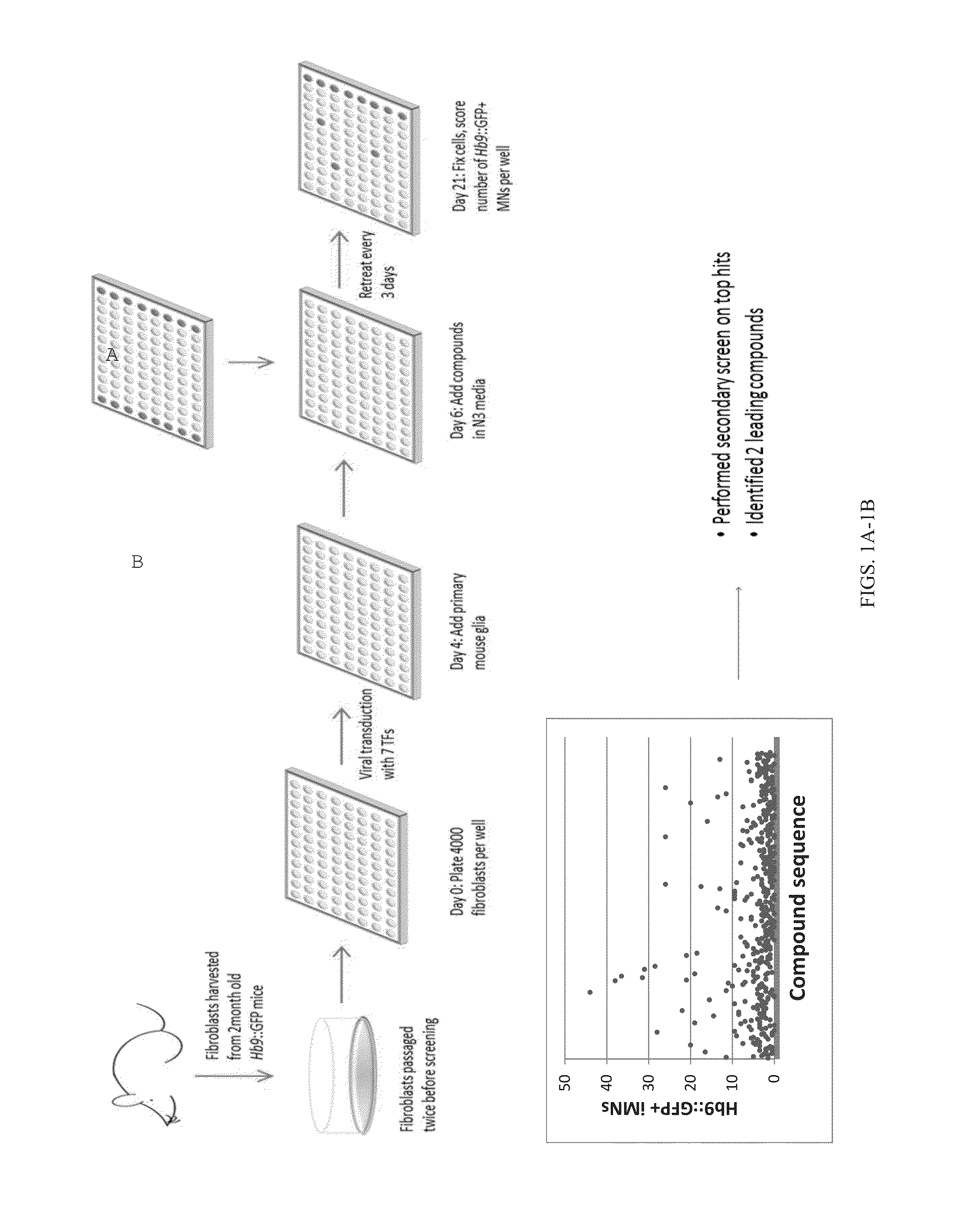
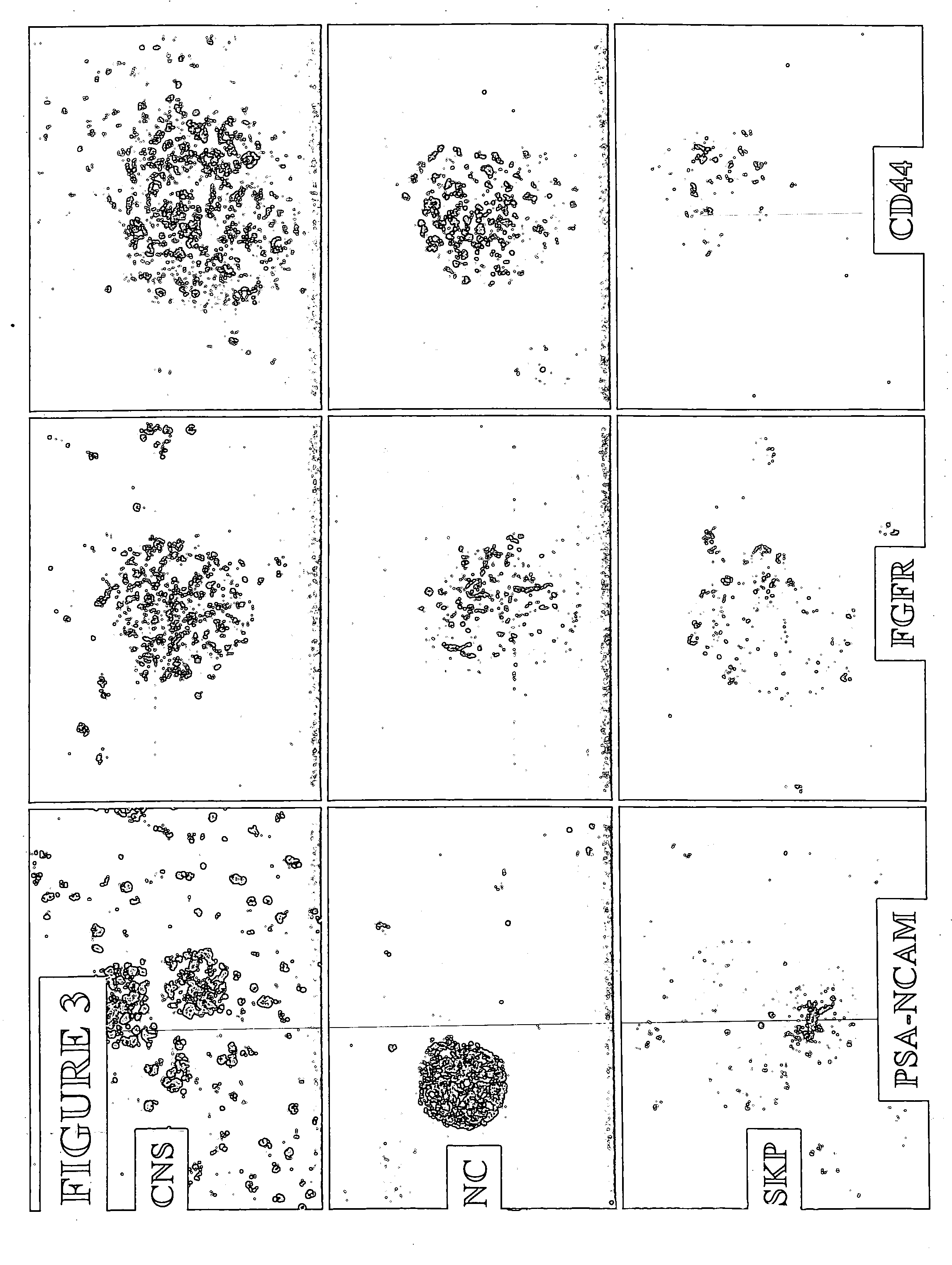
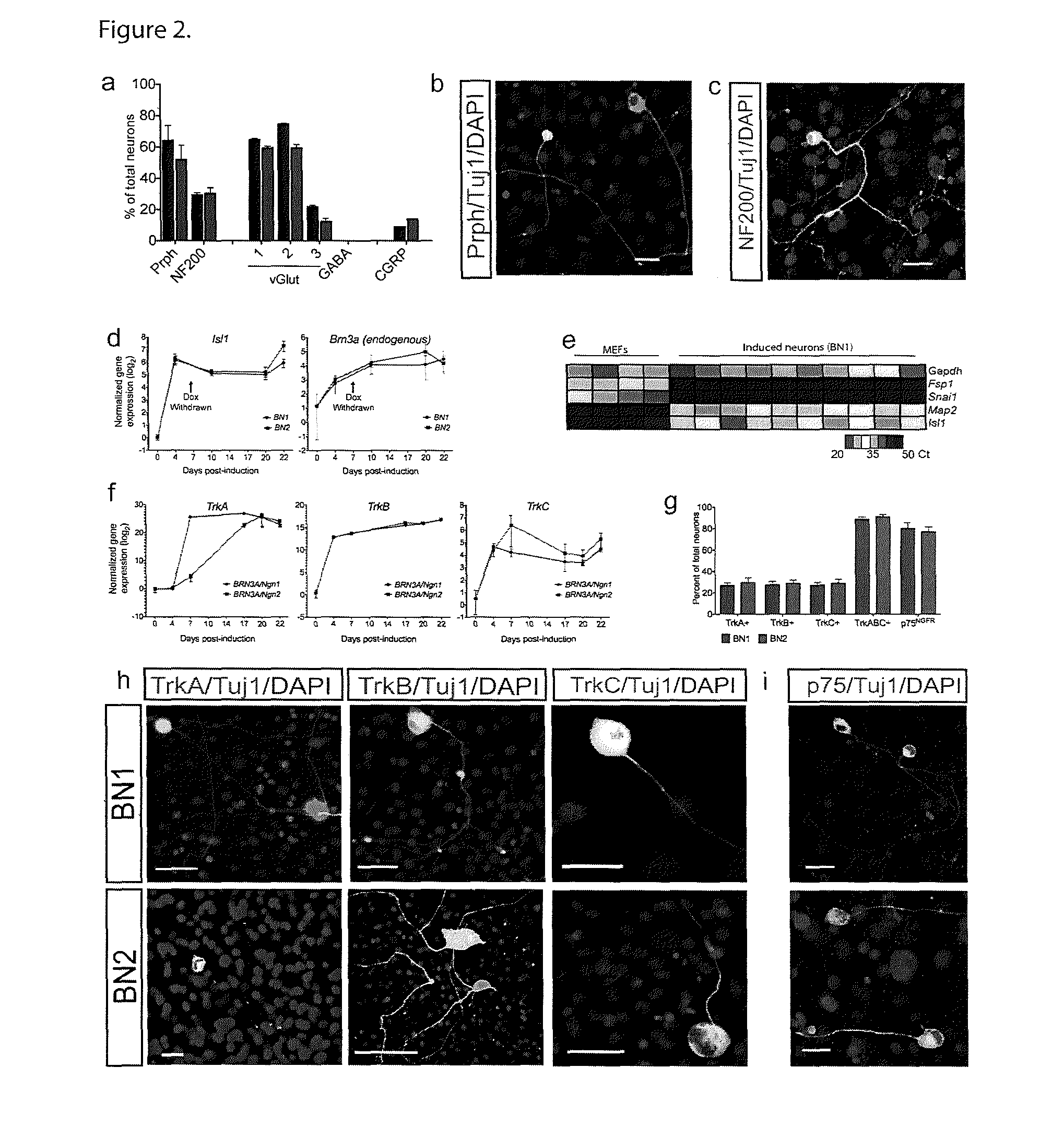
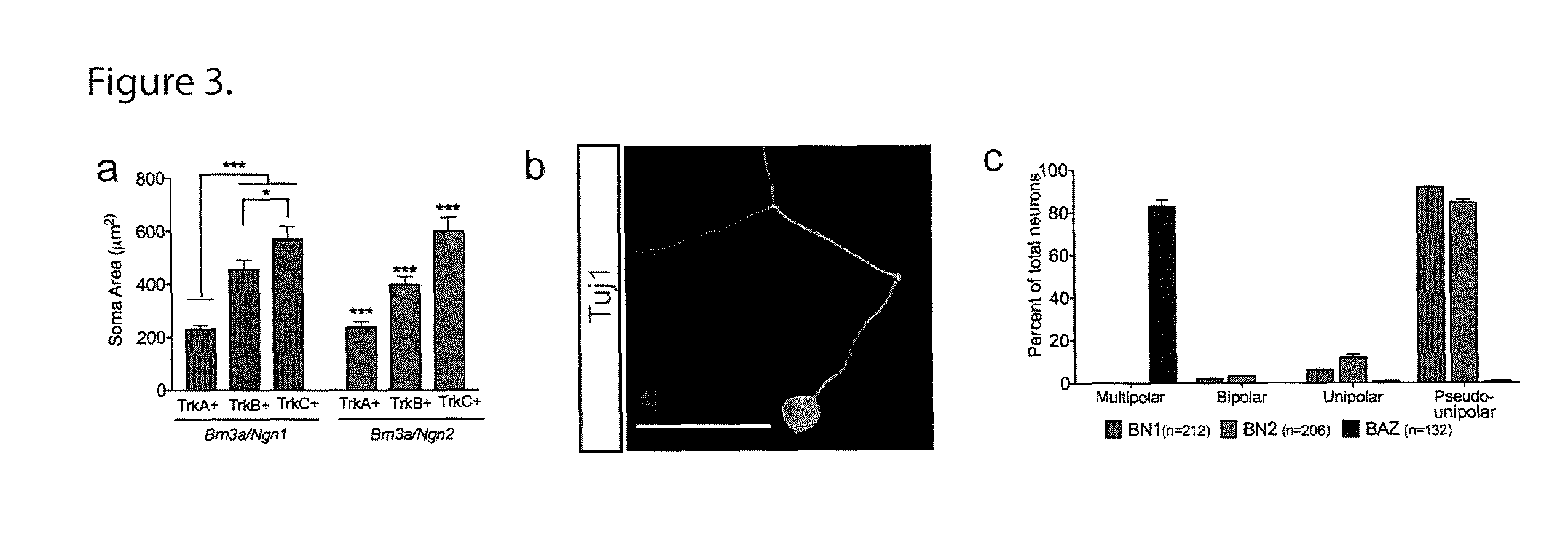
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Nonneuronal cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
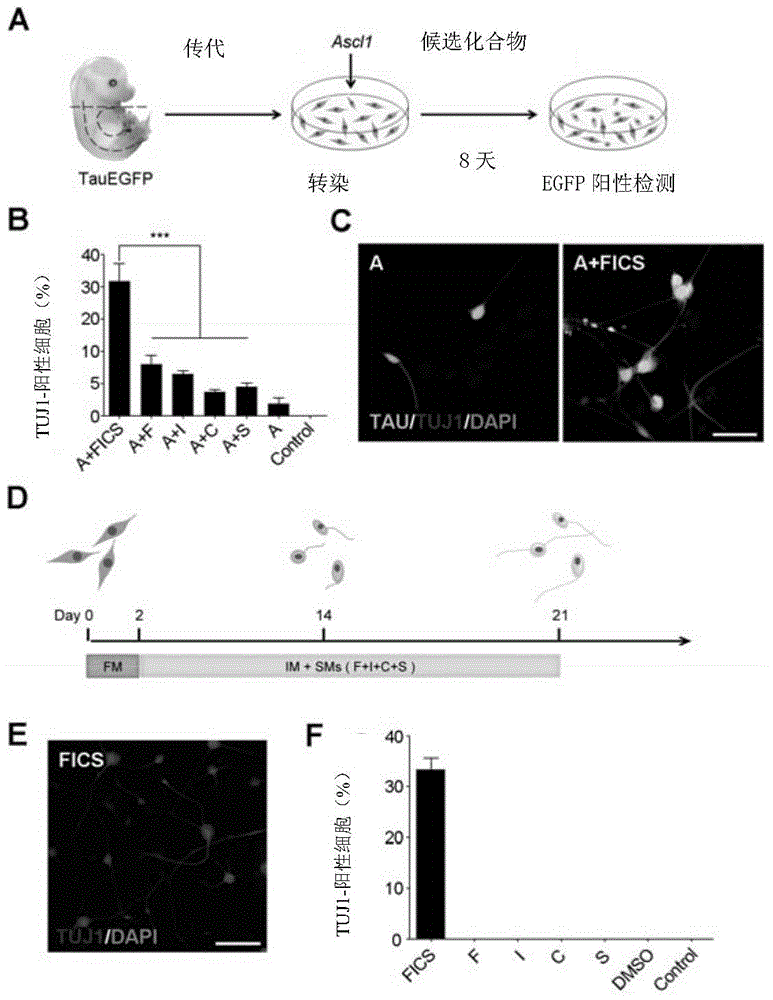
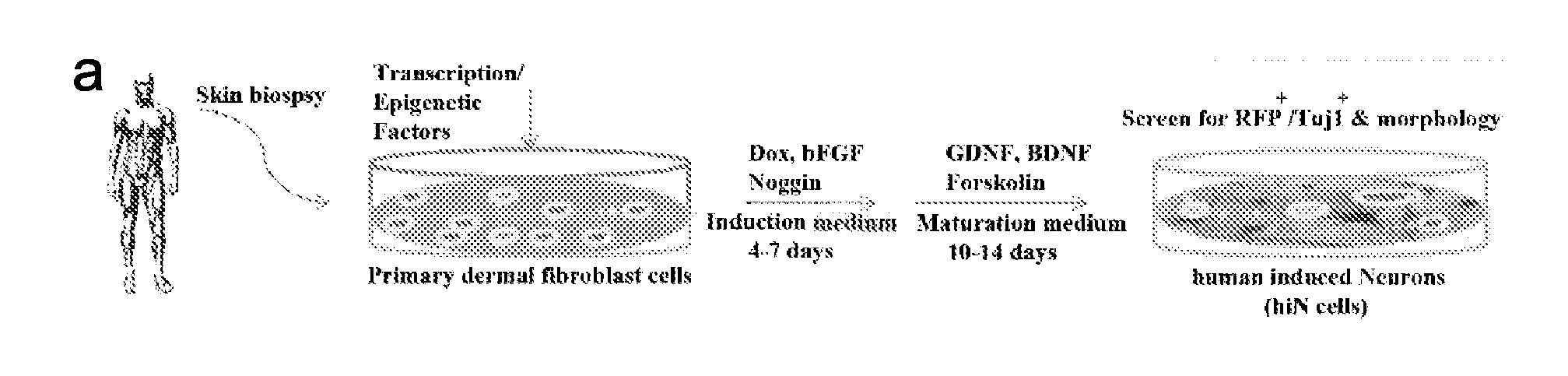
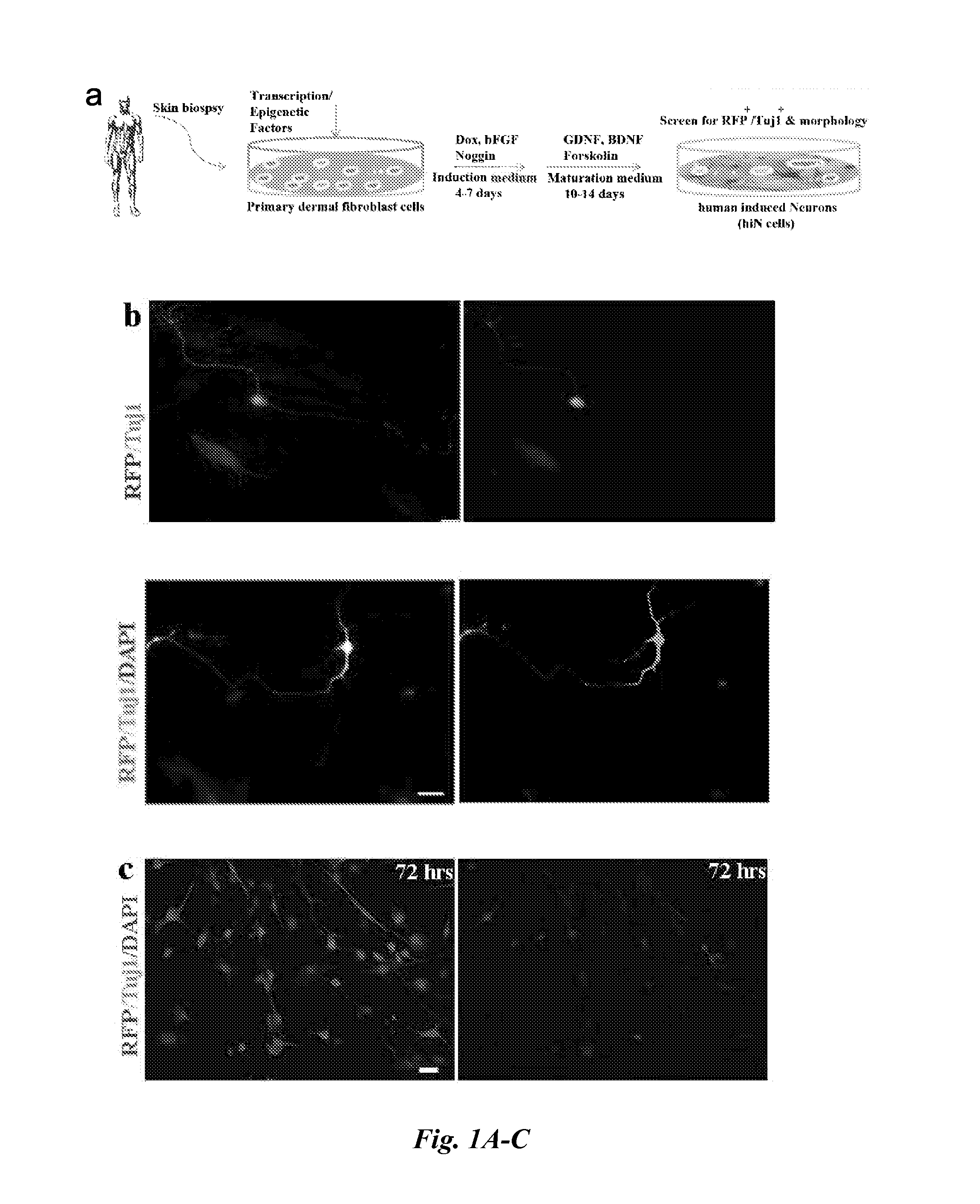
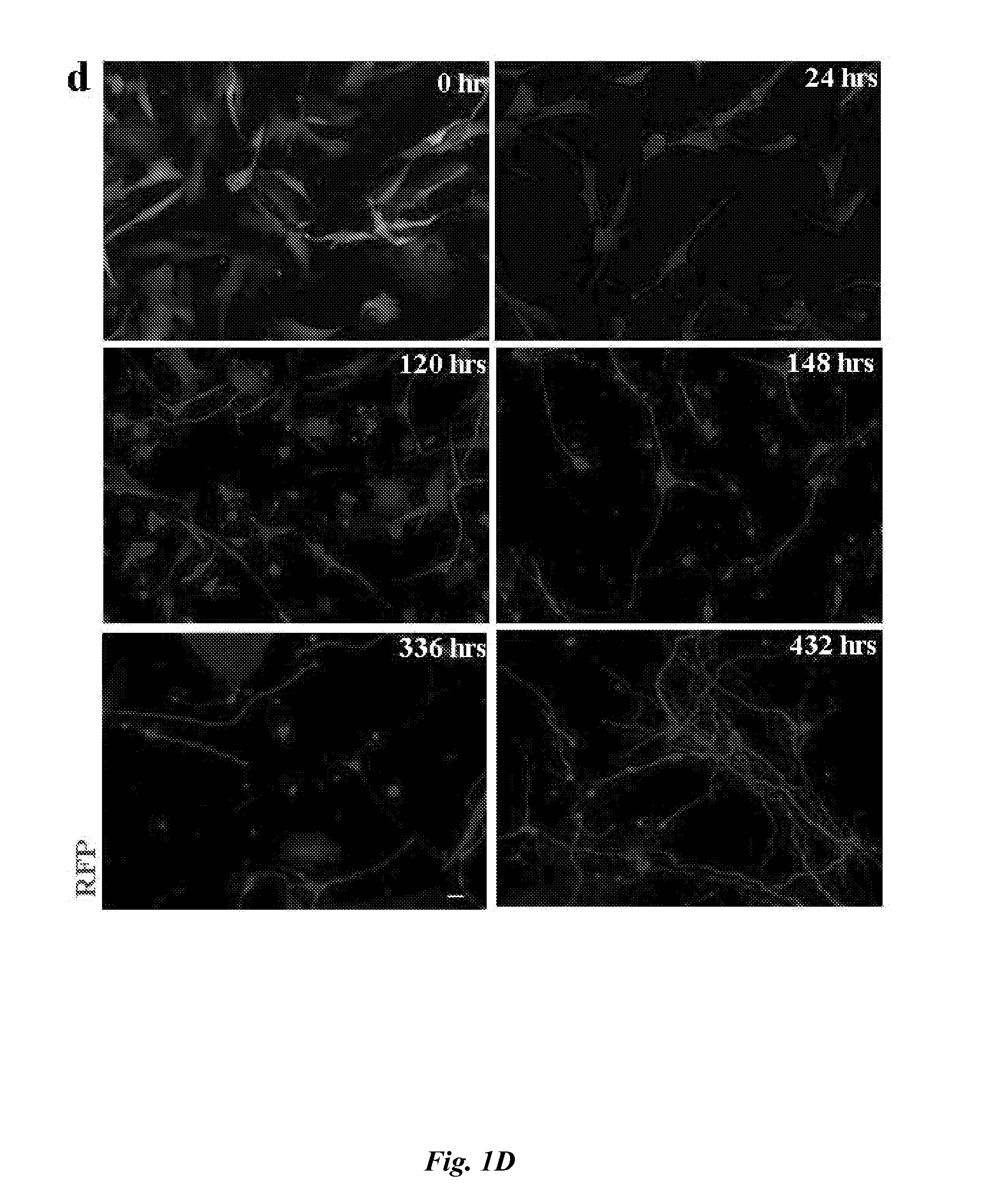
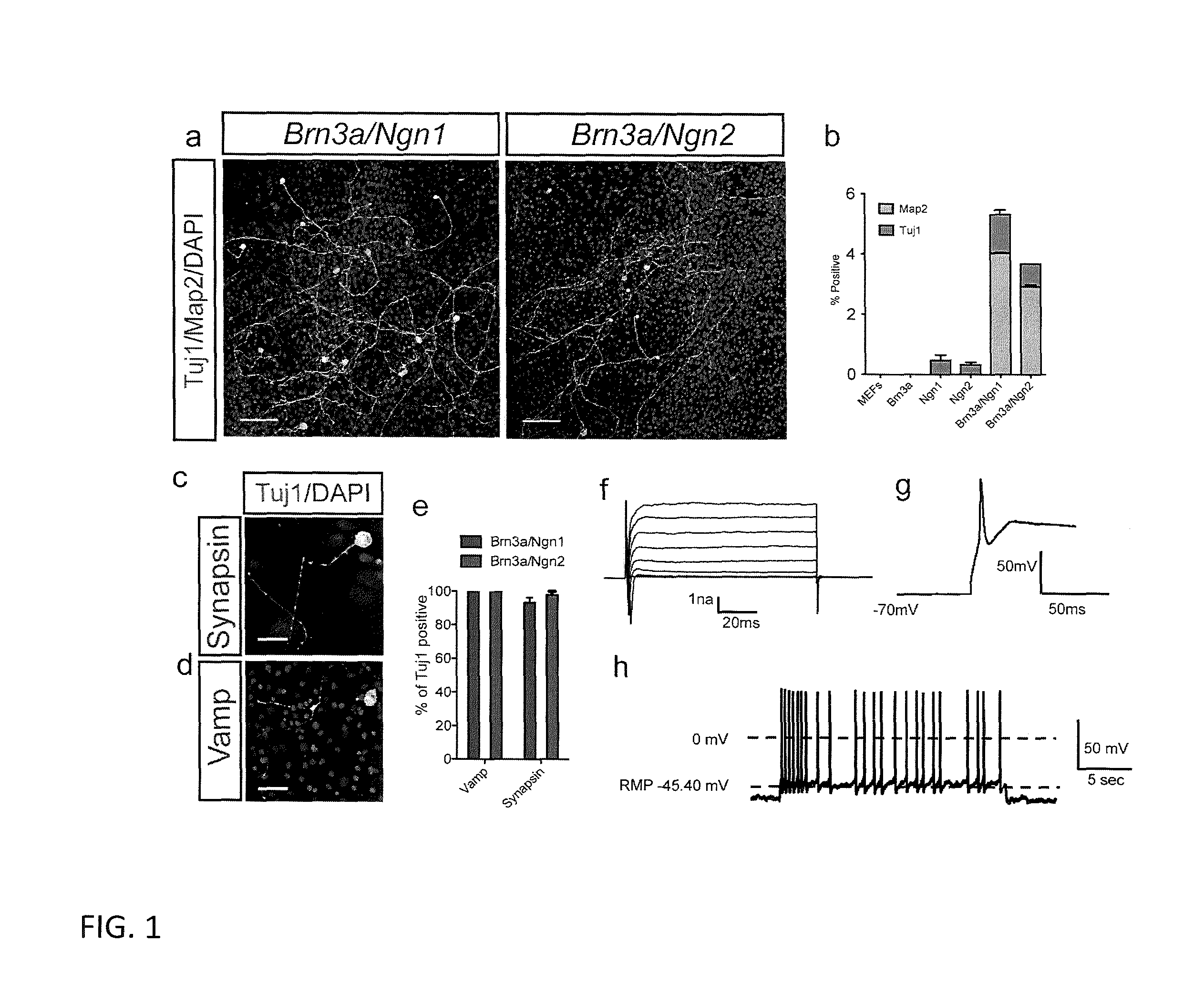
Method and composition used for obtaining neuron-like cells from non-neuronal cells via reprogramming
ActiveCN105039258ALow costEasy to operateNervous disorderDrug screeningPTK InhibitorsEnzyme Inhibitor Agent
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Methods For The Delivery Of Toxins Or Enzymatically Active Portions Thereof
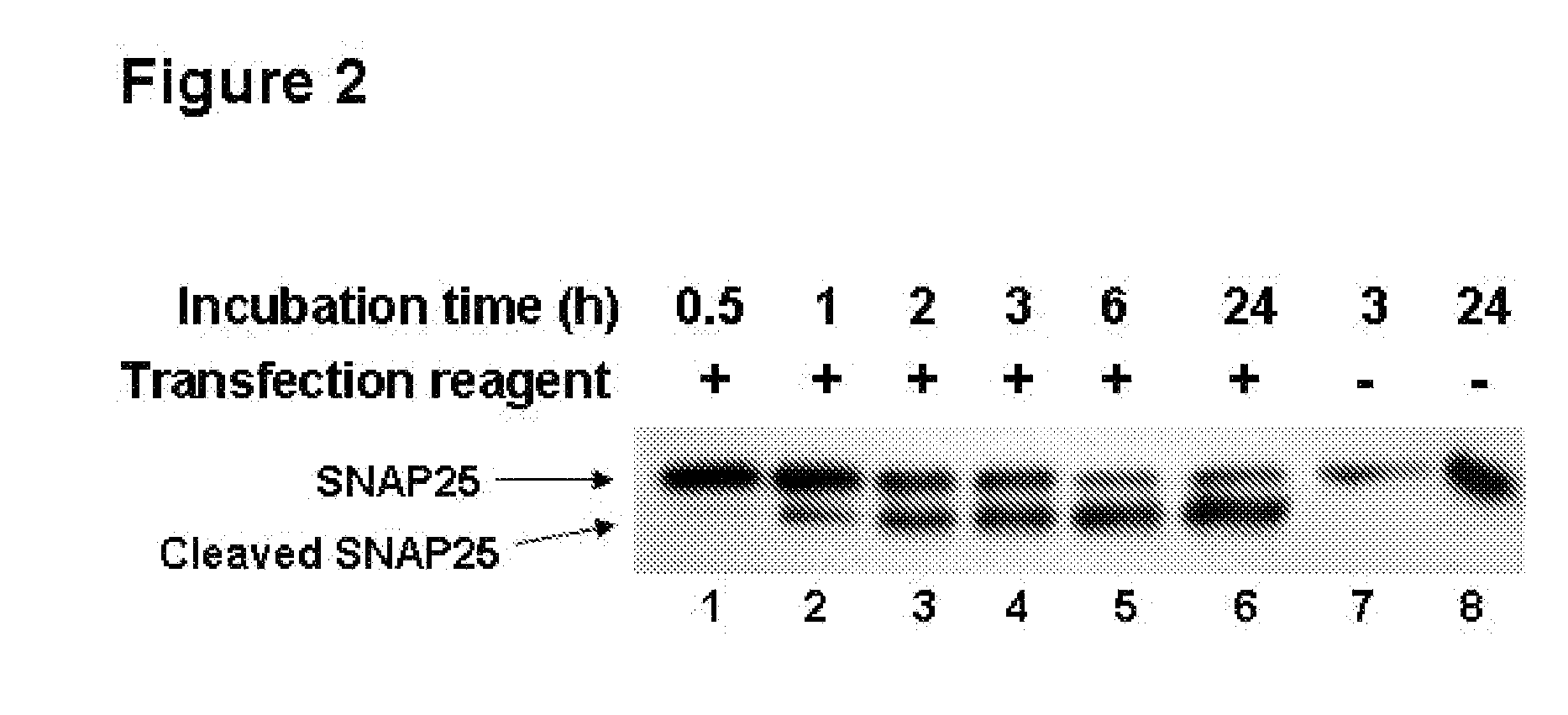
InactiveUS20100209955A1Increase the number of cellsIncrease rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCell based assaysToxin
The present invention relates to methods, systems, and kits for intoxicating cells, neuronal and non-neuronal cells, with a toxin or fragment thereof. This is done by subjecting toxin substrate and a lipid or polymeric carrier (e.g., DNA uptake facilitating agent) to one or more cells for use in cell based assays. In an aspect, the methods of the present invention allow for high throughput assays and, as such, for the evaluation of drug candidates.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Novel Methods and Models for Rapid, Widespread Delivery of Genetic Material to the CNS Using Non-Viral, Cationic Lipid-Mediated Vectors
ActiveUS20100249208A1Facilitate transient deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderLipid formationTherapeutic protein
Provided are safe, non-invasive, non-viral delivery methods for providing a nucleic acid into the neuronal and non-neuronal cells of the central nervous system (CNS) of a subject to protect neuronal and non-neuronal cells from ischemic or traumatic injury, wherein the nucleic acid encodes a therapeutic proteins, specifically providing rapid transient expression and widespread distribution for in vitro or in vivo applications. Further provided are methods for the intrathecal delivery to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a neuroprotective gene sequence, e.g., a heat shock protein (HSP), complexed with cationic lipid compositions to achieve such delivery, and the complexes used therein.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for engineering non-neuronal cells into neurons and using newly engineered neurons to treat neurodegenerative diseases
The invention provides compositions and in vivo, ex vivo and in vitro methods for trans-differentiation of or re-programming mammalian cells to functional neurons. In particular, the invention provides methods for engineering non-neuronal cells into neurons, including fully functional human neuronal cells, and methods for engineering non-neuronal cells into neurons, e.g., fully functional human neuronal cells, in the brain to treat a neurodegenerative disease. In alternative embodiments, the invention provides