Reprogramming of non-neuronal cells into neurons and methods and compositions to treat neurodegenerative diseases and disorders
A neuron cell, reprogramming technology, used in nervous system diseases, nervous system cells, cell culture active agents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0218] Example 1. Expression of miR-9 and Brn2 in astrocytes.
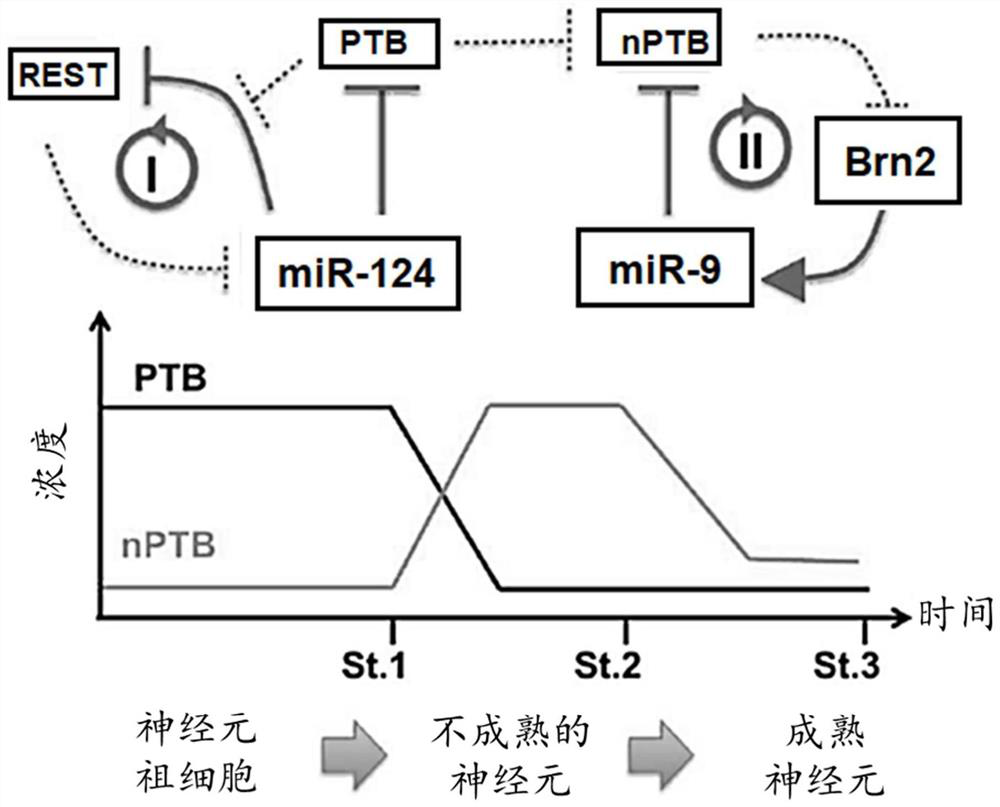
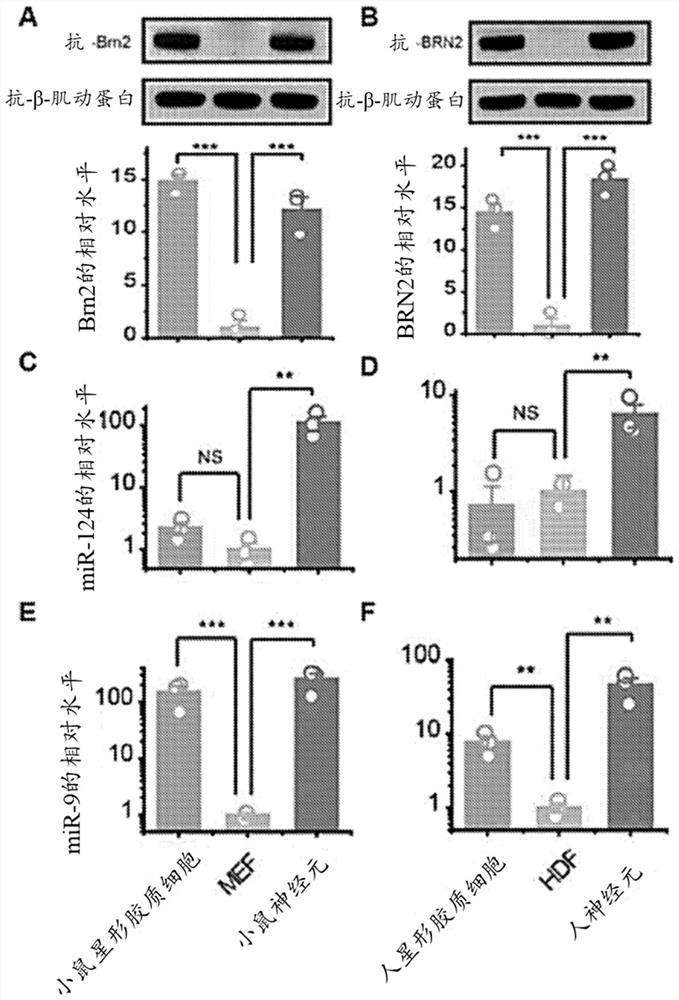
[0219] Testing PTB / nPTB-regulated gene expression programs in mouse and human primary astrocytes. As shown in Figures 2C-2F, both miR-124 and miR-9 were highly expressed in neurons but not in fibroblasts. In human and mouse astrocytes, miR-124 was found to be present at low levels (Fig. 2C and 2D), which may explain the high REST levels in this non-neuronal cell type and suggest that astrocytes Tight PTB-regulated circuits in cells. However, unexpectedly, miR-9 was found to be highly expressed in both mouse and human astrocytes (Fig. 2E and 2F). Brn2 followed the same expression pattern as miR-9, being low in fibroblasts but high in both astrocytes and neurons (Fig. 2A and 2B). These observations are consistent with the idea that astrocytes and neurons may share a common ancestor.
