Nylon roller, motion door mechanism, vehicle and manufacturing technology
A nylon wheel and moving door technology, applied in vehicle parts, building structures, doors, etc., can solve problems such as falling off, and achieve the effects of stable performance, small footprint, and stress dispersion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
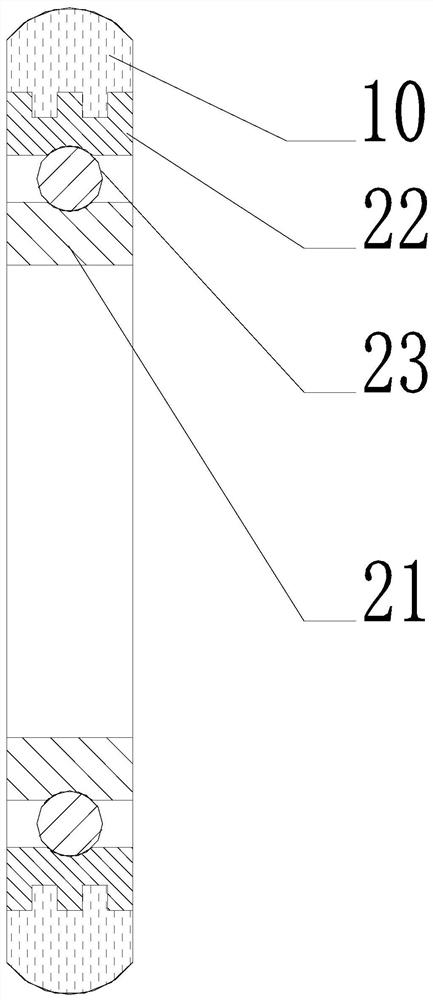
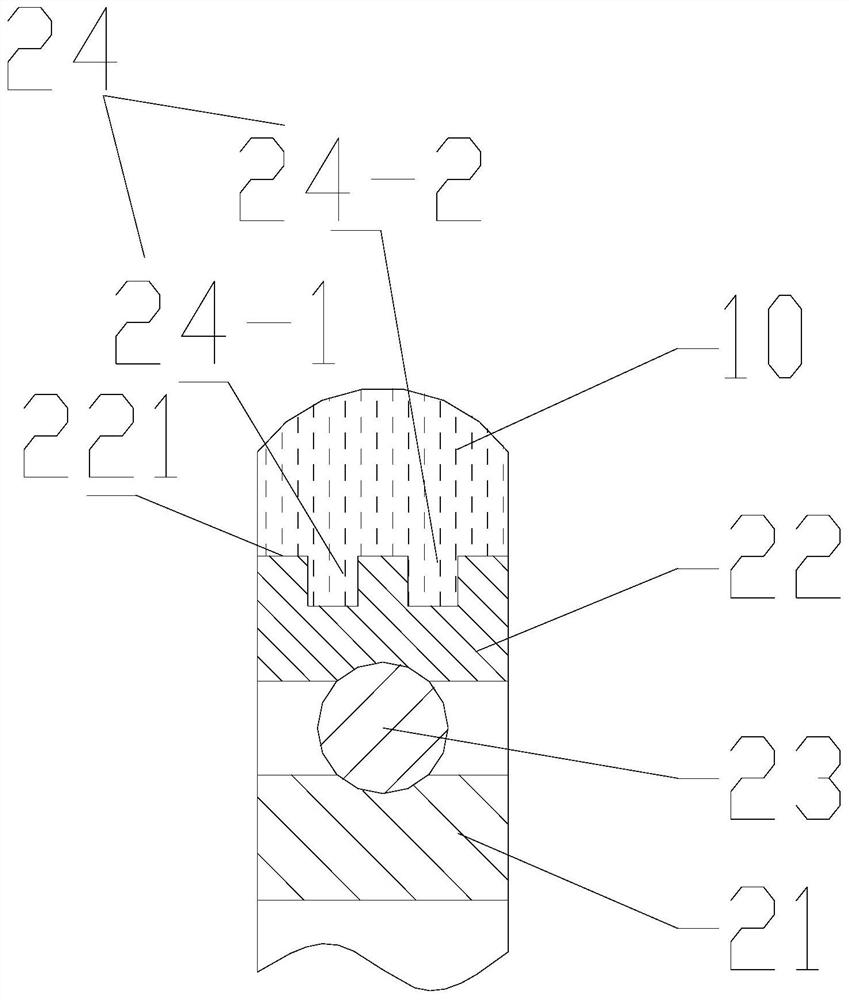
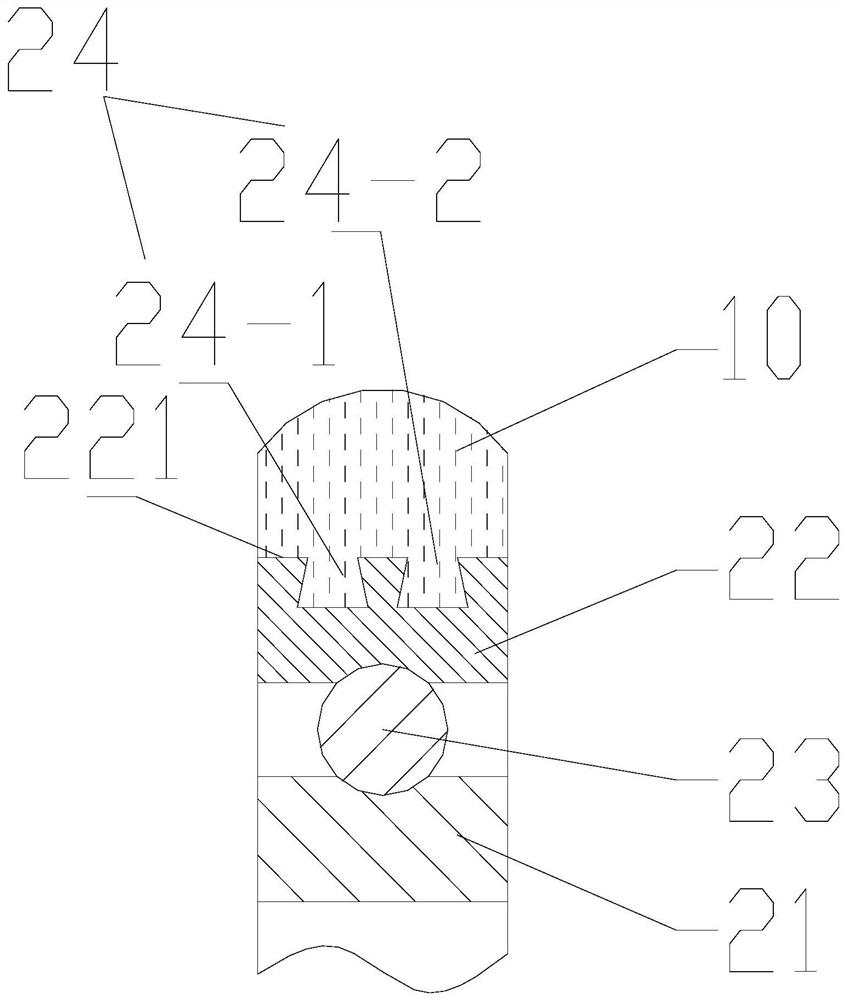
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a nylon roller, which includes a nylon wheel body 10 and a bearing 20 . The bearing 20 includes a bearing inner ring 21 and a bearing outer ring 22 that can rotate relative to the bearing inner ring 21 , and the surface of the bearing outer ring 22 facing away from the bearing inner ring 21 is the outer ring surface 221 of the bearing 20 . Such as Image 6 with Figure 7 As shown, knurling 25 is formed on the outer ring surface 221 of the bearing 20 . Such as figure 2 with image 3 As shown, the outer ring surface 221 of the bearing 20 is formed with a groove 24 sunken toward the inner ring 21 of the bearing; the nylon wheel body 10 is connected to the bearing 20 through the outer ring surface 221 of the bearing 20 .
[0042] The nylon roller in this embodiment adopts the bearing 20 as the main frame structure to realize the function of rolling. Such as figure 1 As shown, the bearing 20 includes a bearing inne...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, the groove 24 surrounds the outer ring surface 221 of the bearing 20 along the circumferential direction of the outer ring surface 221 for a week. In this way, at any position in the circumferential direction of the bearing outer ring 22, a