compositions comprising re-differentiated or re-programmed mammalian cells, such as human cells, of the invention. The invention also provides compositions and methods for direct reprogramming of cells to a second phenotype or differentiated phenotype, such as a neuron, including a fully functional human neuronal cell. The invention also provides formulations, products of manufacture, implants, artificial organs or tissues, or kits, comprising a trans-differentiated or re-programmed cell of the invention, e.g., a fully functional human neuronal cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts to functional neurons under defined conditions
InactiveUS20140051085A1Increase volumeAmount of moreMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsFibroblastReprogramming
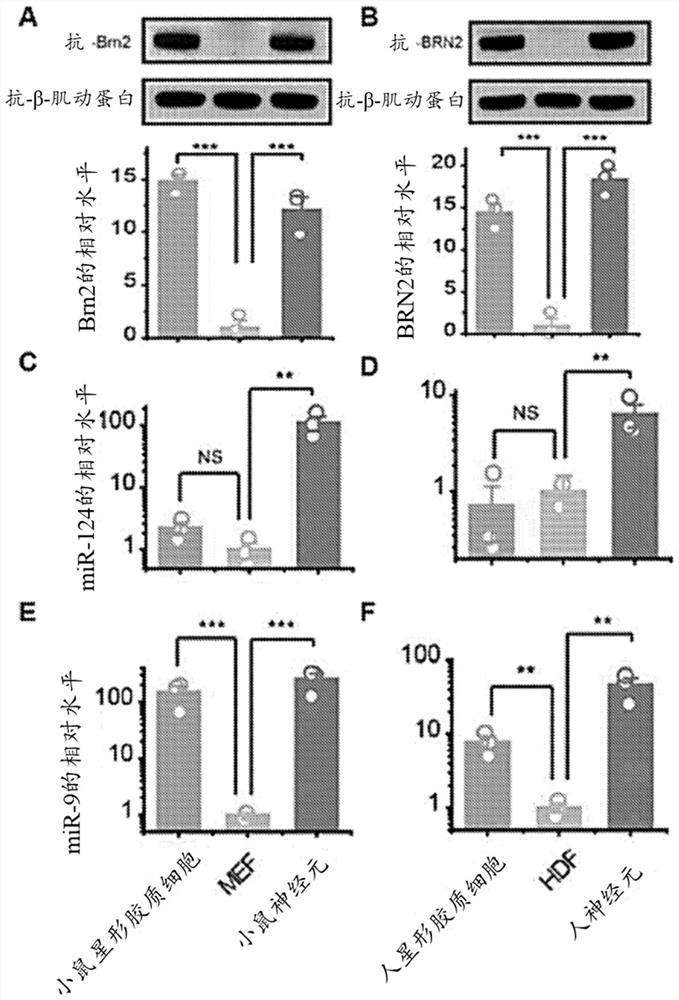
The present invention provides methods of generating a neuronal cell from a differentiated non-neuronal cell by increasing the amount of a miR-124 microRNA, a MYT1L transcription factor, and a BRN2 transcription factor in the differentiated non-neuronal cell.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
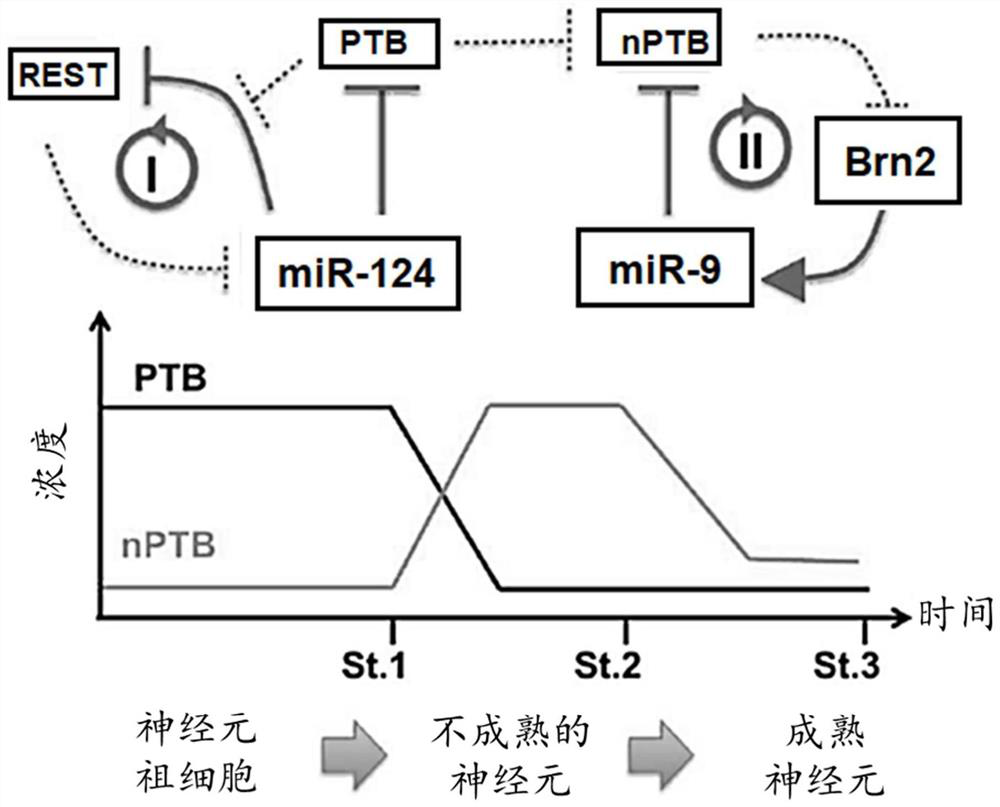
Reprogramming of non-neuronal cells into neurons and methods and compositions to treat neurodegenerative diseases and disorders
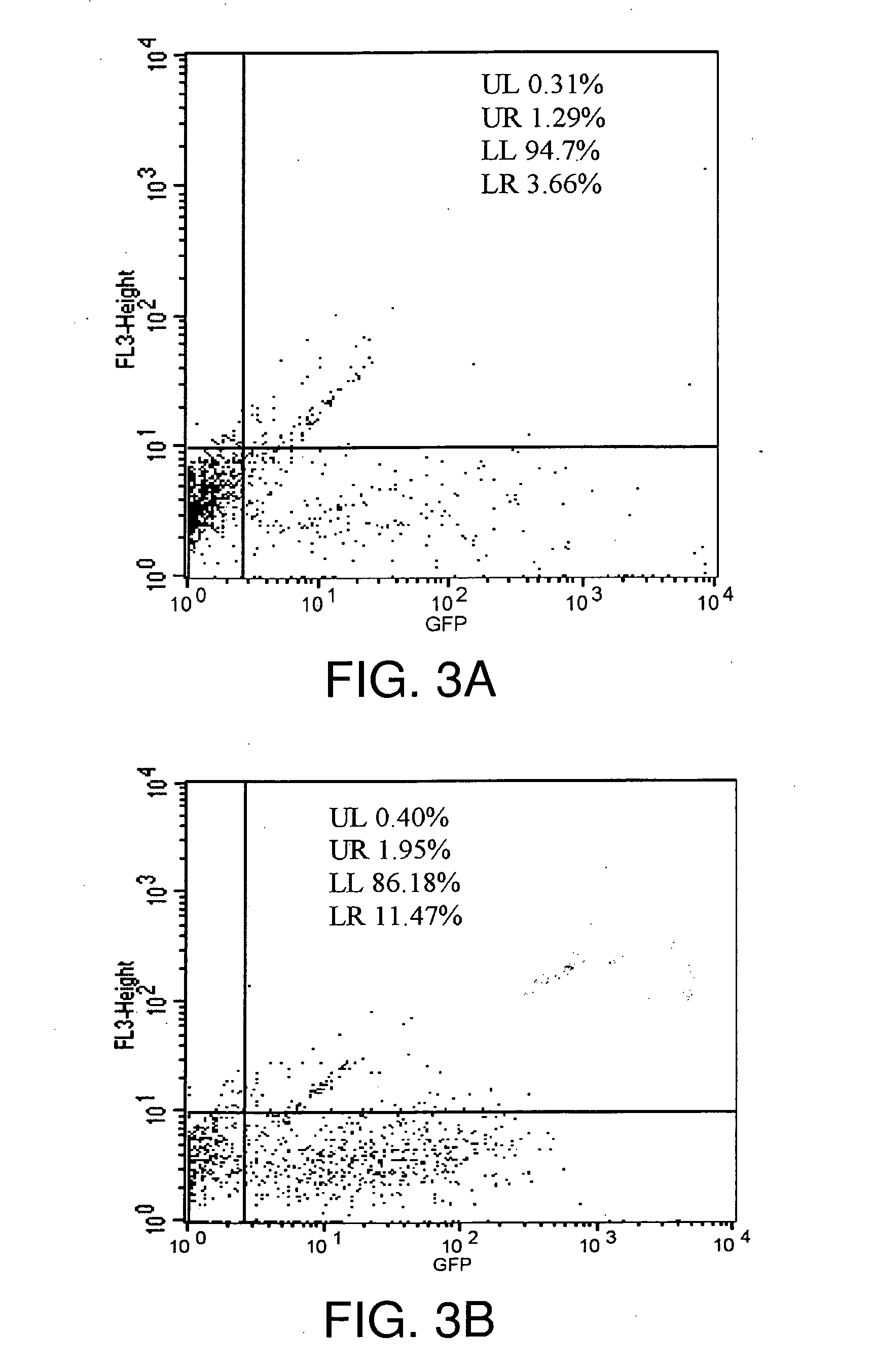
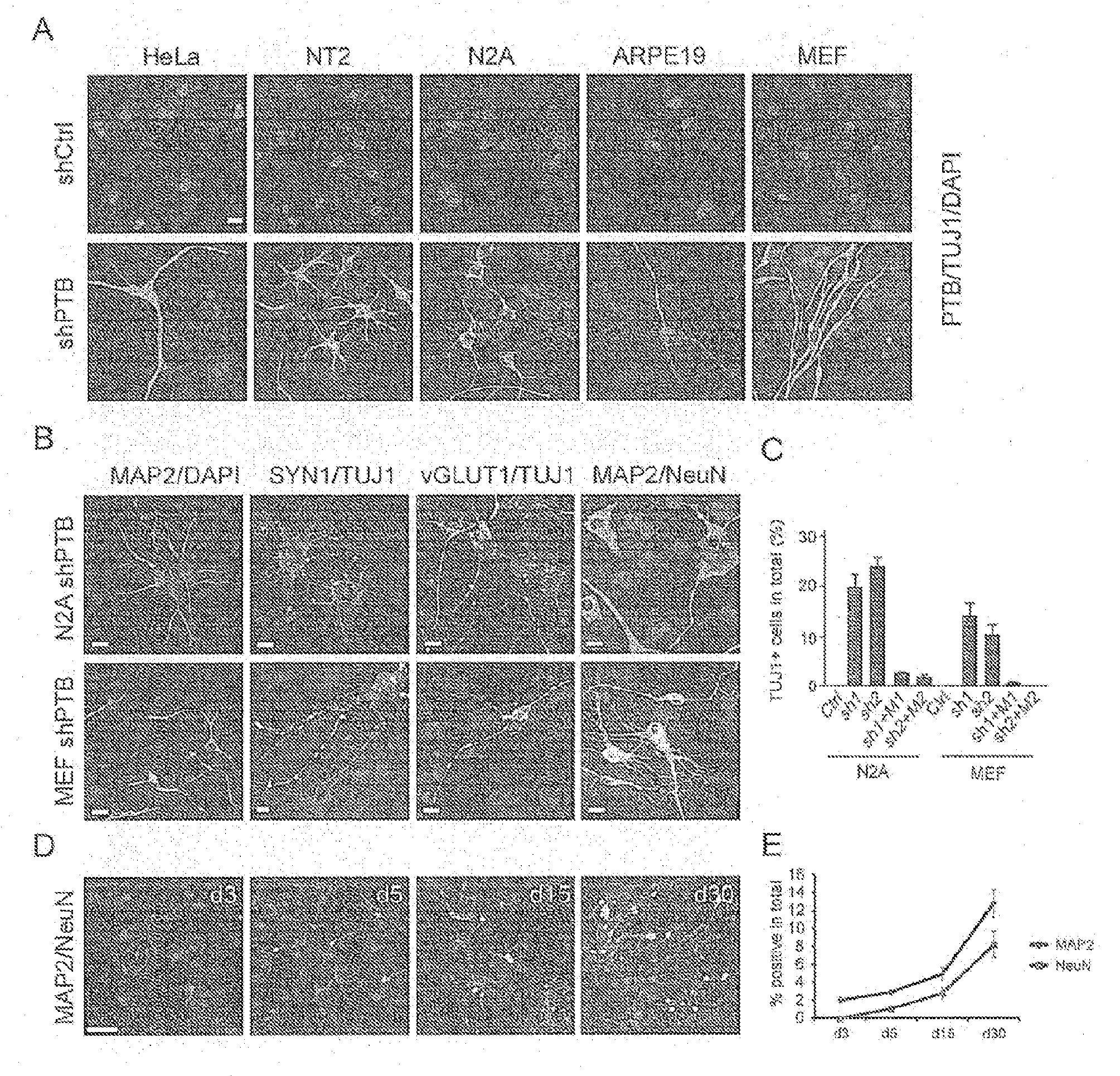
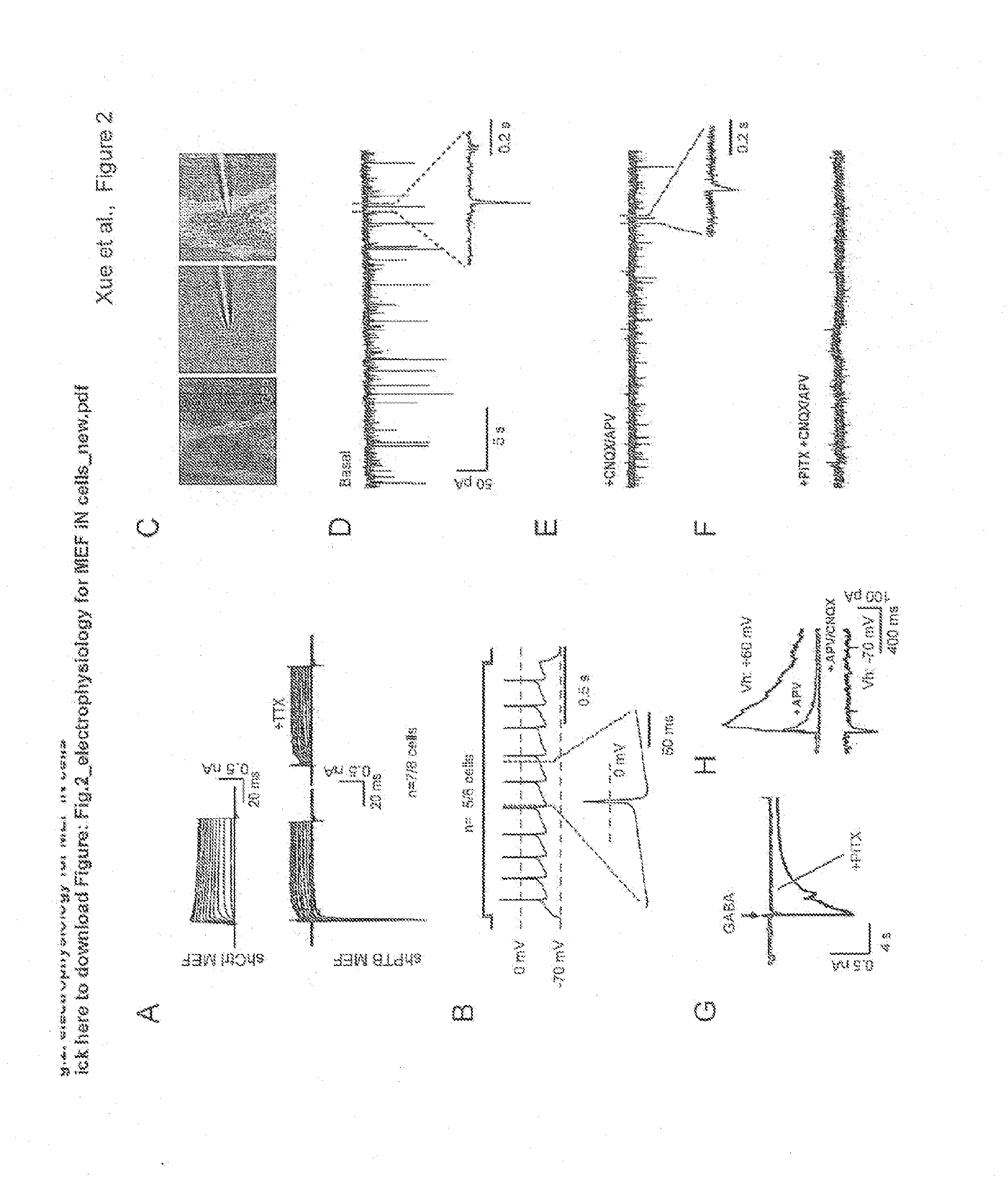
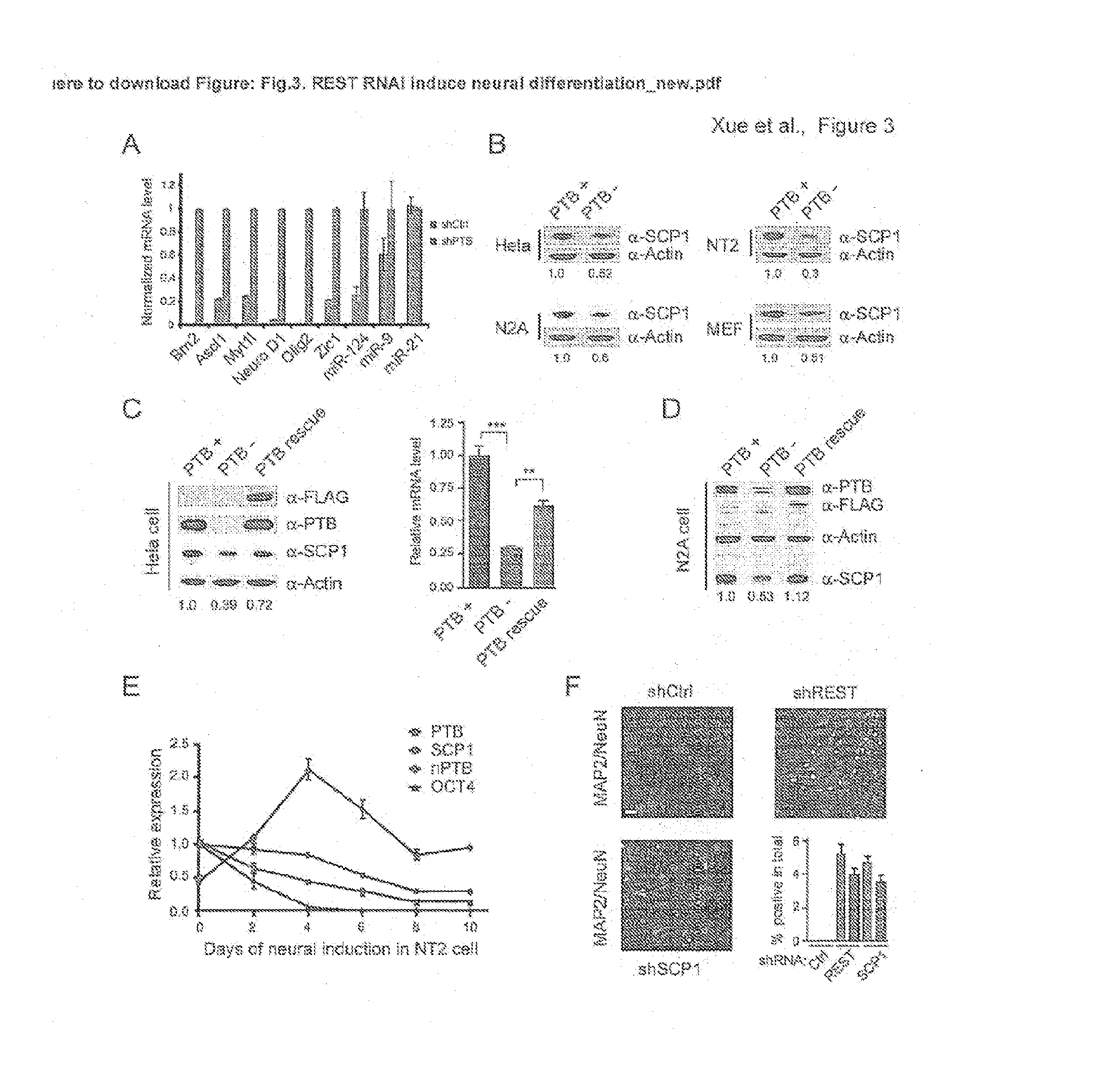
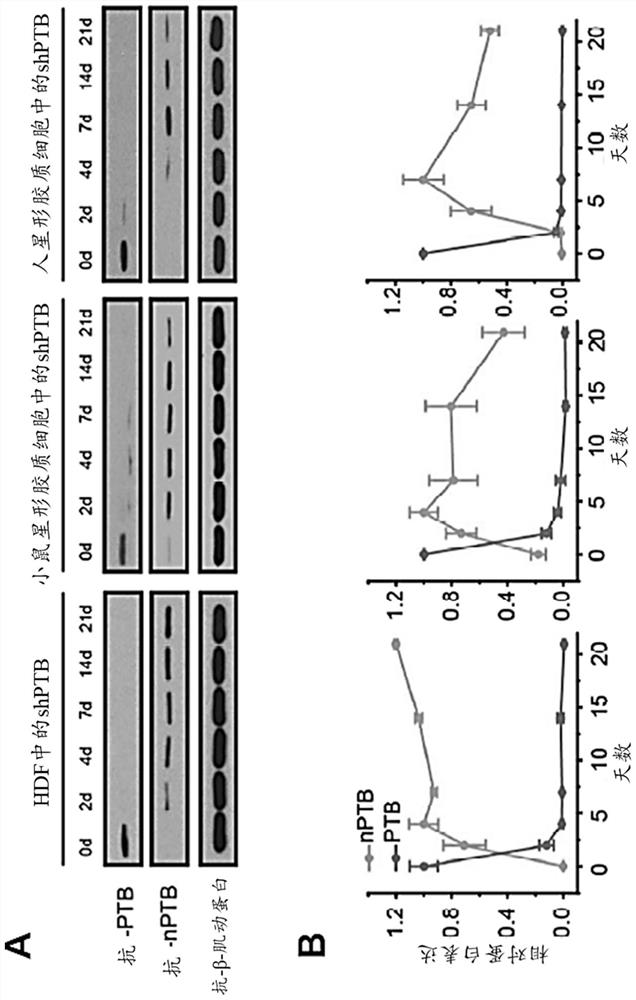
Provided herein is a method of reprogramming a non-neuronal cell to a neuron. Aspects of the present disclosure relate to using cell reprogramming agent suppresses the expression or activity of PTB toconvert a non-neuronal cell into a neuron. Also provided herein is a method of treating neurodegenerative disease by reprogramming non-neuronal cells in vivo to functional neurons.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for the delivery of toxins or enzymatically active portions thereof
InactiveUS8492109B2Increase the number of cellsIncrease rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCell based assaysToxin
The present invention relates to methods, systems, and kits for intoxicating cells, neuronal and non-neuronal cells, with a toxin or fragment thereof. This is done by subjecting toxin substrate and a lipid or polymeric carrier (e.g., DNA uptake facilitating agent) to one or more cells for use in cell based assays. In an aspect, the methods of the present invention allow for high throughput assays and, as such, for the evaluation of drug candidates.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
Conversion of non-neuronal cells into neurons
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for conversion of non-neuronal cells into neurons. The subject invention also concerns methods for screening drugs and other compounds for activity in treating Alzheimer's disease using neuronal cells produced using the subject invention. The subject invention also concerns neuronal cells that have been produced using the methods of the invention. The subject invention also concerns methods for evaluating therapeutic treatment for efficacy in a person or animal having Alzheimer's disease or other neurodegenerative diseases. The subject invention also concerns methods of treating Alzheimer's disease or other neurodegenerative diseases or conditions in a person or animal.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Methods and models for rapid, widespread delivery of genetic material to the CNS using non-viral, cationic lipid-mediated vectors
