integration test and can be also used for providing technical support for solving the harmonic vibration problem and guaranteeing power supply safety of existing lines.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
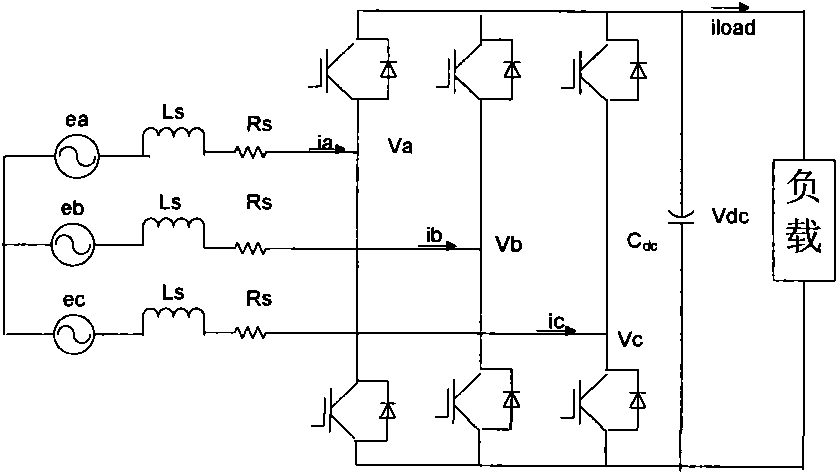
Harmonic wave damping control method for one-phase LCL type grid-connected inverter
ActiveCN103560690AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove the quality of incoming currentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitanceGrid-tie inverter
The invention discloses a harmonic wave damping control method for a one-phase LCL type grid-connected inverter. The harmonic wave damping control method for the one-phase LCL type grid-connected inverter mainly comprises a fundamental wave control loop, a harmonic wave damping loop and a capacitance current inner loop. The fundamental wave control loop enables fundamental wave components in non-error follow current command signals of network-entry currents to change, and grid connection with a high power factor is achieved. The harmonic wave damping loop can inhibit background harmonic voltage of a power grid and the influence on the network-entry currents of the grid-connected inverter from the harmonic wave components of the current command signals at the same time, and provide the network-entry currents with high quality. The capacitance current inner loop is used for improving system damping, inhibits the LCL resonance peak and improves the system stability. The harmonic wave damping control method is easy to achieve, and can improve the ability of the grid-connected inverter to inhibit the harmonic wave components in the background harmonic voltage of the power grid and the current command signals, and the quality of the network-entry currents of the grid-connected inverter is improved. The harmonic wave damping control method is suitable for a grid-connected photovoltaic power generation system, a fuel battery and a wind power generation grid-connected system of an LCL type filter.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
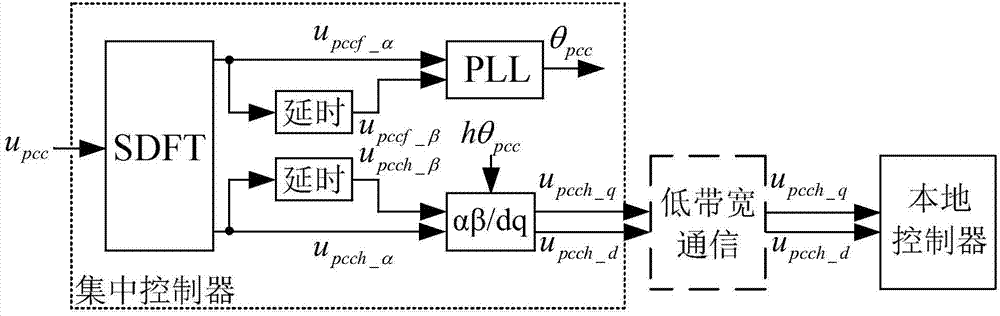
Equalization control method for power of plurality of parallel inverters in island microgrid
InactiveCN104716859ASplit runHarmonic voltage distortion rate reductionAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMicrogridCapacitor voltage
