In-situ XRF reading evaluation and screening method based on data structure
A technology of data structure and screening method, applied in visual data mining, structured data retrieval, electronic digital data processing and other directions, can solve the problems of poor detection effect, poor accuracy and precision, and the test results are not as accurate as indoor XRF, etc. To improve the effect of in-situ measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific examples, but the given examples are not intended to limit the present invention.
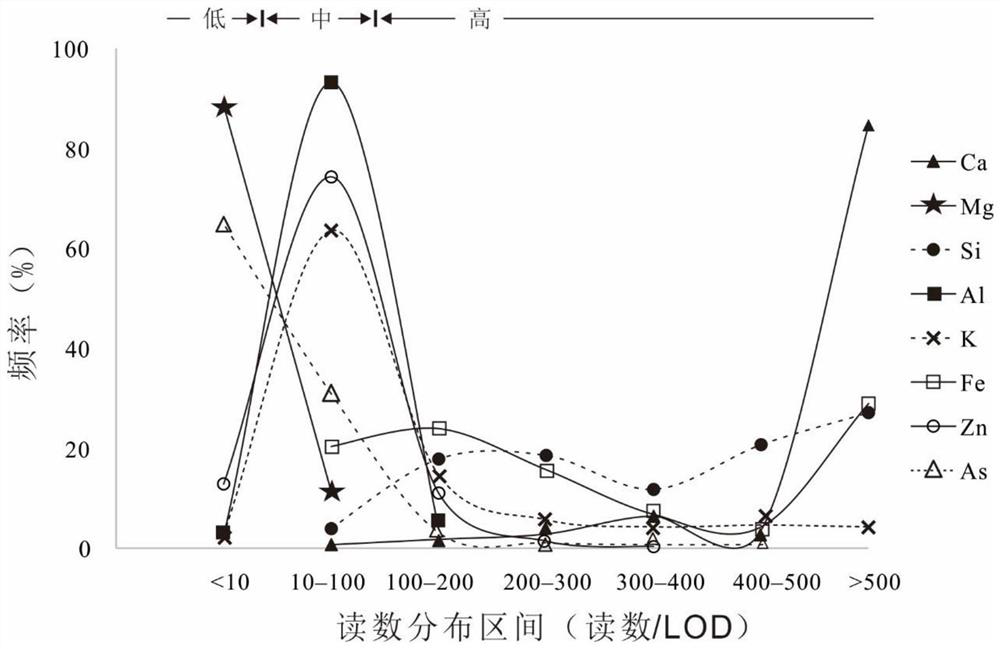
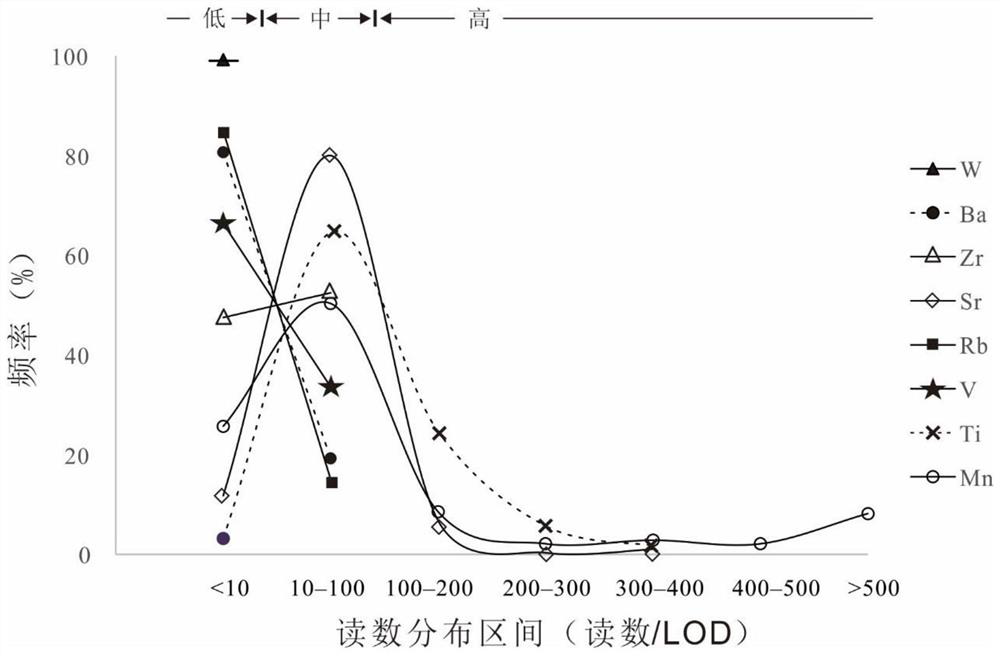
[0023] In this example, a certain granite porphyry-skarn-marble outcrop section is taken as an example. Portable XRF is used to measure 280 points in situ according to a certain grid, and 280 readings are obtained for each element, and all readings are recorded as R ij (i represents different element types, and j represents the readings in different samples or sampling points). Among them, individual measuring points will be displayed as "<LOD" because the concentration of some elements is lower than the lower limit of detection capability of the instrument.
[0024] Measure the instrument detection limit or method detection limit of each element according to the general method, and select it according to the needs. For the convenience of description, it is collectively referr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com