ActiveUS9149543B2Facilitate transient deliveryNervous disorderTissue cultureLipid formationTherapeutic protein
Provided are safe, non-invasive, non-viral delivery methods for providing a nucleic acid into the neuronal and non-neuronal cells of the central nervous system (CNS) of a subject to protect neuronal and non-neuronal cells from ischemic or traumatic injury, wherein the nucleic acid encodes a therapeutic proteins, specifically providing rapid transient expression and widespread distribution for in vitro or in vivo applications. Further provided are methods for the intrathecal delivery to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a neuroprotective gene sequence, e.g., a heat shock protein (HSP), complexed with cationic lipid compositions to achieve such delivery, and the complexes used therein.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Diagnosis of alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN103765218AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTOR signaling pathwayGene expression
The present invention relates to diagnosis and monitoring of Alzheimer's disease in the live subject. More particularly, the invention relates to methods involving the measurement of differential gene expression in non-neuronal cells taken from human subjects suspected of having Alzheimer's disease wherein the genes to be measured are genes within the m TOR signalling pathway.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BIRMINGHAM
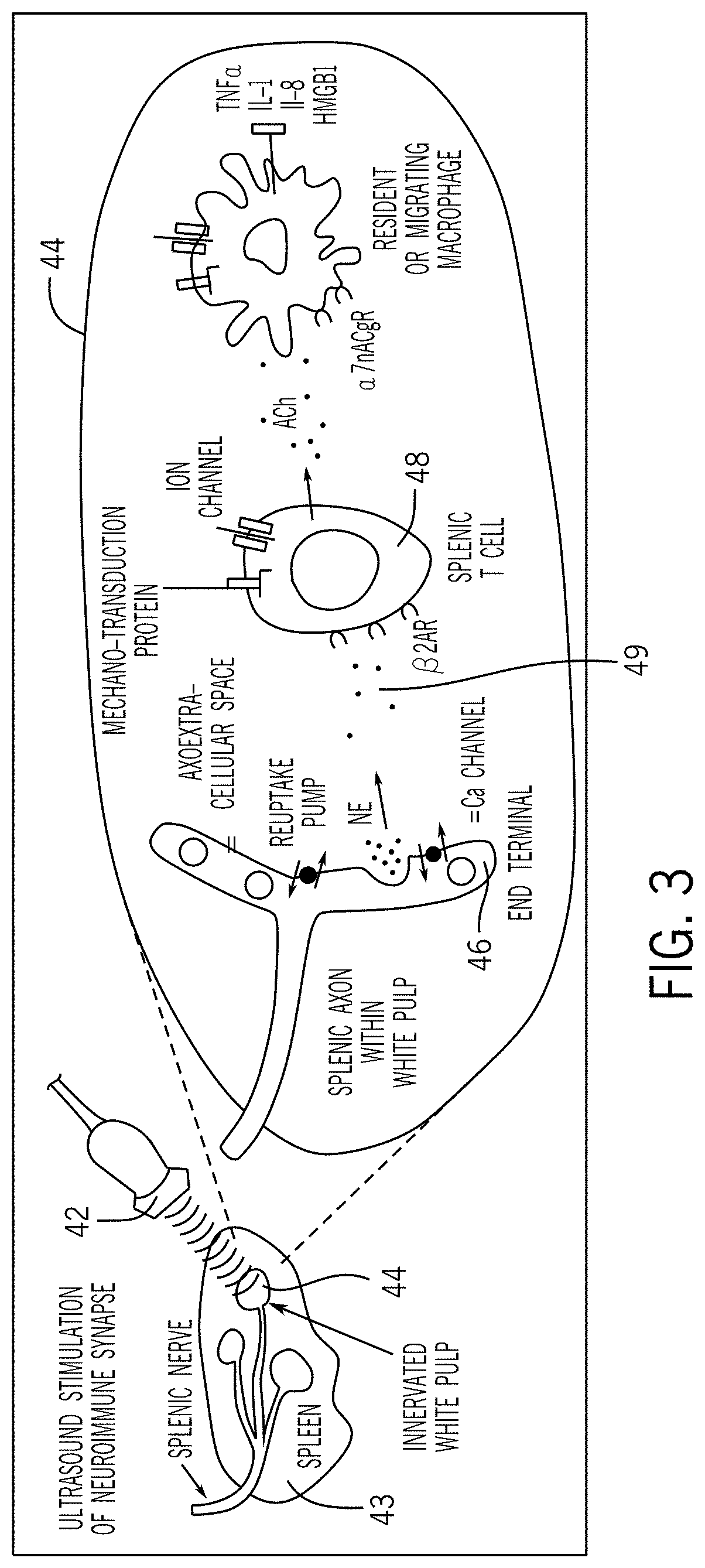
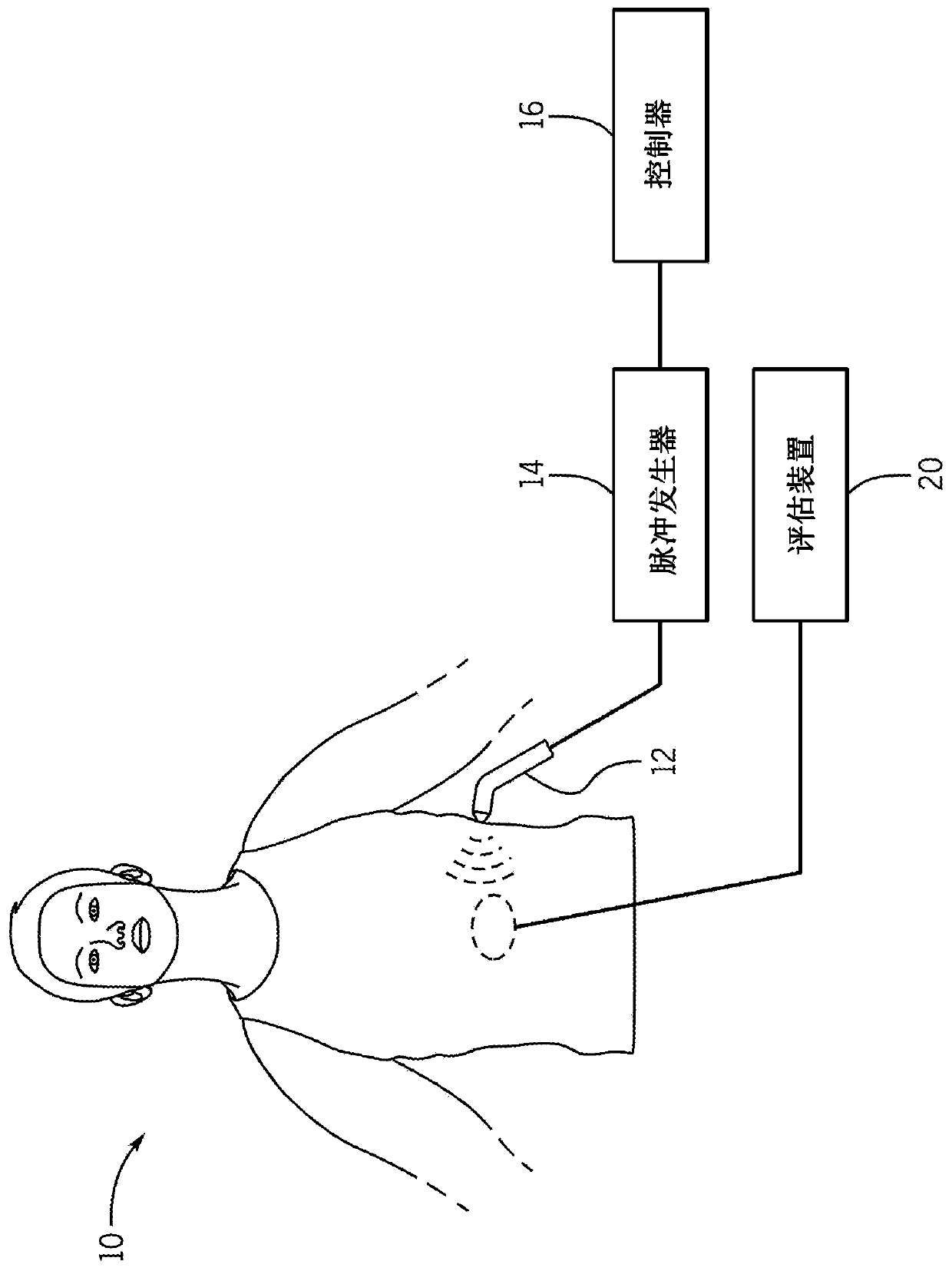
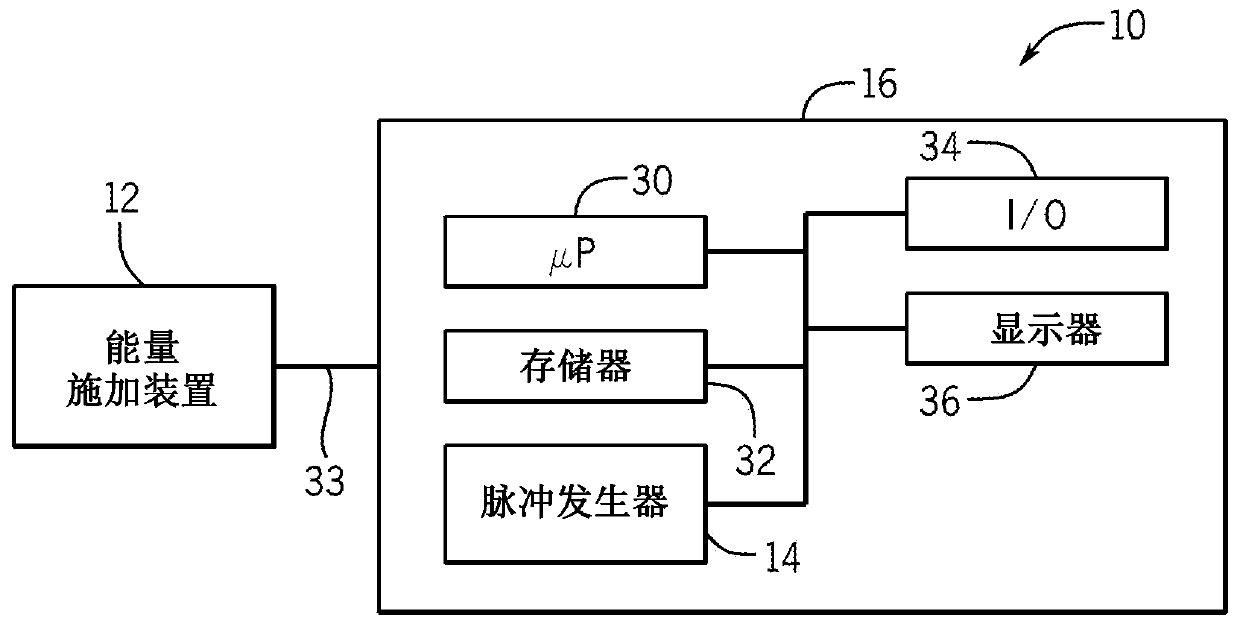
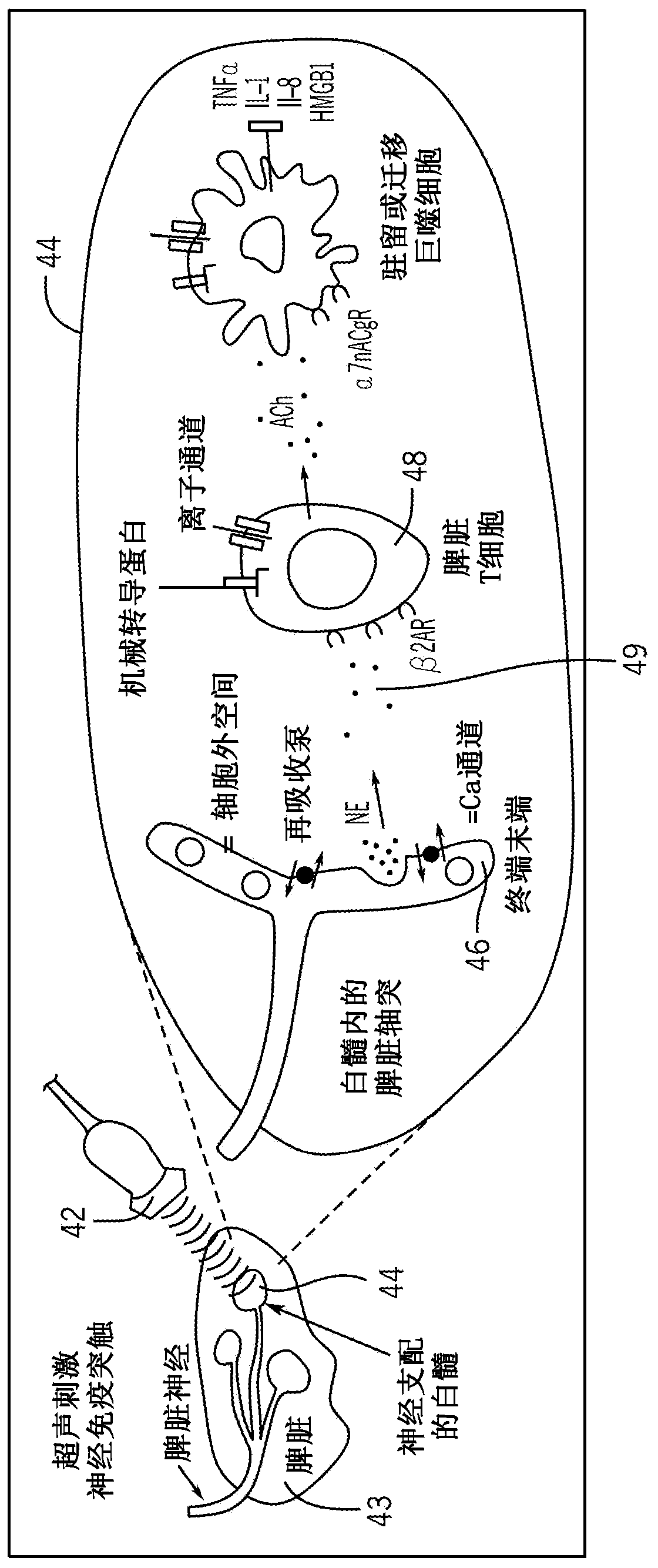
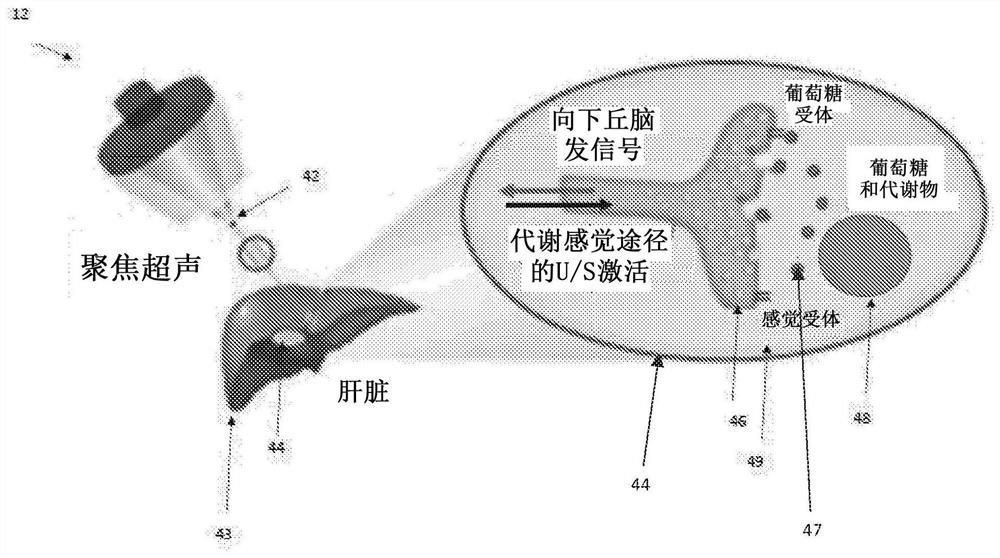
Techniques for neuromodulation
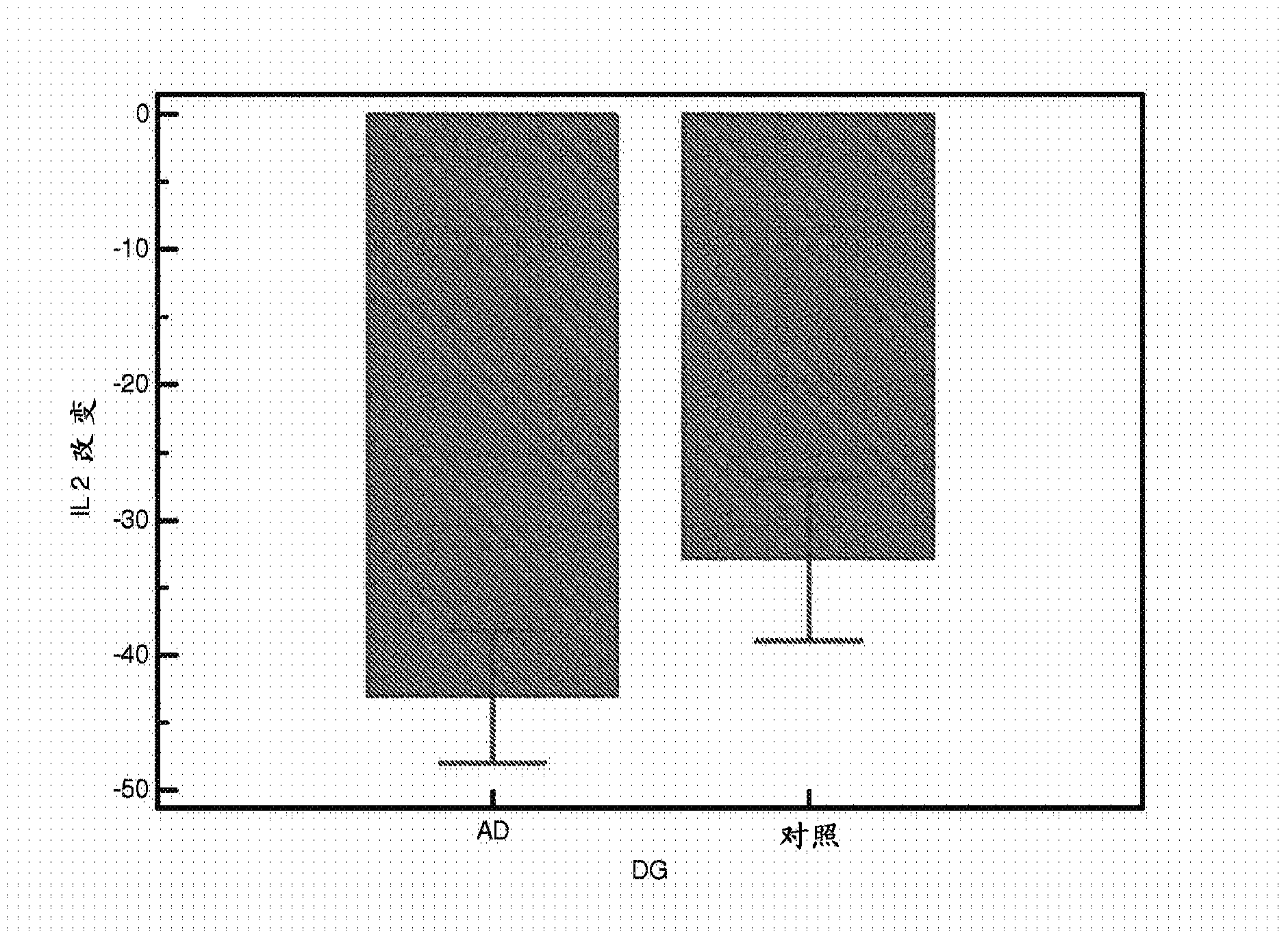
The subject matter of the present disclosure generally relates to techniques for neuromodulation of a tissue that include applying energy (e.g., ultrasound energy) into the tissue to cause altered activity at a synapse between a neuron and a non-neuronal cell.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
Diagnosis for Alzheimer's Disease
InactiveUS20140295425A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseTOR signaling pathway
The present invention relates to diagnosis and monitoring of Alzheimer's disease in the live subject. More particularly, the invention relates to methods involving the measurement of differential gene expression in non-neuronal cells taken from human subjects suspected of having Alzheimer's disease wherein the genes to be measured are genes within the m TOR signalling pathway.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BIRMINGHAM
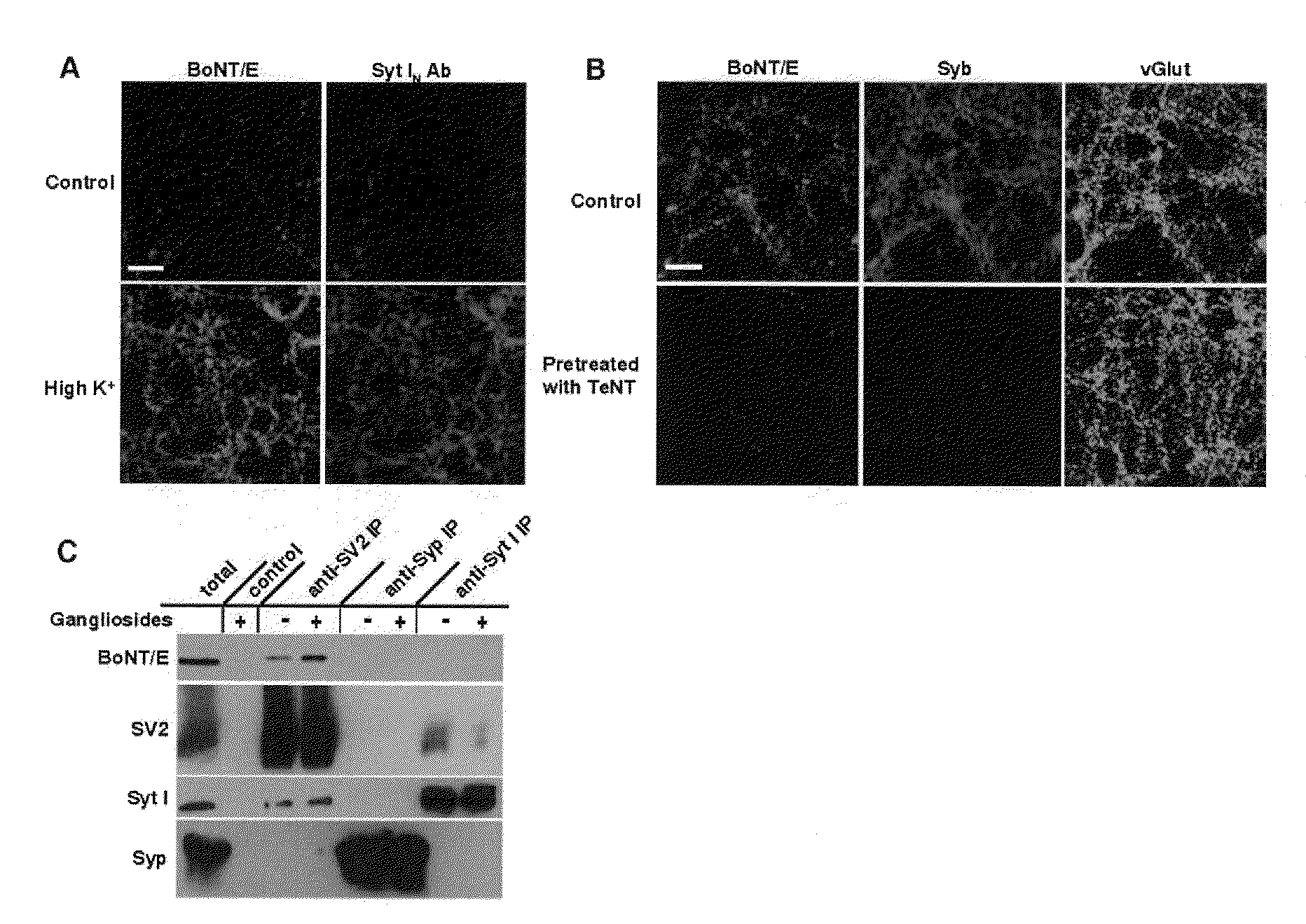
Botulinum neurotoxin E receptors and uses thereof