The invention discloses an equalization control method for the power of a plurality of parallel inverters in an island microgrid. The equalization control method comprises the following steps: constructing an alpha-beta coordinate system in a single-phase control system, and calculating the voltage and the power without need of low-pass filtering in the calculation process; and extracting a phase angle of a filtering capacitor voltage in a local controller of all the inverters, and by using the phase angle as reference, transforming a dq coordinate system back to the alpha-beta coordinate system, wherein electric signals are easily transmitted to the local controller from a centralized controller by low-bandwidth communication. The fundamental component of the voltage of the filtering capacitor participates in adjustment of a first quasi-proportional resonance control for the fundamental voltage; the filtering capacitor voltage containing harmonic voltage participates in adjustment of second quasi-proportional resonance control for the characteristic subharmonic voltage. By application of the equalization control method in an equalization control system for the plurality of parallel inverters in the island microgrid under the complex conditions with non-linear loads, different impedances of feeder lines of all the inverters and inconsistent rated capacities, the inverters also can realize equalization control for the output power, and the loop current among all the inverters is effectively inhibited.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method for measuring factory harmonic wave and measuring instrument
InactiveCN1611953AAccurate Quantitative MeasurementSpectral/fourier analysisTime changesMeasuring instrument
This invention relates to the method of measuring factory harmonic wave and measuring apparatus. The measuring of factory harmonic wave is measuring the system harmonic wave of electric equipment, filter factory harmonic wave source, and the factory harmonic wave that connected with the power supply system. The distribution of harmonic wave process and harmonic wave current level time changes of harmonic wave source electric equipment will be measured, and the filtering parameter of the harmonic wave source