part of the nylon wheel body 10 can be embedded in the groove 24, so that each position of the nylon wheel body 10 can form a firm connection with the bearing outer ring 22. . In addition, the cross section of the groove 24 in this embodiment is rectangular (straight groove structure). The cross section of the groove 24 refers to a cross section parallel to the radial direction of the bearing 20 . The rectangular cross-section is easy to process, and the knurling 25 structure on the outer ring 22 of the bearing can eliminate the phenomenon of stress concentration, effectively preventing the nylon wheel body 10 from falling off when it is loaded and rolling.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Such as image 3 As shown, the groove 24 of the nylon roller in this embodiment surrounds the outer ring surface 221 along the circumferential direction of the outer ring surface 221 of the bearing 20, and the width of the end of the groove 24 near the inner ring 21 of the bearing is greater than It is the width of the end away from the inner ring 21 of the bearing.
[0050] As a preferred embodiment, the groove 24 of this embodiment adopts an inverted "T"-shaped structure, that is, the bottom of the groove 24 (the part close to the axis of the bearing 20) is larger than the top of the groove 24 (closer to the outside of the bearing). The portion of the ring 22 face surface) is wide, so that the opening of the groove 24 is narrowed from the inside to the outside. With the structure of the aforementioned groove 24, the injection-molded nylon wheel body 10 is partially embedded in the groove 24. If the nylon wheel body 10 moves toward the direction away from the bearing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com