ActiveUS8771707B2Reduce sensitivityRestores the binding and entry of BoNT/ECompound screeningNervous disorderExocytosisReceptor
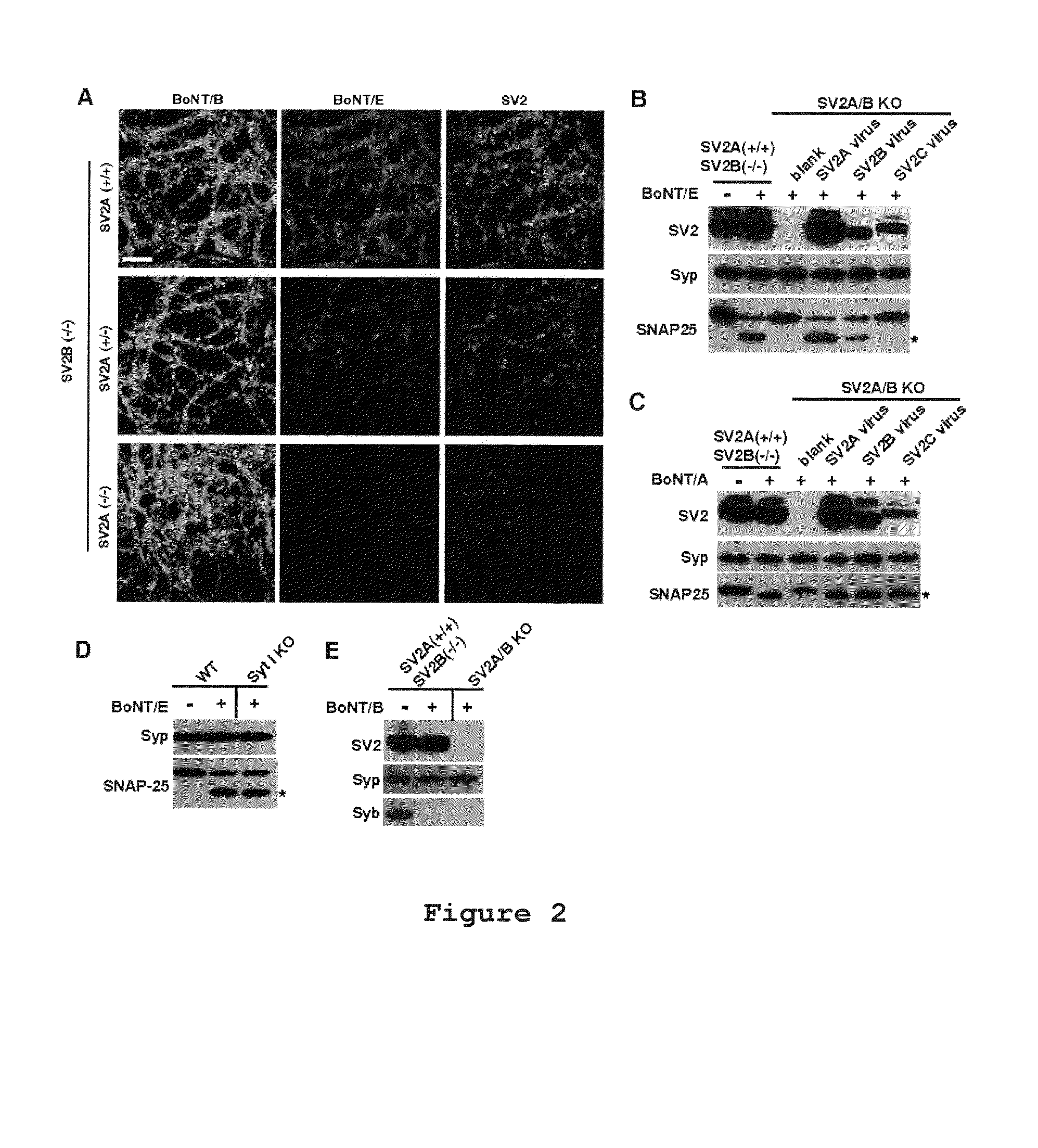
An isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence selected from amino acids 506-582 of SV2A, wherein position 573 is N and is glycosylated, or amino acids 449-525 of SV2B, wherein position 516 is N and is glycosylated. The present invention also provides an antibody that binds specifically to the polypeptide, an isolated nucleic acid comprising a polynucleotide that encodes the polypeptide; a method for reducing BoNT / E toxicity in an animal; a method for identifying an agent that blocks or inhibits binding between BoNT / E and an SV2A or SV2B protein; a method for monitoring synaptic vesicle endo- or exocytosis, a method for specifically delivering a chemical entity to a cell which has a specific receptor to a BoNT toxin. Also provided are a chimeric toxin for targeting a proteolytic domain of a toxin to a cell, the chimeric toxin comprising a catalytic or proteolytic domain of the BoNT toxin, and a ligand or a fragment thereof for a non-BoNT receptor on the cell; a method for targeting a proteolytic domain of a BoNT toxin to a cell, an isolated non-neuronal cell comprising a BoNT toxin receptor; and a method for screening for an inhibitor of a BoNT toxin.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for improving induced neuron generation
InactiveUS20160115447A1Improve survivalAvoid signalingNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsCell culture mediaCell type
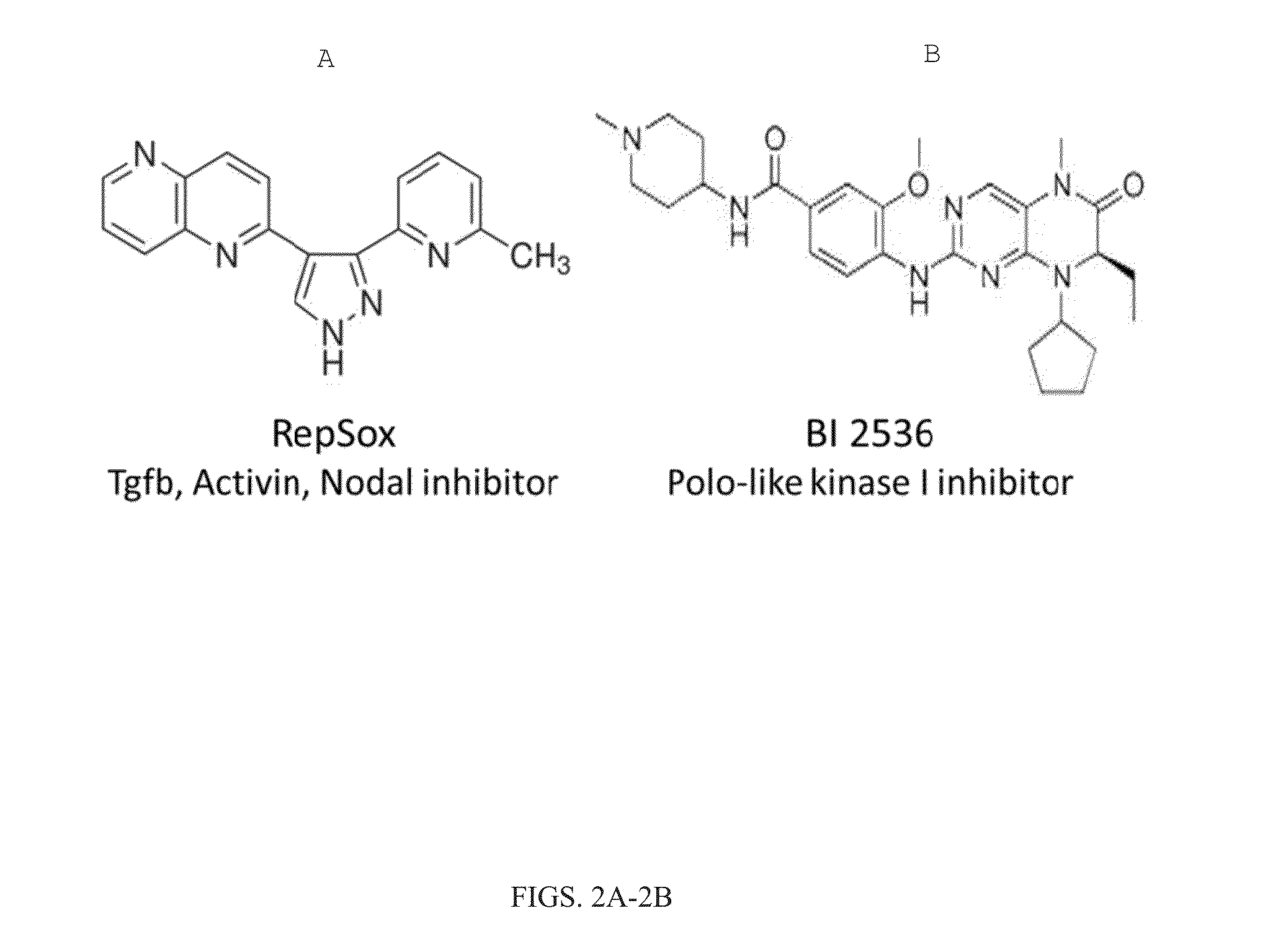
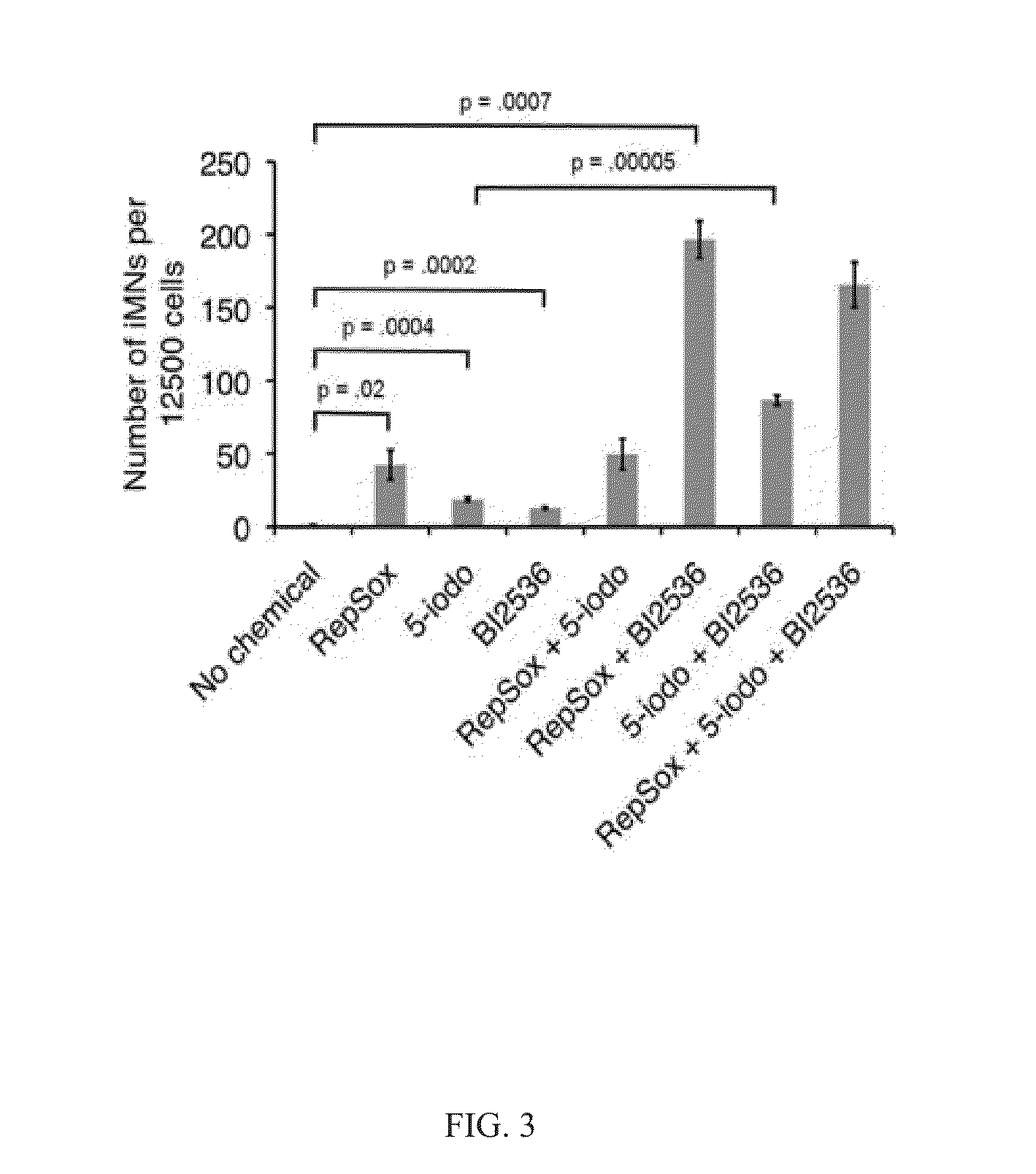
The present inventions relate to methods and compositions useful for improving the efficiency of inducing the generation of neurons from non-neuronal cell types, for example, by contacting the cell or cell culture medium with one or more agents which inhibit Activin and / or PLK1 signaling. Also disclosed are methods for promoting neuron survival, for example, by inhibiting Activin and / or PLK1 signaling, and methods for promoting the survival of intermediates in a cell differentiation pathway, for example, by inhibiting Activin and / or PLK1 signaling.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Conversion of non-neuronal cells into neurons
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for conversion of non-neuronal cells into neurons. The subject invention also concerns methods for screening drugs and other compounds for activity in treating Alzheimer's disease using neuronal cells produced using the subject invention. The subject invention also concerns neuronal cells that have been produced using the methods of the invention. The subject invention also concerns methods for evaluating therapeutic treatment for efficacy in a person or animal having Alzheimer's disease or other neurodegenerative diseases. The subject invention also concerns methods of treating Alzheimer's disease or other neurodegenerative diseases or conditions in a person or animal.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Neural crest stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060263876A1Treat and prevent and reduce diseaseCulture processNervous system cellsHeterologousDamages tissue