Embodiment 2
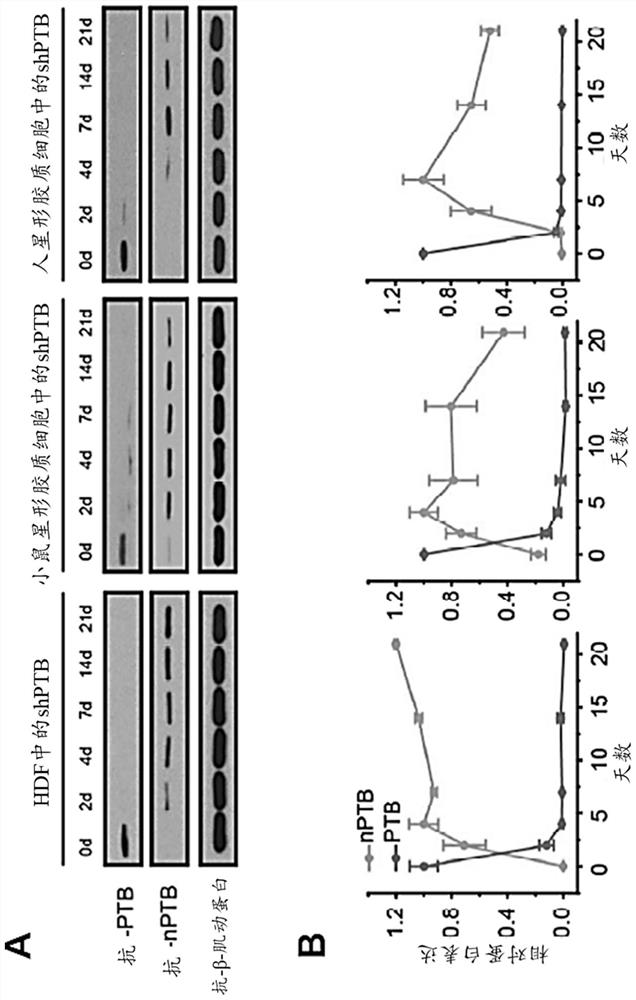
[0220] Example 2. Knockdown of PTB in mouse and human astrocytes leads to nPTB induction followed by nPTB decline.
[0221] Recognizing in the present invention that astrocytes already express factors that may be important for neuronal maturation (such as miR-9 and Brn2), the possibility that miR-9 immediately counteracts nPTB induced by PTB knockdown was tested. In contrast to the PTB / nPTB expression profile in human fibroblasts, it was shown in mouse and human astrocytes that PTB knockdown resulted in nPTB induction followed by nPTB decline (Figures 3A and 3B). Thus, high levels of miR-9 could enhance the stable reprogramming of astrocytes to mature neurons by depleting PTB in astrocytes alone.
Embodiment 3
[0222] Example 3: Knockdown of PTB in vitro efficiently converts astrocytes into functional neurons.
[0223] To explore the possibility that downregulation of PTB would lead to efficient conversion of astrocytes into mature neurons, mouse astrocytes were isolated from the cerebral cortex of pups at postnatal day 4 to 5 (P4-5). were isolated and human fetal astrocytes were obtained from a commercial source (ScienCell). Cells from both sources expressed the expected astrocyte markers GFAP and ALDH1L1, and had no detectable contamination of neuronal cells, as indicated by the absence of markers for neuronal or neural crest progenitor cells ( Figure 4 ).
[0224] Mouse astrocytes were infected with a lentiviral vector expressing a small hairpin RNA (shPTB) against PTB. Four weeks after transduction, approximately 50% of shPTB-treated cells maintained in standard neuronal differentiation medium containing a panel of small molecules showed neuronal morphology and positive staini...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com