Multistage separating micro-fluidic chip for cells
A microfluidic chip, cell technology, applied in laboratory containers, enzymology/microbiology devices, methods of supporting/immobilizing microorganisms, etc. The problem of low recovery purity, etc., achieves the effects of easy integration, miniaturization, high-purity sorting, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
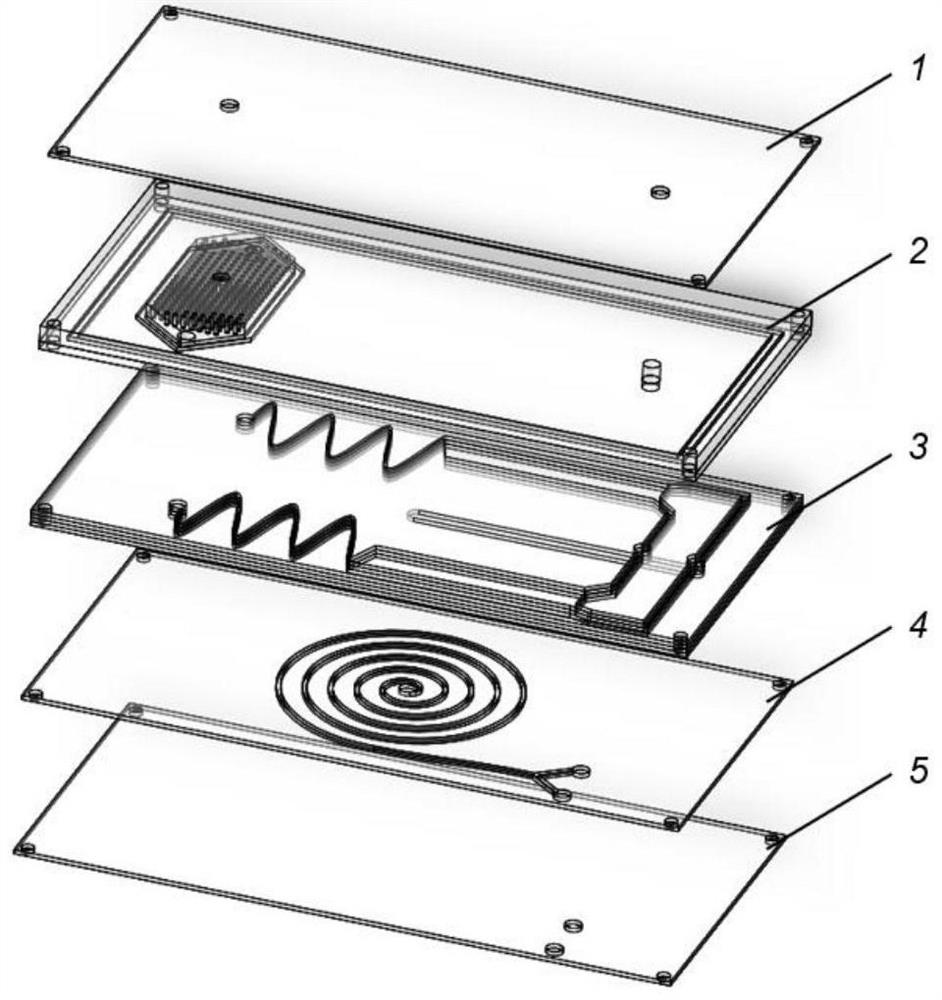
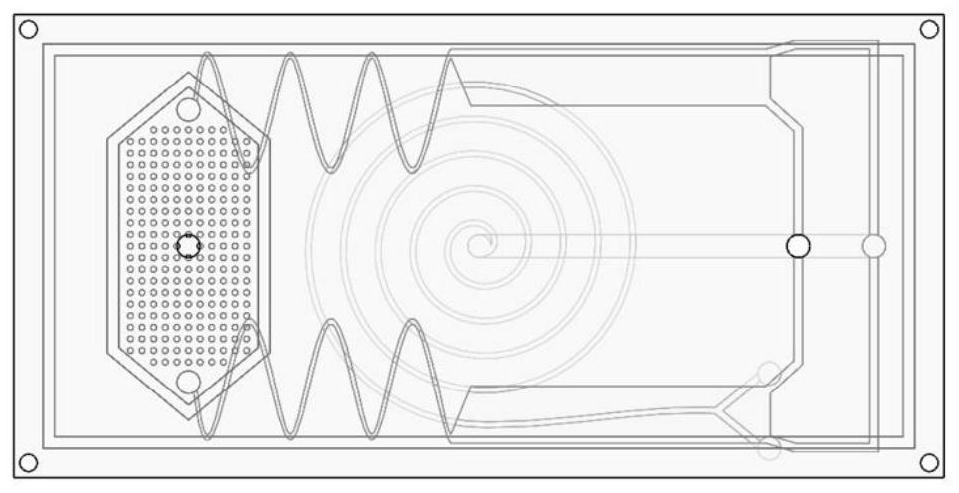
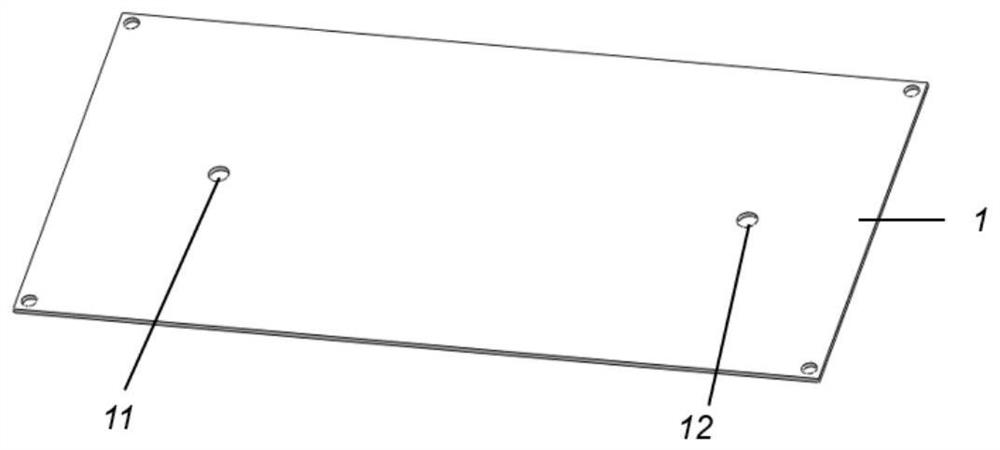
[0018] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the multi-stage sorting microfluidic chip for cells is composed of an upper cover plate 1, a filter layer 2, a magnetic separation layer 3, a spiral separation layer 4 and a lower cover plate 5, as shown in image 3 , Figure 5 As shown, the upper cover plate 1 is provided with a first sample liquid inlet 11 and a first magnetic bead channel 12, and the filter layer 2 is provided with a second sample liquid inlet 21 communicating with the first sample liquid inlet 11, a filter cavity Chamber 22, the second magnetic bead channel 25 communicated with the first magnetic bead channel and the magnetic bead outlet 35, and the sample liquid outlet 24 communicated with the third sample liquid inlet 31, the filter chamber 22 is provided with a circular cross section Filter microcolumn 23, such as Image 6 as shown, Figure 7 As shown, the magnetic separation module 3 is composed of three separation layers and one flow guide layer 37. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com