This present invention features methods and composition for the isolation and proliferation of neural crest stem cells (NCSCs) from embryonic tissues as well as from tissues from a post-natal mammal. According to this invention, NCSCs are capable of producing non-neuronal and neuronal cells under the appropriate conditions. The cells of the invention therefore provide an accessible source for autologous and heterologous transplantation into the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system, as well as other damaged tissues.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
Method for generating functional noradrenaline neurons through reprogramming
The invention relates to a method for generating functional noradrenaline neurons through reprogramming. According to the method, a plurality of transcription factors are overexpressed in non-neuronalcells, and differentiated somatic cells are induced into functional noradrenaline neurons in vitro. The noradrenaline neurons generated by the method disclosed by the invention can survive after being transplanted into a body, and can be used for developing medicines for preventing, improving or treating various nervous system diseases.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN BRAIN SCI & INTELLIGENCE TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
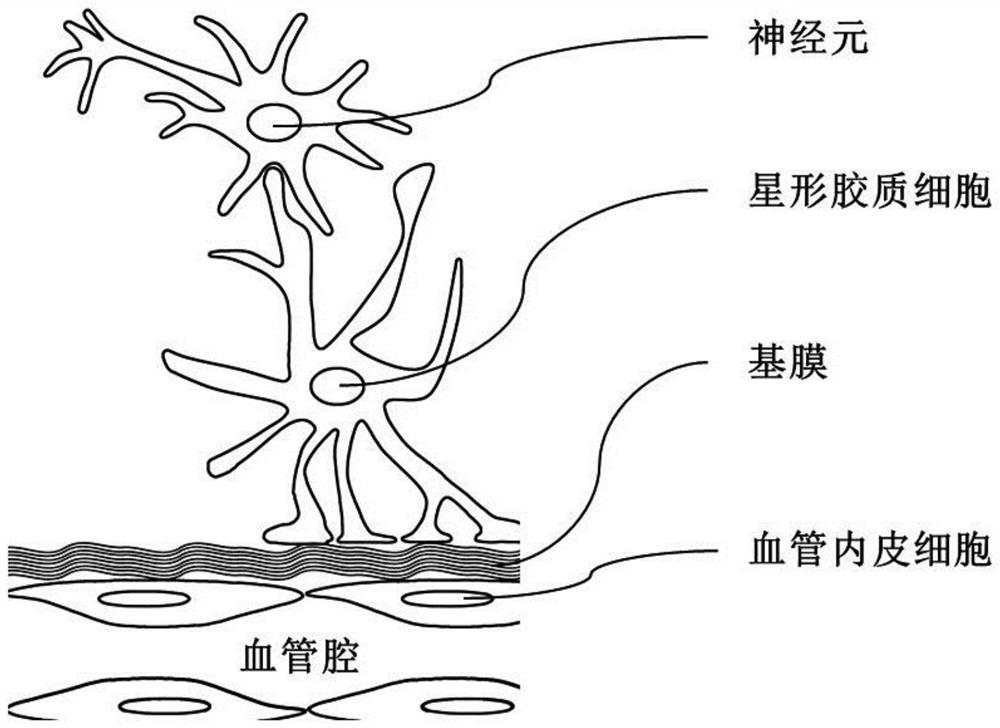
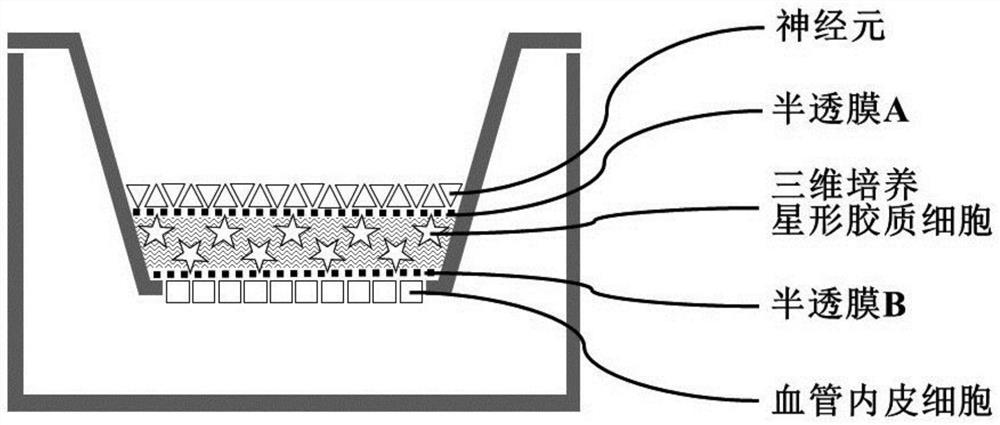
Bionic three-dimensional nerve blood vessel unit direct contact co-culture system and construction method thereof
PendingCN114480284AEffective simulationEasy to detectNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsVascular endotheliumBiochemistry
The invention discloses a bionic three-dimensional nerve blood vessel unit direct contact co-culture system which at least comprises neurons, semipermeable membranes, three-dimensional cultured astrocytes, semipermeable membranes and vascular endothelial cells, the three-dimensional cultured astrocytes are attached to the non-vascular endothelial cell side of a semipermeable membrane-vascular endothelial cell complex, and the semipermeable membrane-vascular endothelial cell complex is attached to the non-vascular endothelial cell side of the semipermeable membrane-vascular endothelial cell complex. And the semi-permeable membrane is attached to the non-neuron cell side of the semi-permeable membrane-neuron complex to form a direct contact co-culture system of vascular endothelial cells, three-dimensional culture astrocytes and neurons. The invention further discloses a construction method of the bionic three-dimensional nerve blood vessel unit direct contact co-culture system. According to the bionic three-dimensional nerve and blood vessel unit direct contact co-culture system and the construction and culture method thereof provided by the invention, physiological functions of blood brain barrier, nutrition coupling, electrophysiological coupling and the like of the nerve and blood vessel unit in vivo can be comprehensively and effectively simulated.
