Region division and combination method based on depth-first traversal
A technology of depth-first traversal and area division, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as table distortion, unfavorable cell sorting, and not considering concave polygon areas, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing transition distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
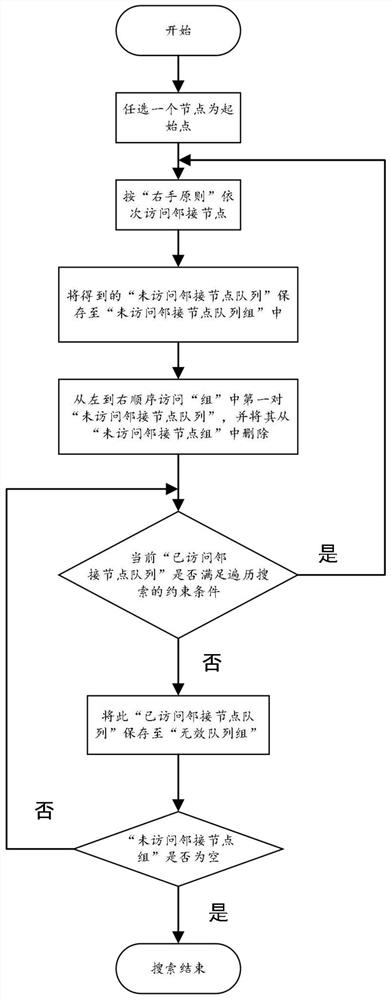
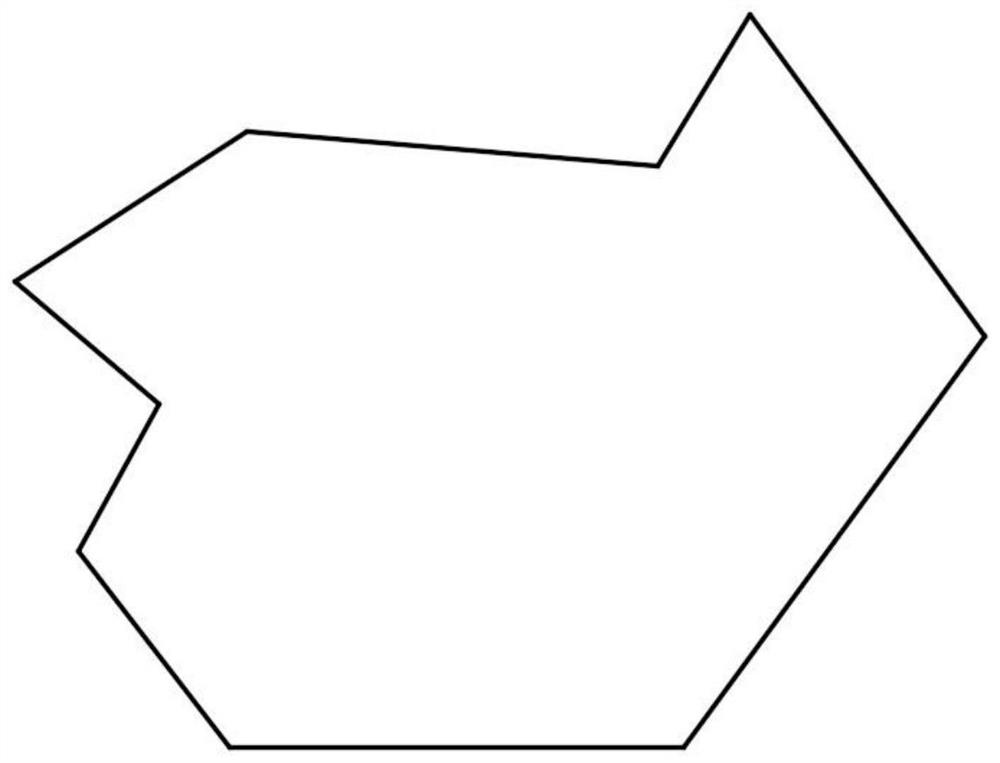
[0026] The improved depth-first traversal method is to divide and merge a concave polygonal area, which is selected in this embodiment figure 2 To illustrate. figure 1 It is the implementation flowchart of the concave polygon area division method based on the improved depth-first traversal algorithm of the present invention, combined below figure 1 Introduce the specific implementation steps.
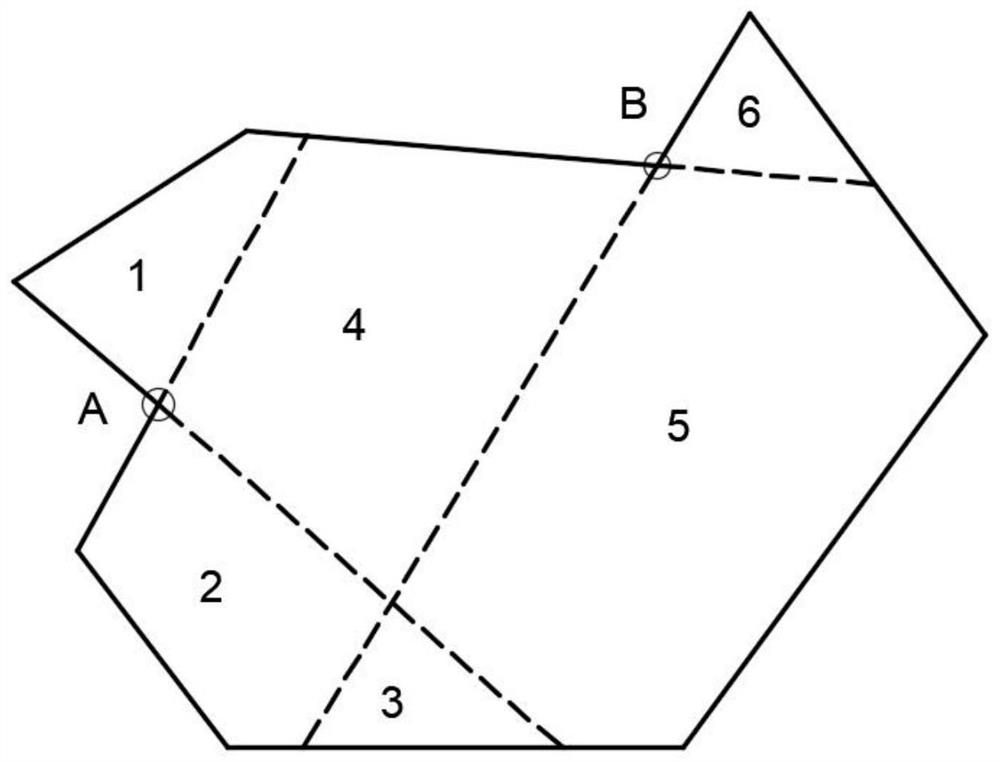
[0027] Step 1, first put figure 2 The area is divided according to the method of "extending the concave edge" to obtain multiple smaller convex polygons. like image 3 As shown, A and B are the concave corner vertices of the target area. First, the sides of each concave corner are extended until they intersect with the boundary of the concave polygon. At this time, the concave polygon area is divided into six sub-regions. In the process of extens...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com