electric equipment and systematic equipment network that includes compatible power and compatible running with power supply system, filter and the mutual bus bar electric equipment will also be measured. The factory that uses this method can directly measure and manage the system harmonic wave of the factory harmonic wave. This invention synchronizing measuring the harmonic current and harmonic voltage drop level time changing of the common junction and its bus bar, and the distribution feature of the common junctions.
Owner:贺守正
Active damping scheme for multiple LCL inverter resonant coupling
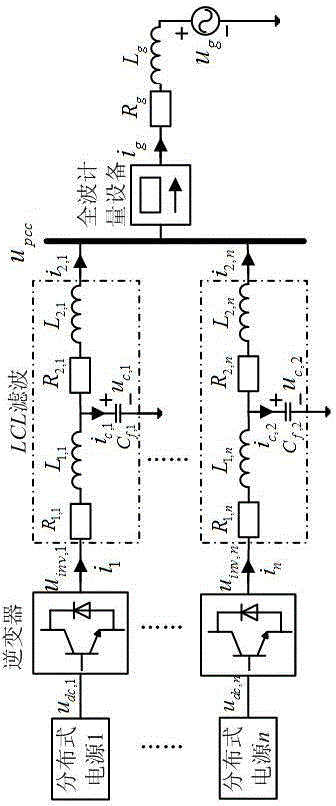
InactiveCN104821706AReduce Harmonic Distortion RateImprove reliabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementReference currentFull wave
The invention provides an active damping scheme for multiple LCL inverter resonant coupling. The active damping scheme comprises a distributed grid-connected power generation system formed by the series connection of a plurality of photovoltaic LCL inverters and a full wave energy metering device. The control structure of the current and active damping control link of each of the LCL inverters comprises an inverter reference output current calculation link, a photovoltaic power front feed reference current compensation link, an inverter output current deadbeat control link and an active damping compensation link. According to the control method of the invention, the harmonic distortion rate of grid-connected total current can be reduced, the metering data reliability of the full wave energy metering device is effectively improved, the specific harmonic amplification interference of inverter output current by the self resonant point of a single inverter filtering link is effectively reduced, the parallel connection resonant coupling among multiple inverter filtering links is effectively reduced, the independence of each inverter output current is ensured, and the interference of the inverter output current by power grid harmonic voltage is effectively reduced. According to the active damping scheme, the safe and stable operation of an inverter parallel system can be ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop
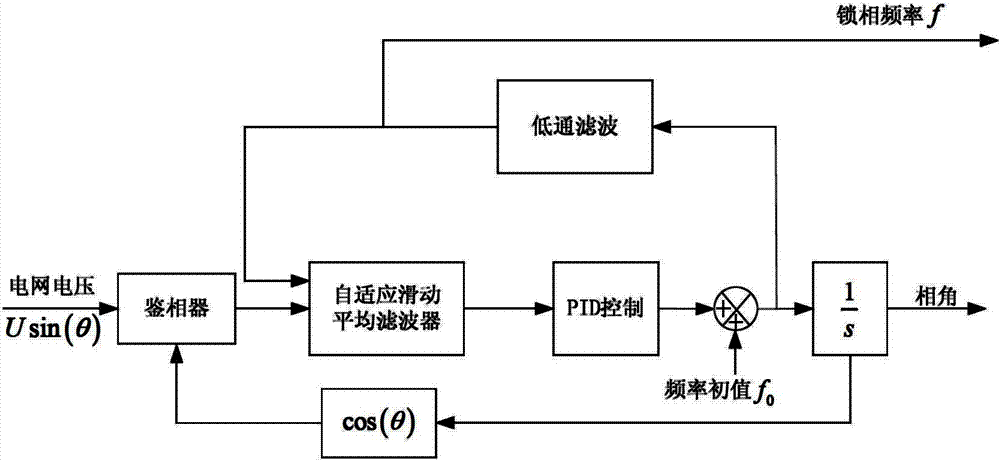