Owner:吕田明 +1
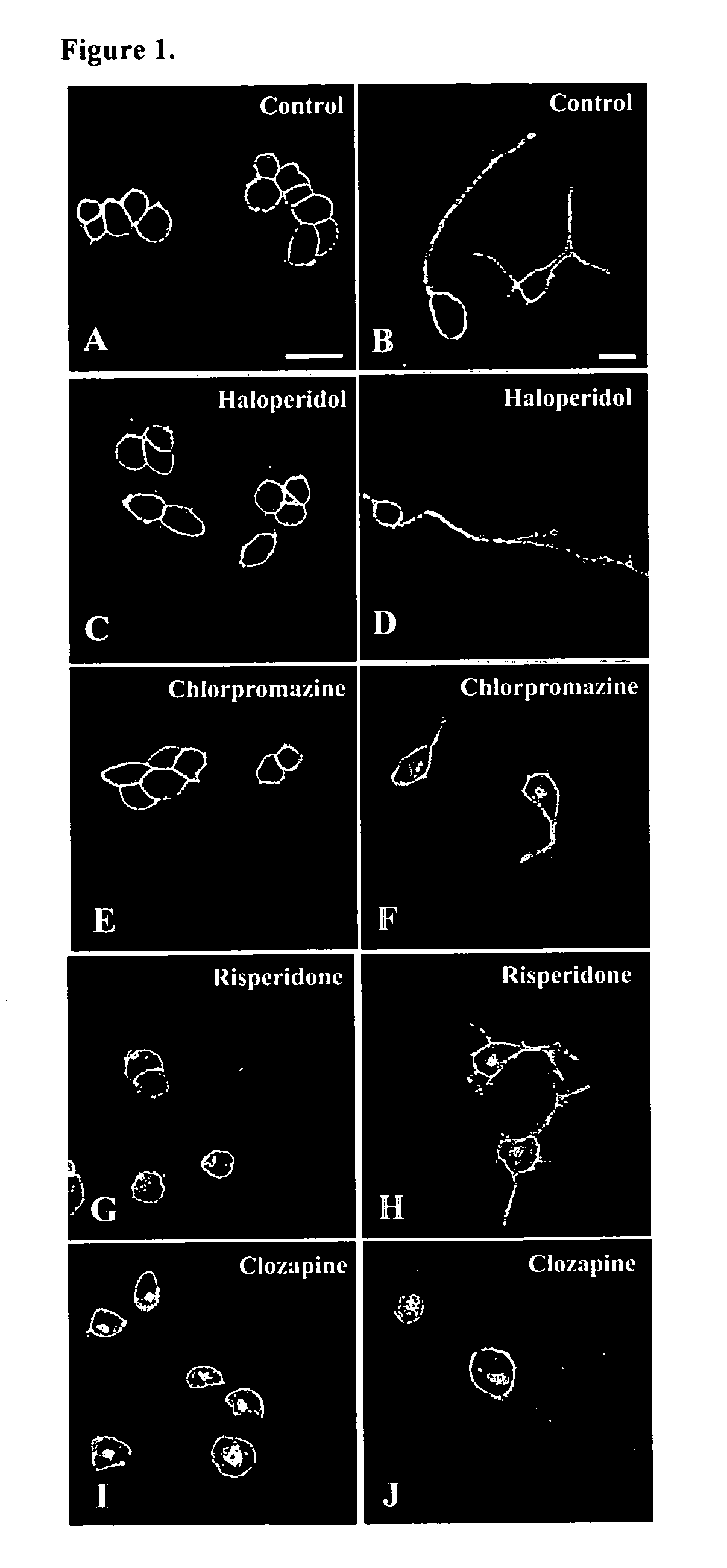
Novel assay for screening antipsychotic drugs
InactiveUS20060252103A1Easy to observeQuick and easy determinationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPsychosis drugSerotonin 2A Receptors
A novel assay method suitable for screening of novel antipsychotics wherein the drugs may be selected based on the differential internalization of the 5-HT2A receptor in neuronal and non-neuronal cell lines effect for it to predict the extrapyramidal symptoms that may be induced by an antipsychotic without having to carry out in vivo experiments.
Owner:TATA INSTITUTE OF FUNDAMENTAL RESEARCH
Biomarkers for the early detection of parkinson's disease
ActiveUS20190049466A1Reduce expressionReduce functionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAssayReticulum cell
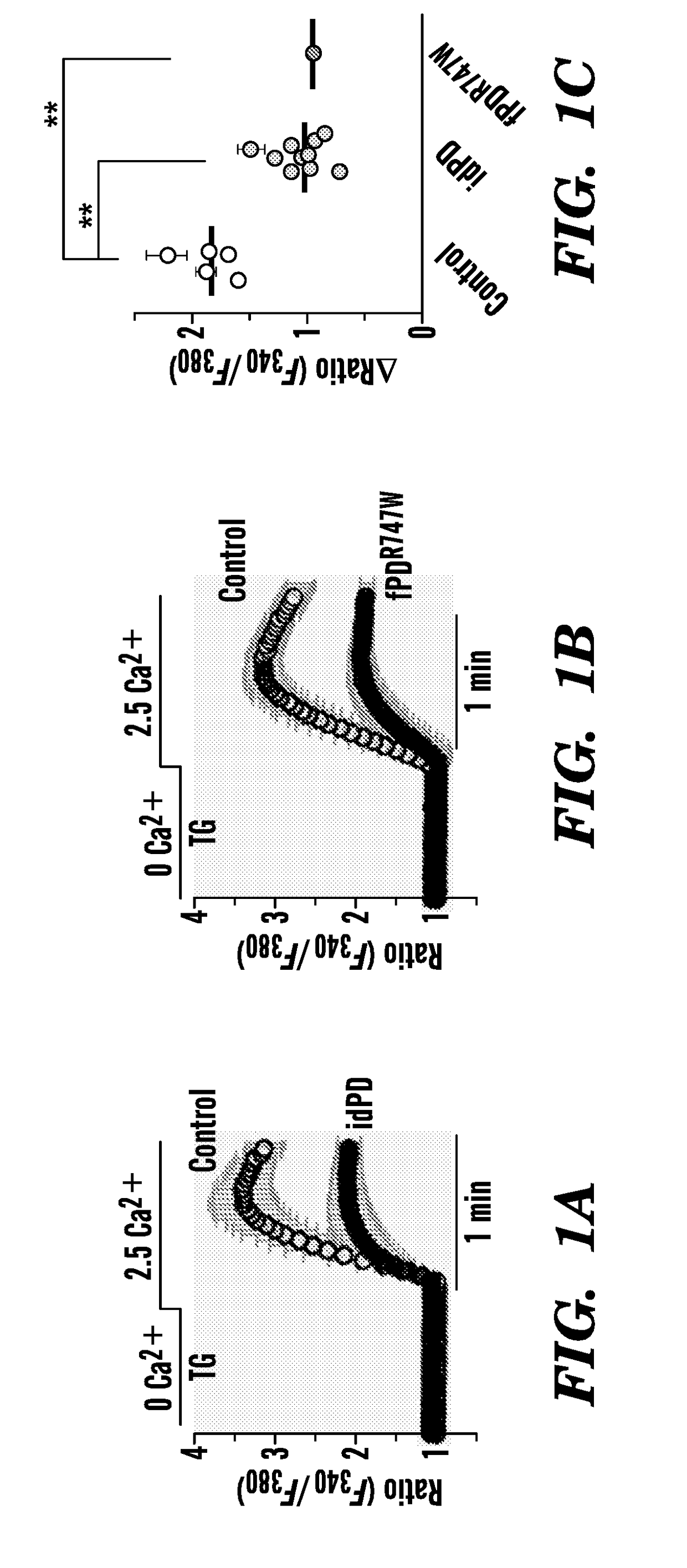
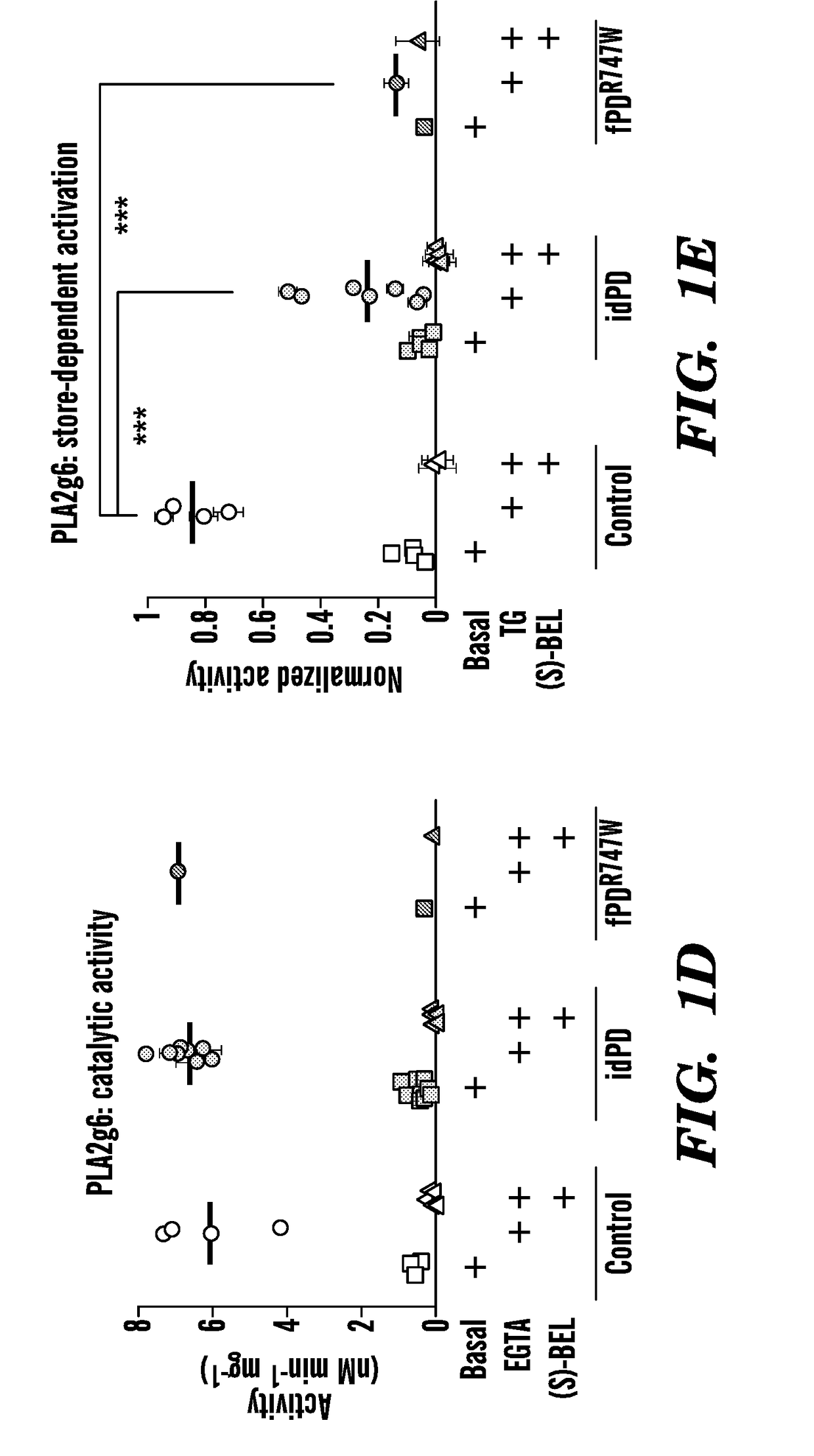
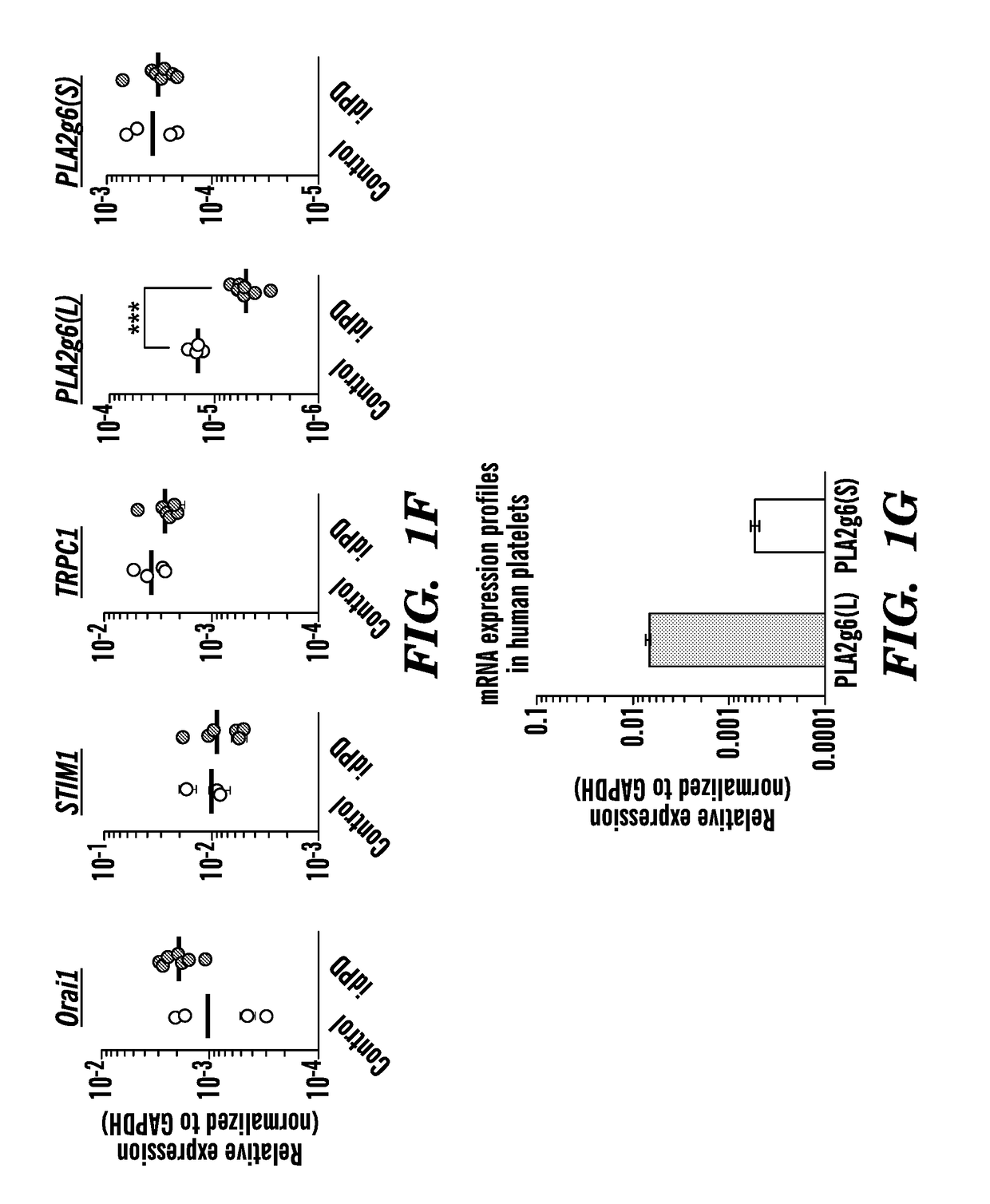
Disclosed are biomarkers for Parkinson's disease (PD), including idiopathic PD (idPD). The present invention relates generally to assays, kits, compositions, solid supports and methods that measure a decrease in the expression or function of PLA2g6(L) variant of PLA2g6 (PARK 14) gene in a sample from the subject, including non-neuronal cells as a biomarker for preclinical (prodromal) or early stage Parkinson's disease (PD) and idiopathic PD (idPD), as well as assays, kits, compositions and methods that can detect the functional consequences of decreased expression of PLA2g6(L), including decreased store operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE), deficit of Ca2+ in endoplasmic reticulum stores, and autophagic dysfunction in the cells obtained from the subjects in preclinical (prodromal) and early stage PD diagnosis and for monitoring Parkinson's Disease progression.
