Angle calibration method of absolute magnetic encoder based on vernier code channel
A technology of magnetic encoder and calibration method, which is applied in the direction of instruments, using electric/magnetic devices to transmit sensing components, etc., can solve problems such as mechanical installation errors and inability to obtain accurate absolute position information, and achieve easy implementation and simplified calibration process and calibration cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
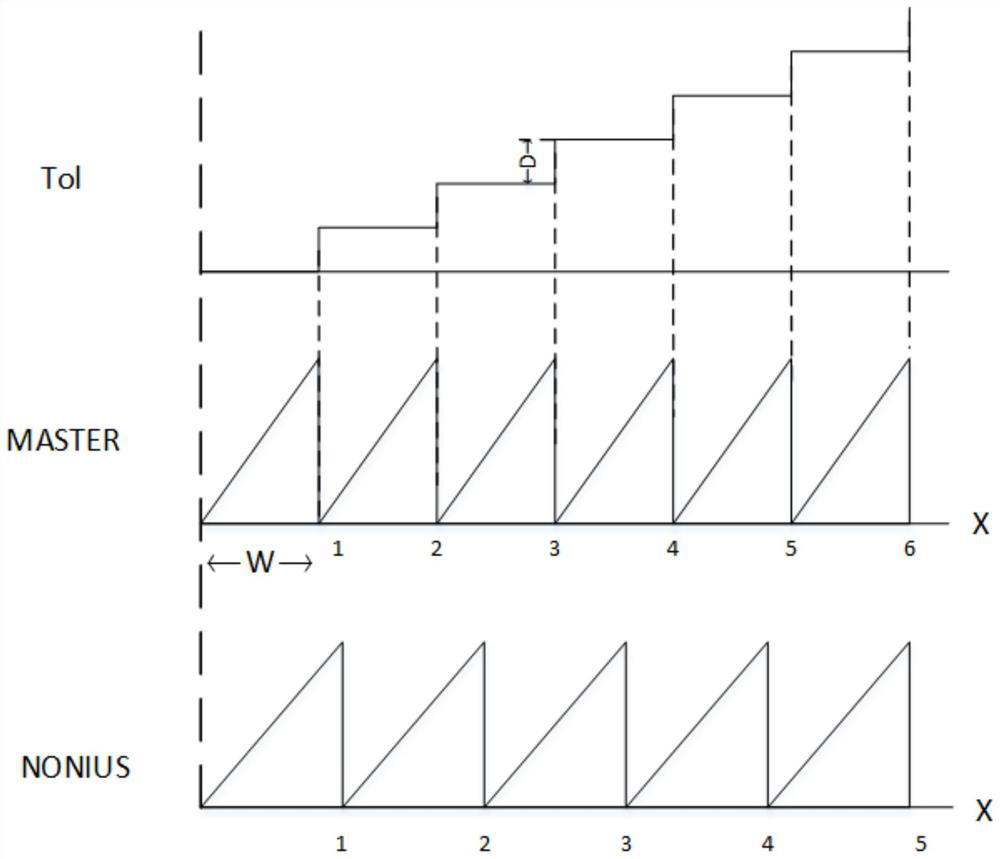
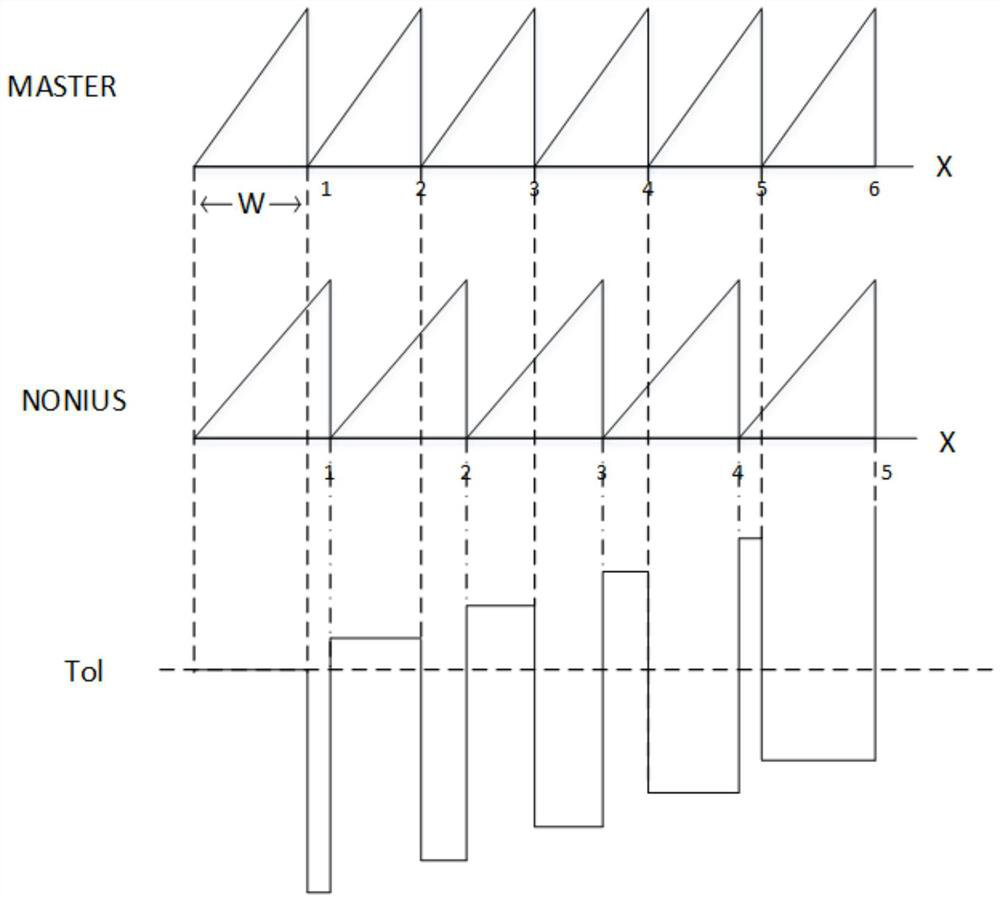
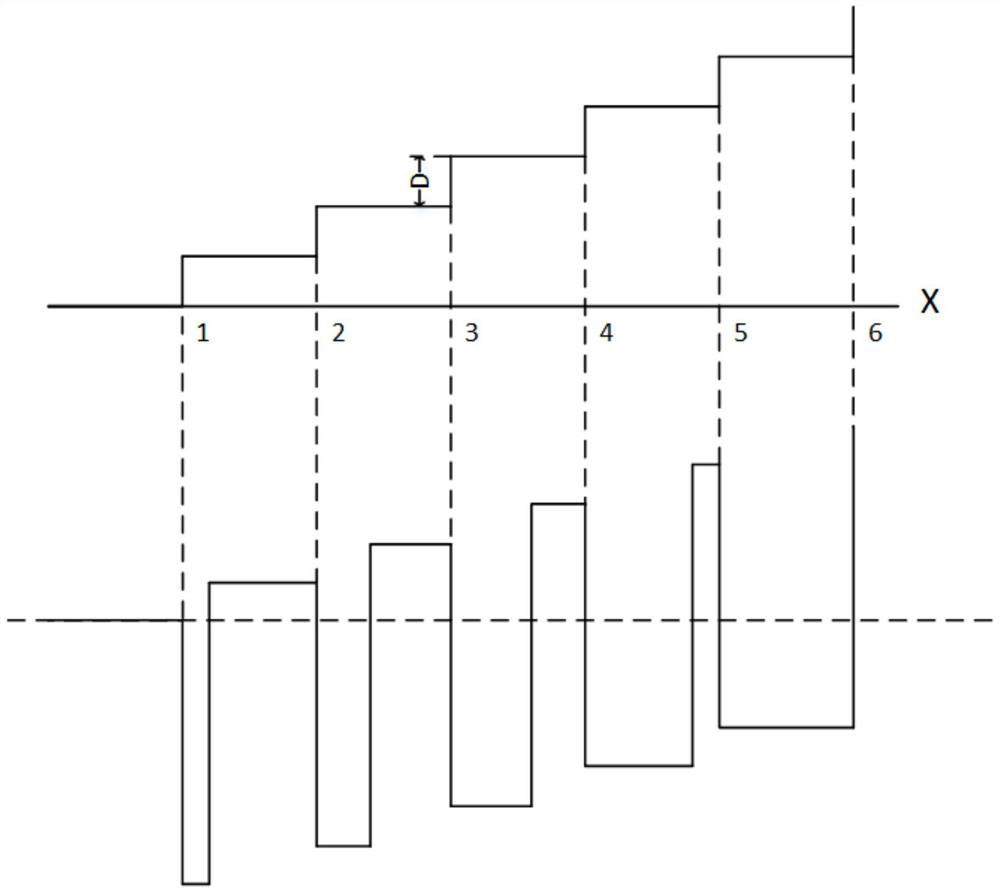
[0017] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 4 This embodiment will be described. The angle calibration method of the absolute magnetic encoder based on the vernier code track described in this embodiment, the method is specifically implemented through the following steps:
[0018] Step 1: Obtain the original data of the main code track and the vernier code track of the sensitive chip;
[0019] Step 2: Intercept the original data obtained in Step 1 to obtain data within a complete circle;
[0020] Step 3: Calculate the deviation value of each intermediate variable used to solve the absolute position according to the obtained data in the complete circle;
[0021] Step 4: Use the deviation value calculated in Step 3 to obtain calibration values for calibrating each intermediate variable;
[0022] Step five: use the calibration values obtained in step four to calibrate each intermediate variable to obtain calibrated intermediate variables; obtain absolute posit...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0023] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: the specific process of the step one is:
[0024] When the joint rotates in one direction, the original data p is collected according to the predetermined sampling period j , j=0,1,2,...,k-1,p j Represents the jth raw data collected, and k represents the number of raw data collected by the absolute magnetic encoder;
[0025] According to the collected original data, calculate the original data m of the main scale j and vernier raw data n j .
[0026] In this embodiment, the sampling period is determined according to the rotation speed of the joint (magnetic sensor) and the calibration time, so as to ensure that the position information of a complete circle and a certain number of sampling points are obtained during the entire calibration process (2000 sampling points / circle during the test).
[0027] The collected raw data is spliced from the ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode two is: the specific process of said step two is:
[0030] Raw data of main scale m j and vernier raw data n j Form the original data sequence (m j ,n j ), j=0,1,2,...,k-1, perform cursor calculation on the original data sequence, and obtain the uncalibrated position sequence pos_raw j , j=0,1,2,...,k-1;
[0031] Intercept the subsequence pos with an angle value in the range of 0 degrees to 360 degrees from the uncalibrated position sequence j′ , j′=j 0 ,j 0 +1,...,j 1 , j 0 is the subscript of the first position value of 0 degree in the intercepted circle, j 1 is the subscript whose last position is 360 degrees, then the intercepted subsequence pos j′ The corresponding original data subsequence is (m j′ ,n j′ ), remark the subscript of the intercepted subsequence as j′=0,1,2,…,k 1 -1,k 1 = j 1 –j 0 +1,k 1 is the number of elements in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com