A Saccharomyces cerevisiae suitable for brewing tea wine and its application
A technology for Saccharomyces cerevisiae and tea wine, which is applied in the preparation of alcoholic beverages, microorganism-based methods, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of easy acid production, heavy sour and astringent taste, and no screening, and achieves complete fermentation degree and alcohol conversion rate. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
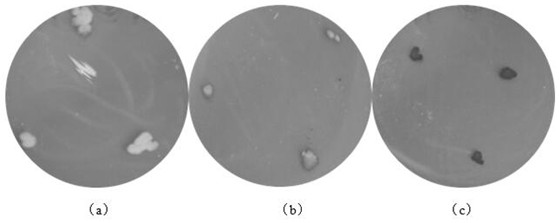
[0027] Example 1: Screening to obtain Saccharomyces cerevisiae GXSJ77
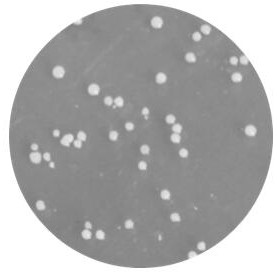
[0028] 1. Seed collection: collect fresh leaves with one bud and two or three leaves, spread them overnight at room temperature, place them in a withering tank at 32°C for withering, and use a rapid moisture analyzer to detect the water content in the withered leaves until the leaves are withered. Moisture is 60~64%. After the withering is completed, use a rolling machine to knead the withered leaves according to light kneading-heavy kneading-light kneading for 15 minutes each. Put the rolled leaves in a constant temperature and humidity box at 30°C and a relative humidity of 90% to ferment for 2 to 3 days, until the fermented leaves have an obvious wine smell. Select fermented black tea leaves with obvious wine taste and pleasant aroma, rinse the above fermented leaves with sterile water, and obtain a bacterial liquid containing yeast.
[0029] 2. Isolation of pure species: Take 10 mL of the above bacte...
Embodiment 2
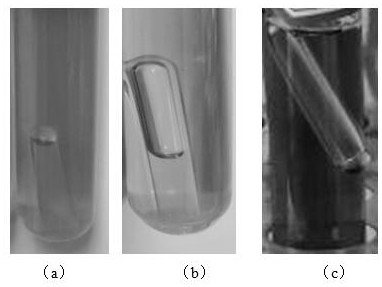
[0042] The genomic DNA of the bacterial strain GXSJ77 screened in Example 1 was extracted by using the Ezup column yeast genomic DNA extraction kit, and using this as a template, the ITS fragment was amplified by PCR with general primers, and the PCR product was detected by 1.7% agarose electrophoresis ( See Figure 4 ), and commissioned Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. to perform sequencing. The determined sequence was compared with the sequence in GenBank by BLAST and identified as Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It was preserved in the China Typical Culture Collection Center, address: Wuhan University Collection Center, Luojia Mountain, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, preservation date: December 16, 2019, preservation number: CCTCC M 20191049.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Using commercial active dry yeast (named SY) as a control, the strain GXSJ77 screened out in Example 1 and the control strain SY were respectively inoculated in black tea medium for fermentation to prepare black tea wine.
[0045] Firstly, seed liquid culture was carried out: 50 μL of the strain preserved at low temperature was inoculated into 100 mL of YPD medium, and cultured at 30 °C and 150 rpm for 24 h. Then carry out fermentation culture: inoculate the cultured seed solution in 10 L of black tea culture medium, and culture it statically at 28°C. Samples were taken every two days to determine the amount of bacteria (absorbance at 600nm) and alcohol content until the end of fermentation (see Figure 5 ). The highest cell mass of strain GXSJ77 was 9.2 times that of commercial active dry yeast, indicating that compared with commercial active dry yeast, strain GXSJ77 can adapt to the tea juice system well. The highest alcohol content of strain GXSJ77 was 3.16 times t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com