Owner:BOSTON MEDICAL CENTER INC
Techniques for neuromodulation
The subject matter of the present invention generally relates to techniques for neuromodulation of a tissue that include applying energy (e.g., ultrasound energy) into the tissue to cause altered activity at a synapse between a neuron and a non-neuronal cell.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
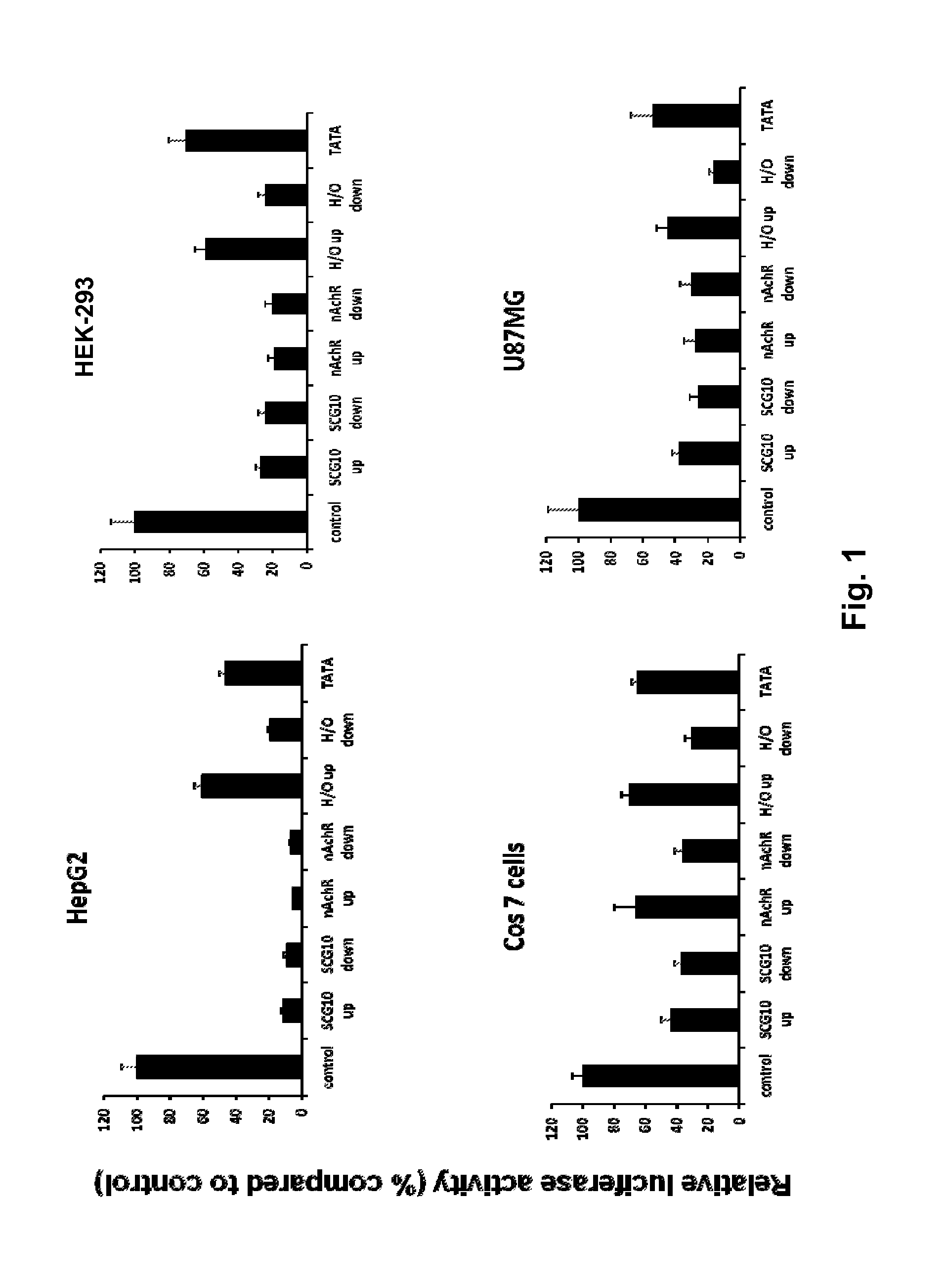
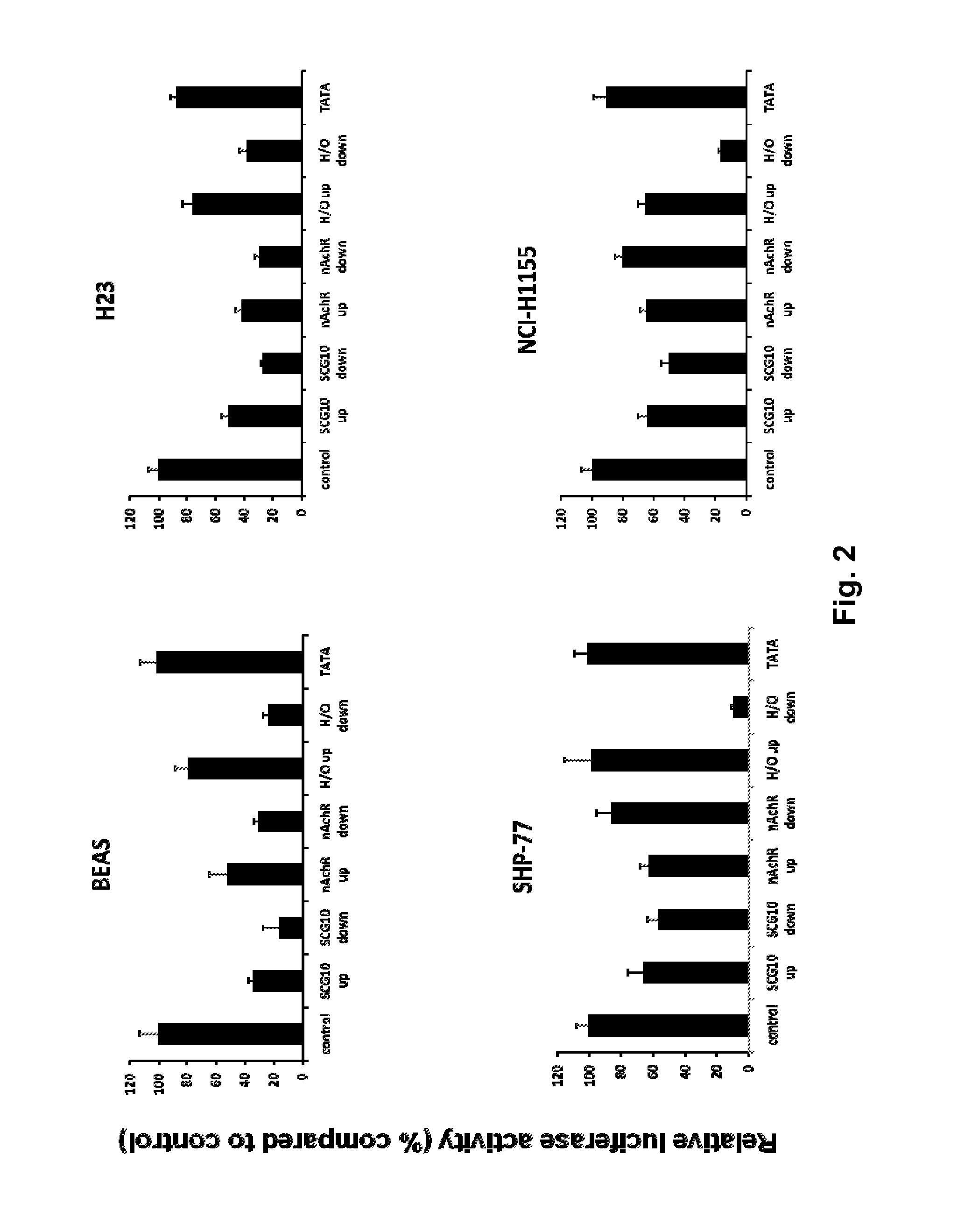
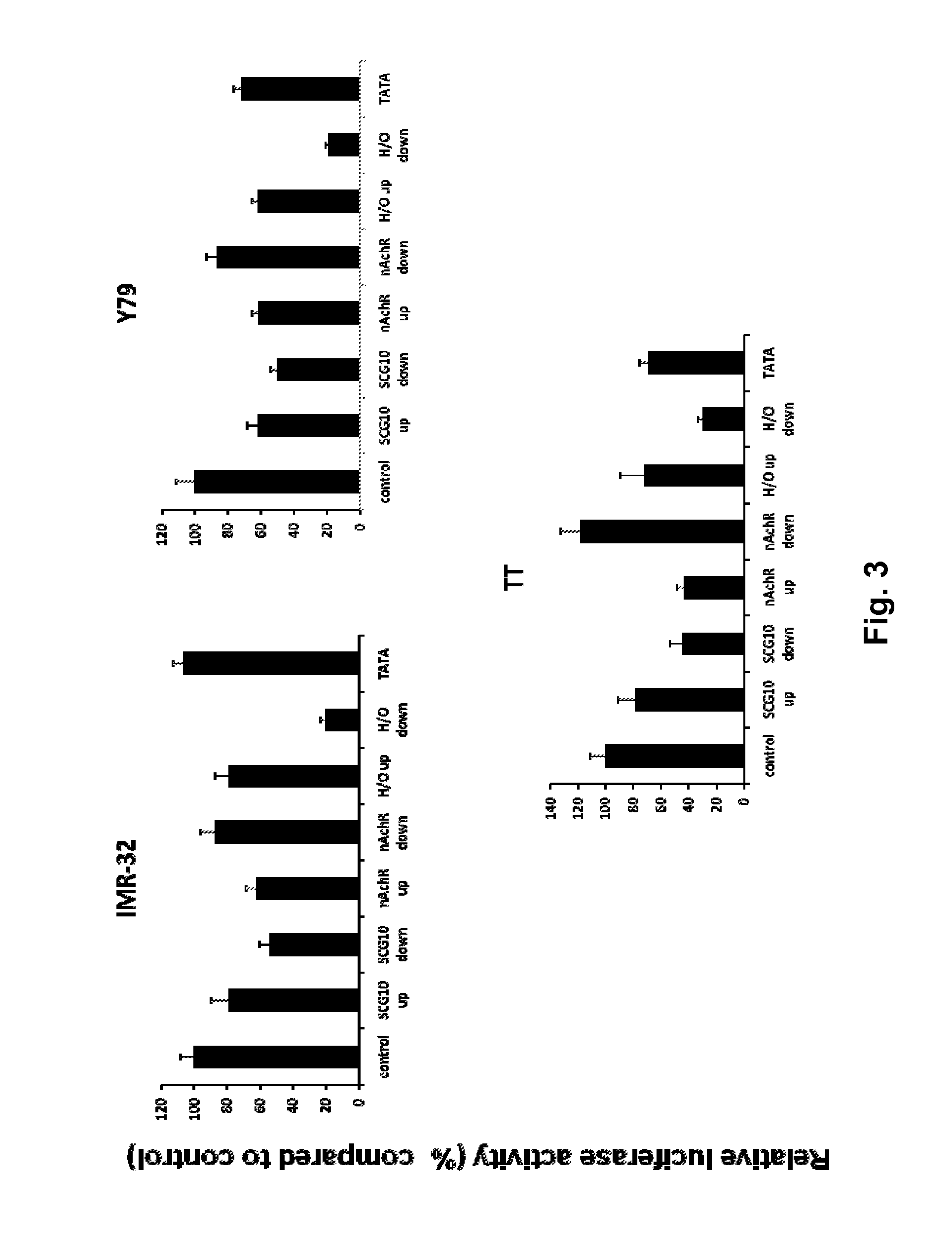
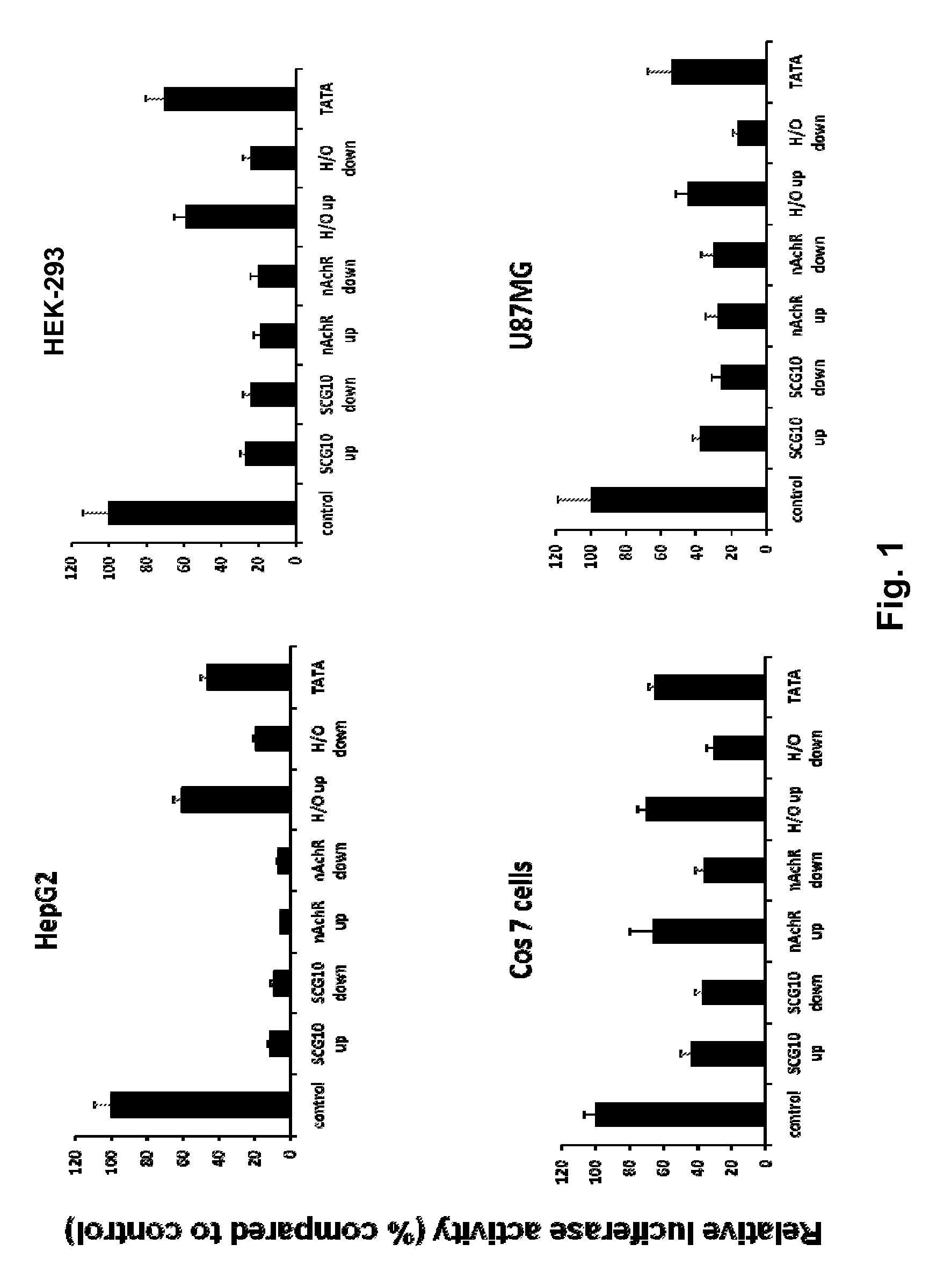
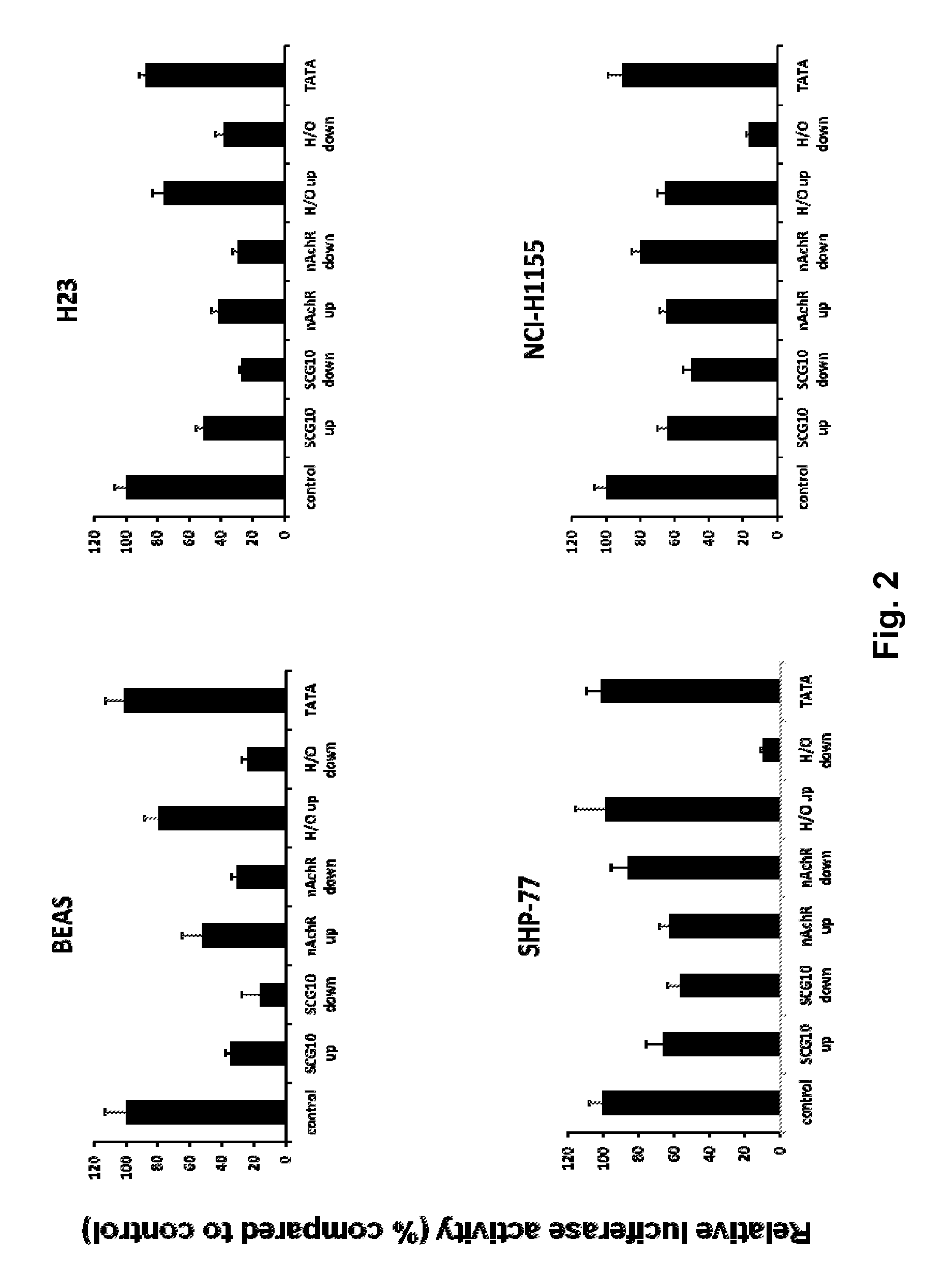
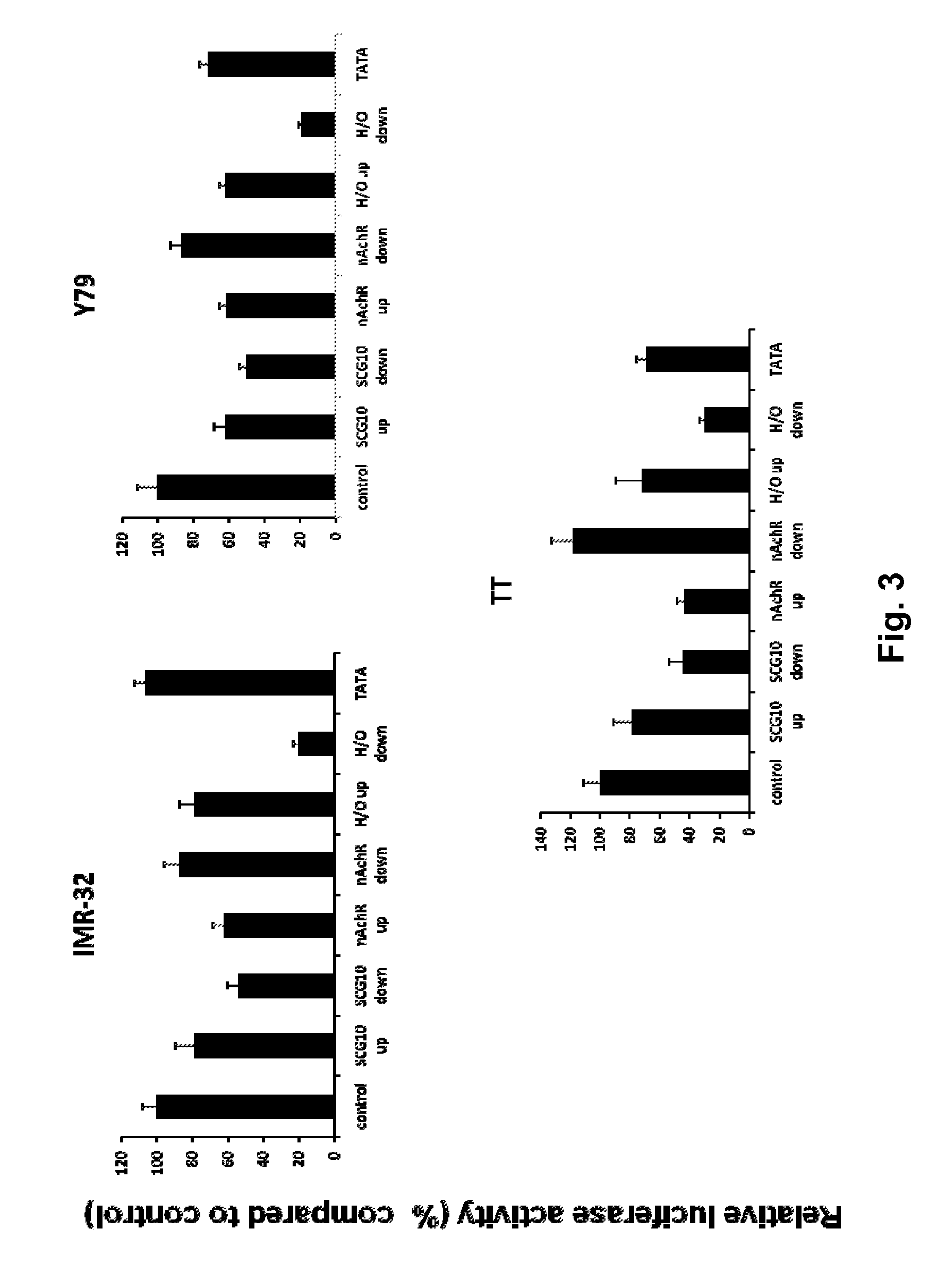
Modified INSM1-Promoter for Neuroendocrine Tumor Therapy and Diagnostics
ActiveUS20120316225A1Improve effectiveness and safetyImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPromoter activityTumor therapy
A modification of the existing INSM1 promoter region has been discovered that incorporated DNA elements that silence expression of neuronal genes in non-neuronal cells and that has increased the effectiveness and safety of using the INSM1 promoter for tumor treatment. One modification was addition of one or two tandem copies of neuronal restrictive silencer elements (NRSEs) derived either from the mouse nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) or the rat superior cervical ganglion 10 (SCG10) promoters. These NRSEs were placed in the expression construct either directly upstream or downstream of the INSM1 promoter sequence. The most effective expression construct was the nAChR NRSE element positioned downstream of the INSM1 promoter. This expression construct increased the tissue specificity of the INSM1 promoter without a significant decrease in its activity. In addition, the modified INSM1 promoter was placed into a viral vector, adenovirus 5. Constructs with an insulator element, the chicken HS4 β-globin insulator element, with the INSM1 promoter was shown to decrease the interference of the viral genome on its expression. Constructs have been made that do not decrease the INSM1 promoter activity but significantly augment the tumor specificity of the promoter. Linking the construct to a reporter gene allowed for detection of the placement of the viral vector, and this detection can be used for diagnosing or locating neuroendocrine tumors.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Ultrasound neuromodulation techniques
The subject matter of the present disclosure generally relates to techniques for neuromodulation of a tissue that include applying energy (e.g., ultrasound energy) into the tissue to cause altered activity at a synapse between a neuron and a non-neuronal cell. In one embodiment, the energy is applied to cause persistent effects as a result of repeated application of energy within a predefined treatment window.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Botulinum neurotoxin e receptors and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100104560A1Reduce sensitivityRestores the binding and entry of BoNT/ECompound screeningNervous disorderExocytosisNucleotide
An isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence selected from amino acids 506-582 of SV2A, wherein position 573 is N and is glycosylated, or amino acids 449-525 of SV2B, wherein position 516 is N and is glycosylated. The present invention also provides an antibody that binds specifically to the polypeptide, an isolated nucleic acid comprising a polynucleotide that encodes the polypeptide; a method for reducing BoNT / E toxicity in an animal; a method for identifying an agent that blocks or inhibits binding between BoNT / E and an SV2A or SV2B protein; a method for monitoring synaptic vesicle endo- or exocytosis, a method for specifically delivering a chemical entity to a cell which has a specific receptor to a BoNT toxin. Also provided are a chimeric toxin for targeting a proteolytic domain of a toxin to a cell, the chimeric toxin comprising a catalytic or proteolytic domain of the BoNT toxin, and a ligand or a fragment thereof for a non-BoNT receptor on the cell; a method for targeting a proteolytic domain of a BoNT toxin to a cell, an isolated non-neuronal cell comprising a BoNT toxin receptor; and a method for screening for an inhibitor of a BoNT toxin.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for assessment of neural function by establishing analysis module