ActiveCN102904568AGuaranteed speedGuaranteed dynamic performancePulse automatic controlMoving averageDiscriminator
The invention discloses a self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop. The self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop comprises a phase discriminator, a low pass filter, a loop filter and an integrator module, wherein the loop filter is composed of a self-adaptive moving average filter and a proportion integration differentiation (PID) regulator, the phase discriminator is a multiplication phase discriminator, an input signal is a trigonometric function of an output angle of power grid voltage and a phase-locked loop, and an output signal is transmitted into the moving average filter; an input signal of the moving average filter is output of the phase discriminator and output of the low pass filter, and the output signal is transmitted to the PID regulator; and an input signal of the PID regulator is an output signal of the moving average filter, and the output signal is transmitted into the low pass filter and the integrator module. The self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop has the advantages that the loop filter is improved, effects of secondary ripple and harmonic voltage on phase lock result in the steady state are eliminated, and simultaneously the rapidity of the phase lock is guaranteed.
Owner:西安奥特迅电力电子技术有限公司 +2
Novel power quality control system with fault current-limiting function and control method thereof
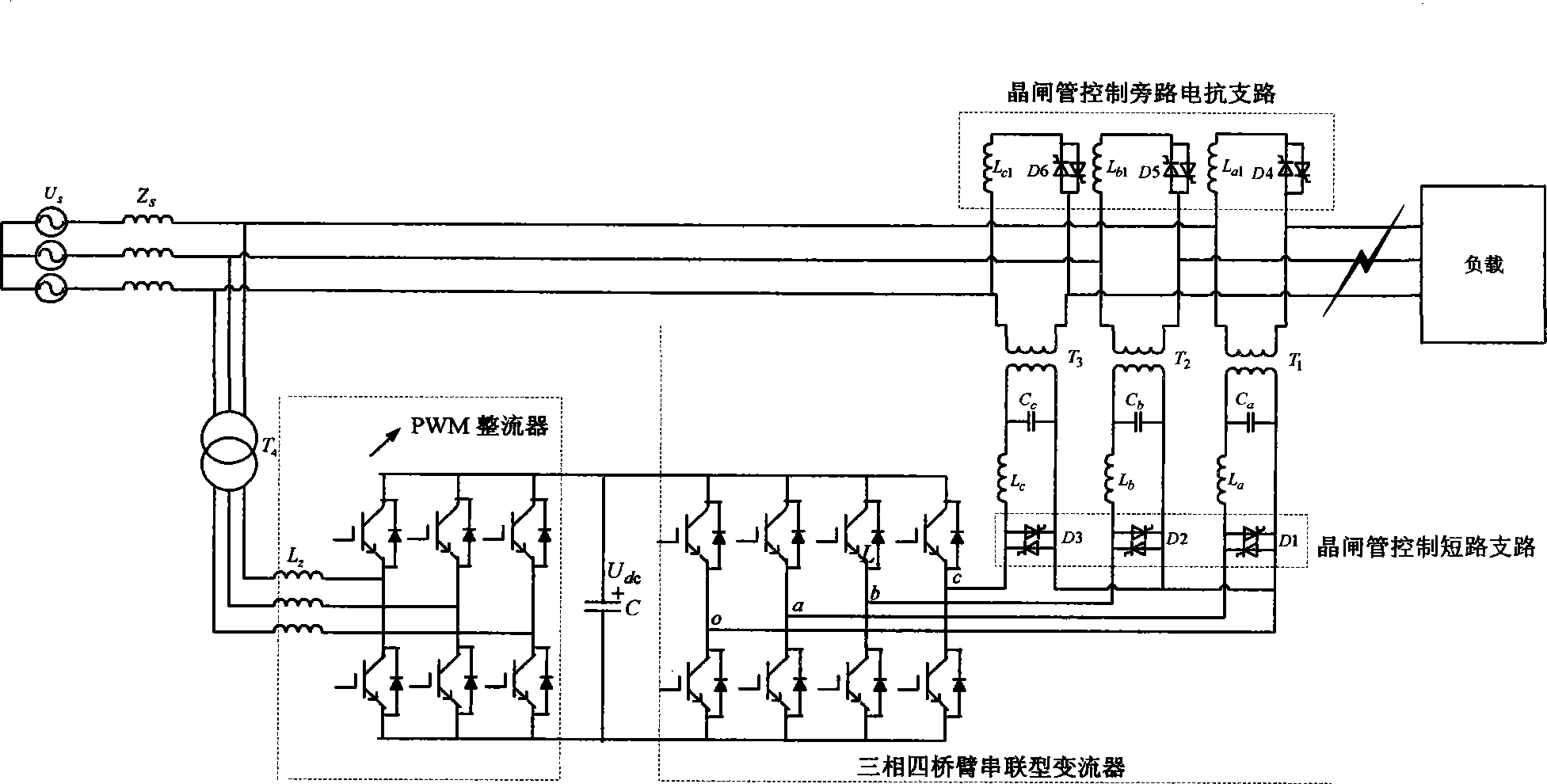
InactiveCN103280811AImprove power supply reliabilityImprove stabilityPower network operation systems integrationAc network voltage adjustmentEmbedded systemElectric power
The invention discloses a novel power quality control system with a fault current-limiting function and a control method thereof. The novel power quality control system with the fault current-limiting function comprises a three-phase H-leg PWM rectifier, a three-phase four-leg series converter, a thyristor controlled short-circuit branch, a thyristor controlled bypass reactance branch and a corresponding control method. The PWM rectifier and the three-phase four-leg series converter share one direct current side to achieve bidirectional energy conversion, the series converter compensates the fall, the raising and three-phase imbalance of the grid voltage and solves the quality problem of the harmonic voltage, at the same time, the system controls the series converter, the thyristor controlled short-circuit branch and the thyristor controlled bypass reactance branch to limit the current when various short-circuit faults occur on the grid, and thus the purposes of stabilizing the loaded supply voltage, improving power supply quality, protecting the grid and load equipment when short-circuit faults occur and improving the safety and stability of the electric power system are achieved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV +1
Distribution method based on waveform matching for harmonic voltage responsibility
ActiveCN106019026ASimple methodPromote engineering applicationSpectral/fourier analysisData processing applicationsDistribution methodHarmonic pollution
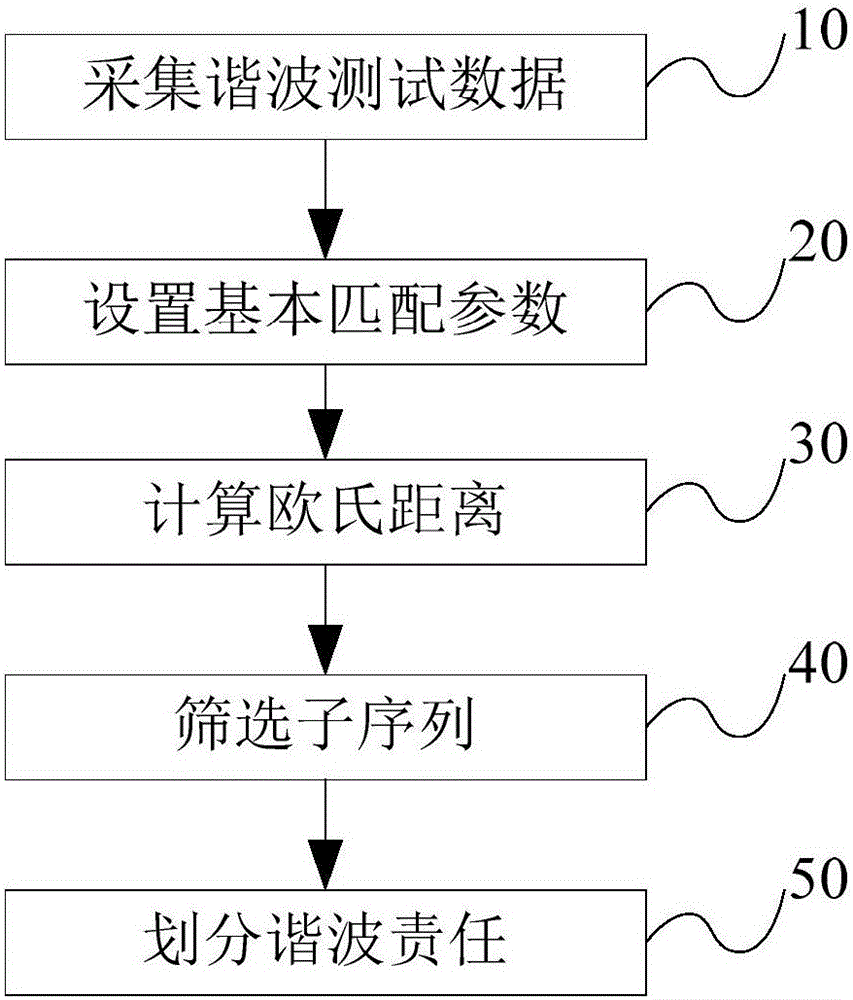
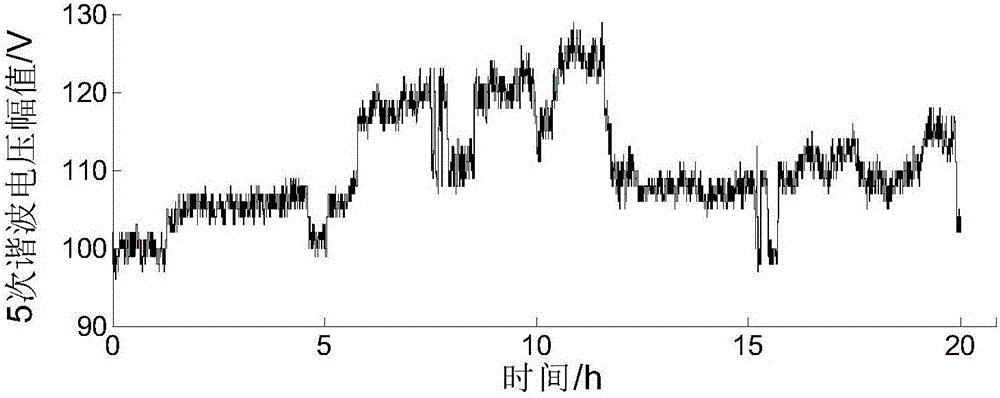
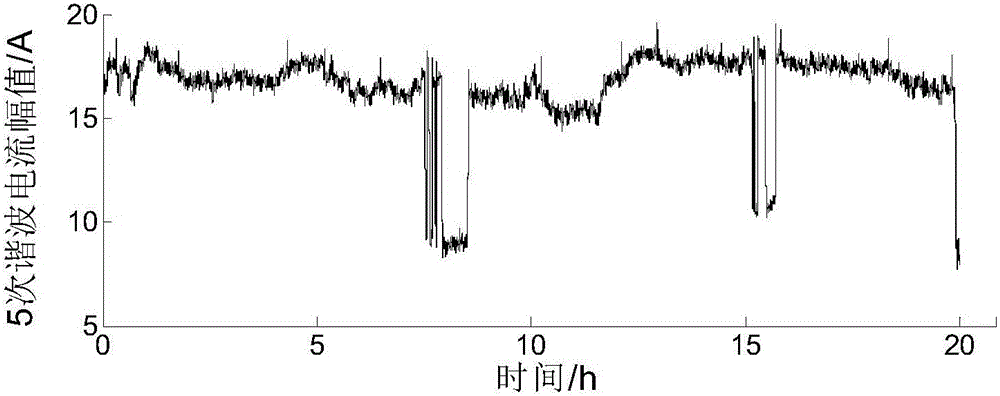
The invention discloses a distribution method based on waveform matching for harmonic voltage responsibility. The distribution method comprises the steps of: step 10) acquiring harmonic test data, and forming a harmonic data sequence; step 20) setting basic matching parameters; step 30) calculating an Euclidean distance, wherein normalization processing is performed on the harmonic data sequence which is formed in the step 10) according to a sequence of subsequences based on the basic matching parameters set in the step 20) to obtain harmonic sample data, and the Euclidean distance between a harmonic voltage and a harmonic current in the harmonic sample data is calculated; step 40) screening the subsequences, wherein similarity of each subsequence is calculated, and the subsequence with the similarity not less than a set value is screened out; step 50) and distributing harmonic responsibility, wherein system-side equivalent harmonic impedances of the screened subsequences is estimated by adopting a least square method, and a mean value of the equivalent harmonic impedances is utilized for calculating the harmonic voltage responsibility. The distribution method can quantify harmonic pollution liability of a feeder by utilizing harmonic amplitude data, and is suitable for engineering practice.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com