ActiveUS20160266101A1Quick analysisQuick checkCompound screeningApoptosis detectionImaging analysisCultured cell
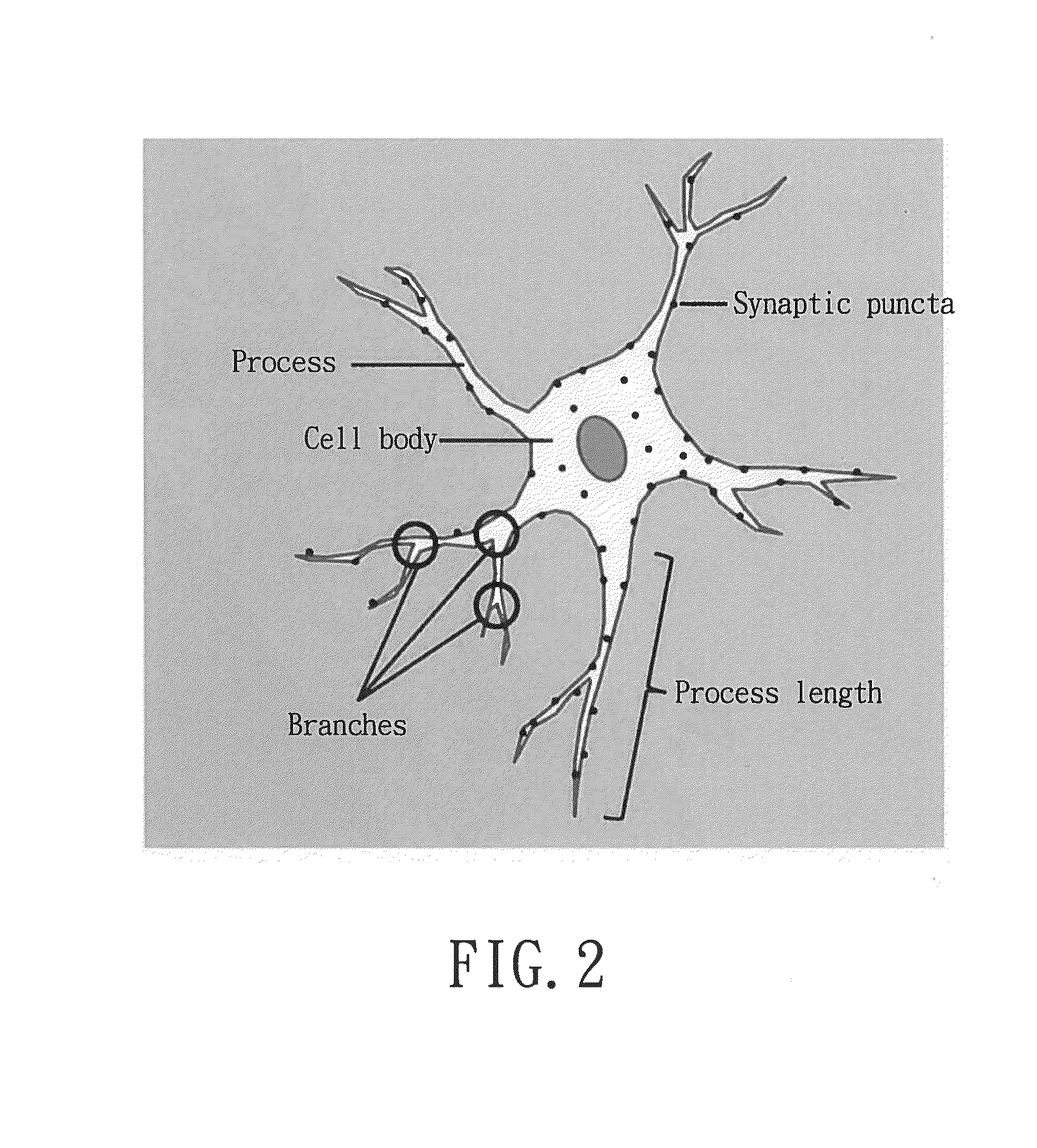
A method for assessment of neural function by establishing an analysis module is revealed. The first step of the method is to capture images of the cultured cells with a plurality of fluorescence labeling by a fluorescence microscopy system for image analysis. The cultured cells include neurons and non-neuronal cells. Then select neurons with neurites having fluorescence labeling and exclude non-neuronal cells according to an area and a fluorescence intensity of nucleus. Also calculate an area of the neuronal cell body, a length of the neurites and a number of processes and branches to verify outgrowth of the neurites of the neurons. Next calculate a number of synaptic puncta having fluorescence labeling on the area of the neurites having fluorescence labeling defined in Step 2 to verify formation of the synaptic puncta of the neurons for assessment of neural function.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV +1
Methods and compositions related to induced sensory neurons
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
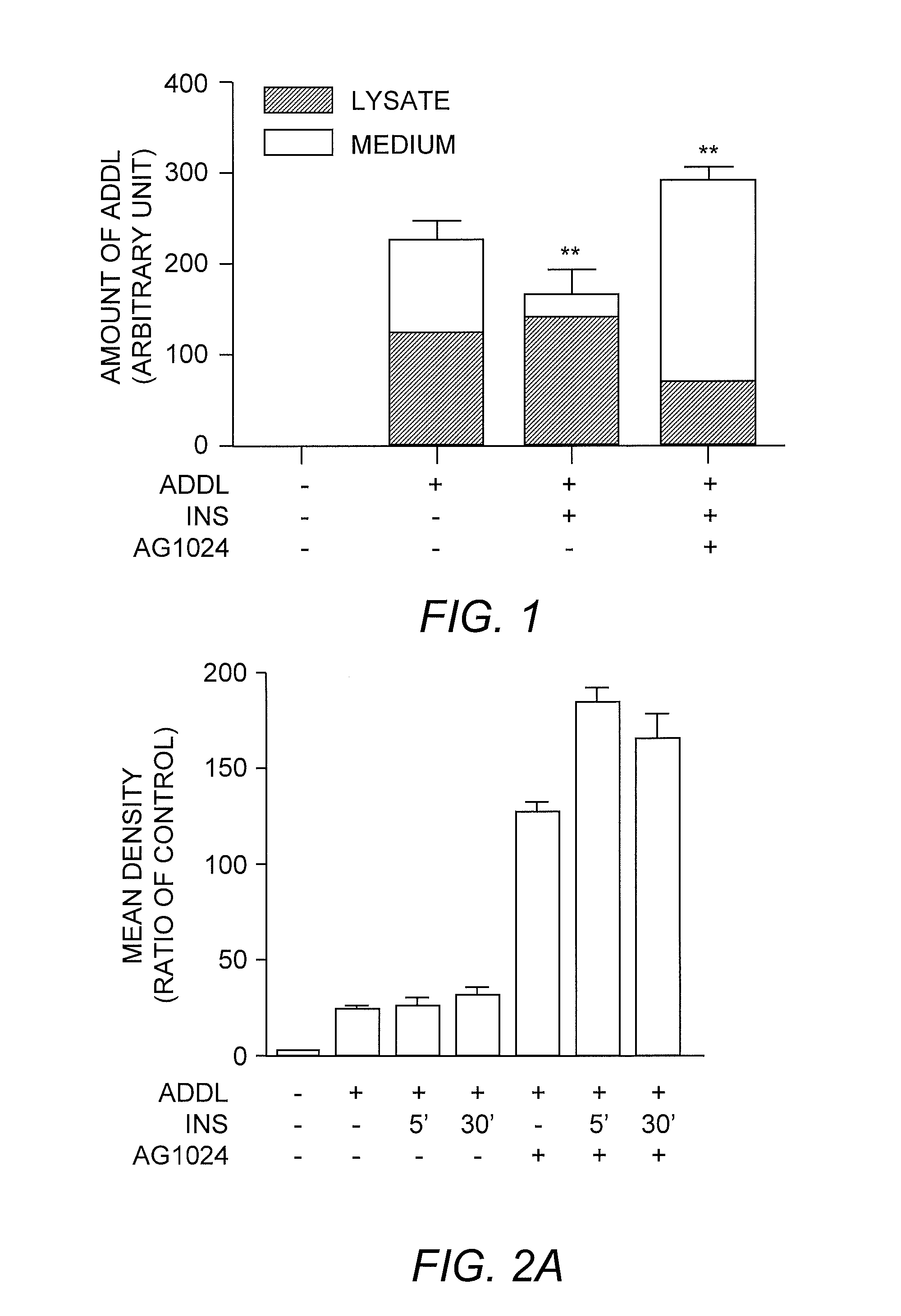
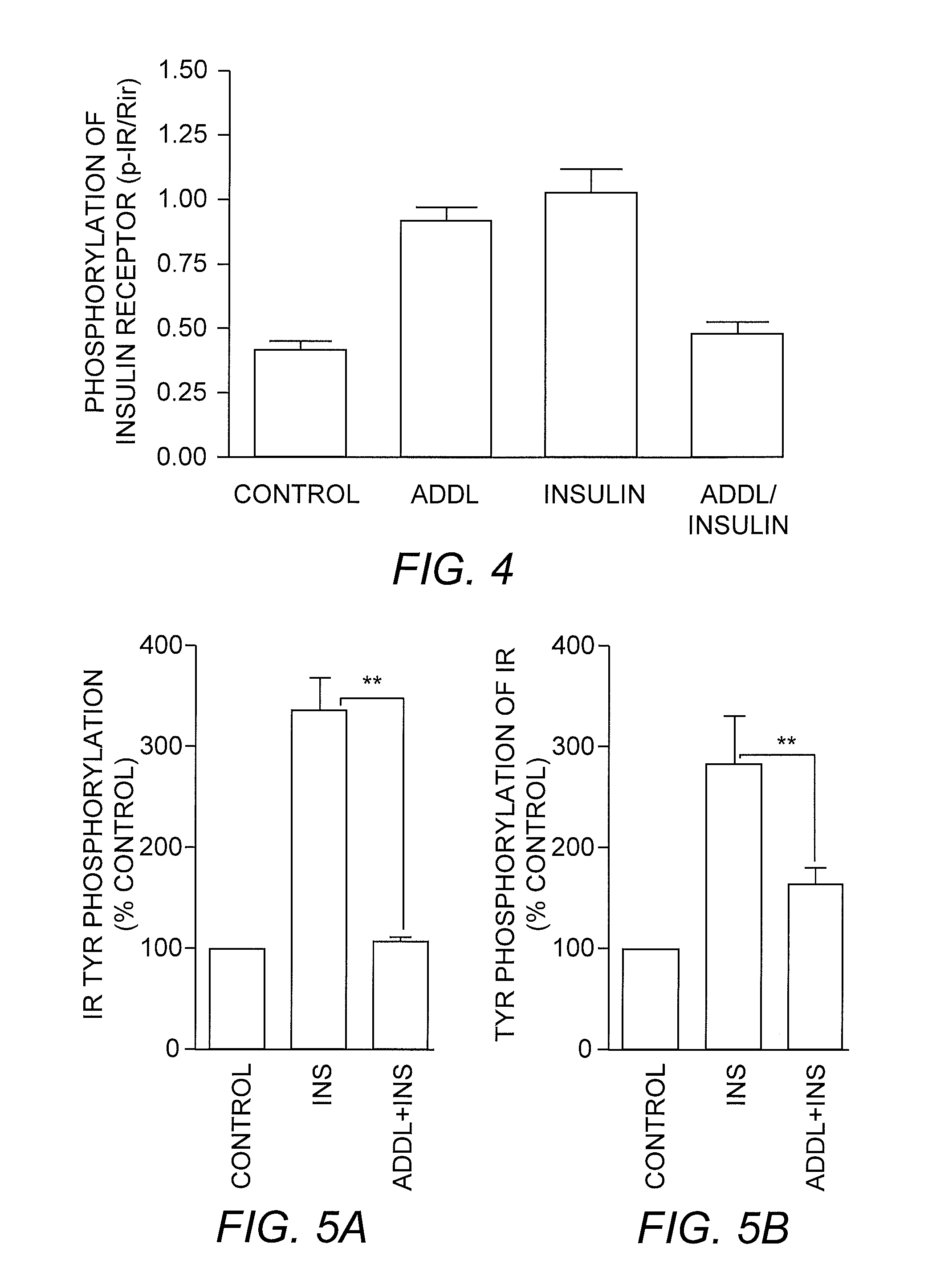
Compositions and methods for the enhancement of soluble amyloid beta oligomer (ADDL) uptake and clearance
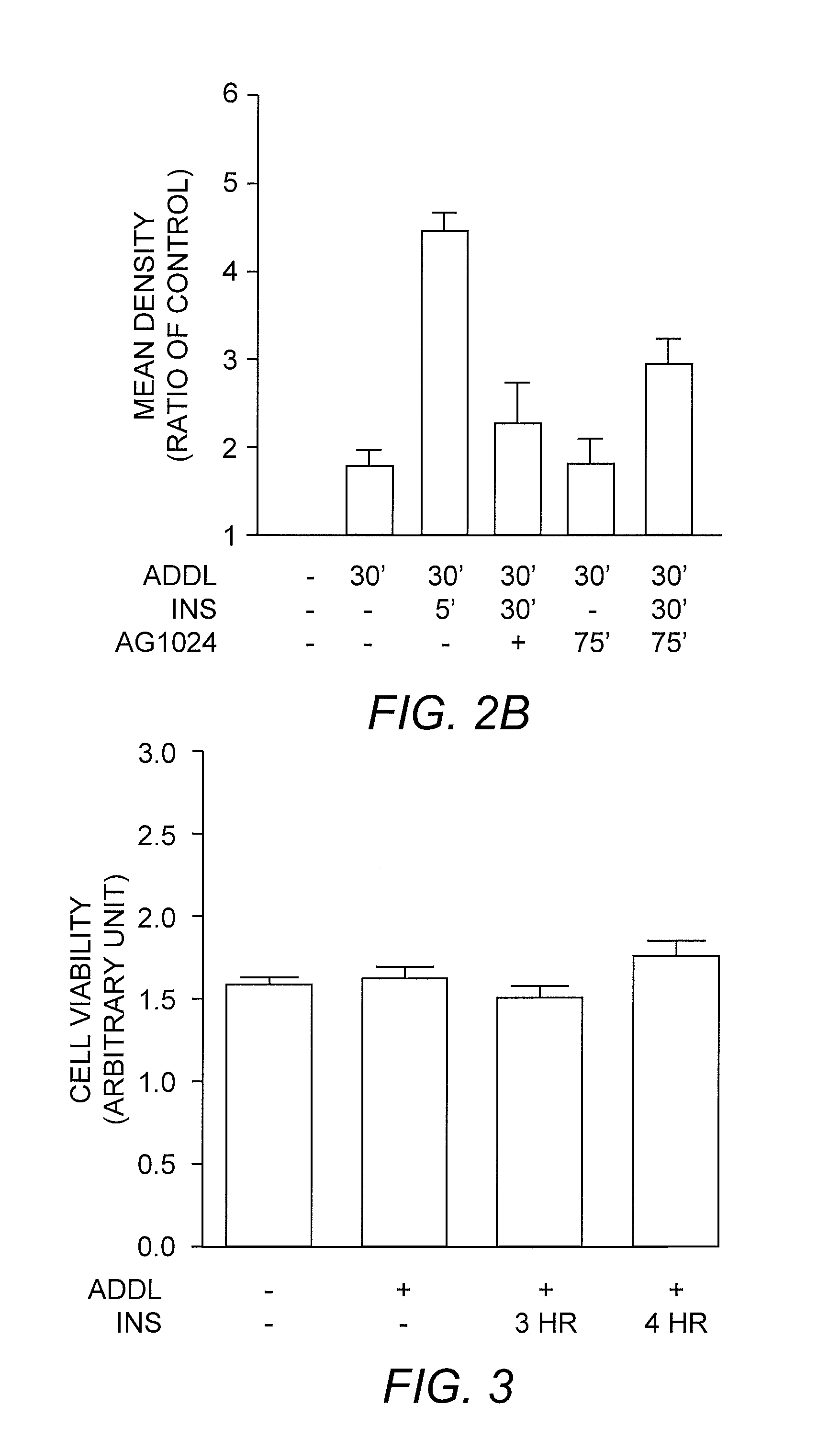
ActiveUS20070264669A1Enhancing cellular uptakeEnhances insulin receptor signalingCompound screeningNervous disorderProphylactic treatmentTherapeutic treatment
The present invention relates to methods for enhancing the cellular uptake and clearance of soluble oligomeric Aβ peptide assemblies from the environment surrounding both neuronal and non-neuronal cells. Oligomeric Aβ peptide assembly uptake and clearance is achieved via an agent that enhances insulin receptor signaling. Such ADDL uptake enhancers represent effective anti-ADDL therapeutics for use in the therapeutic treatment and / or prophylactic treatment of diseases including Alzheimer's disease, Down's syndrome, and the like, in which compromised nerve cell function is linked to the formation and / or the activity of soluble oligomeric Aβ peptide assemblies, also known as ADDLs, and ADDL-related assemblies.
Owner:ACUMEN PHARMA +1
Modified INSM1-promoter for neuroendocrine tumor therapy and diagnostics
ActiveUS9090907B2Improve effectiveness and safetyImprove securityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsPromoter activityTumor therapy
A modification of the existing INSM1 promoter region has been discovered that incorporated DNA elements that silence expression of neuronal genes in non-neuronal cells and that has increased the effectiveness and safety of using the INSM1 promoter for tumor treatment. One modification was addition of one or two tandem copies of neuronal restrictive silencer elements (NRSEs) derived either from the mouse nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) or the rat superior cervical ganglion 10 (SCG10) promoters. These NRSEs were placed in the expression construct either directly upstream or downstream of the INSM1 promoter sequence. The most effective expression construct was the nAChR NRSE element positioned downstream of the INSM1 promoter. This expression construct increased the tissue specificity of the INSM1 promoter without a significant decrease in its activity. In addition, the modified INSM1 promoter was placed into a viral vector, adenovirus 5. Constructs with an insulator element, the chicken HS4 β-globin insulator element, with the INSM1 promoter was shown to decrease the interference of the viral genome on its expression. Constructs have been made that do not decrease the INSM1 promoter activity but significantly augment the tumor specificity of the promoter. Linking the construct to a reporter gene allowed for detection of the placement of the viral vector, and this detection can be used for diagnosing or locating neuroendocrine tumors.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
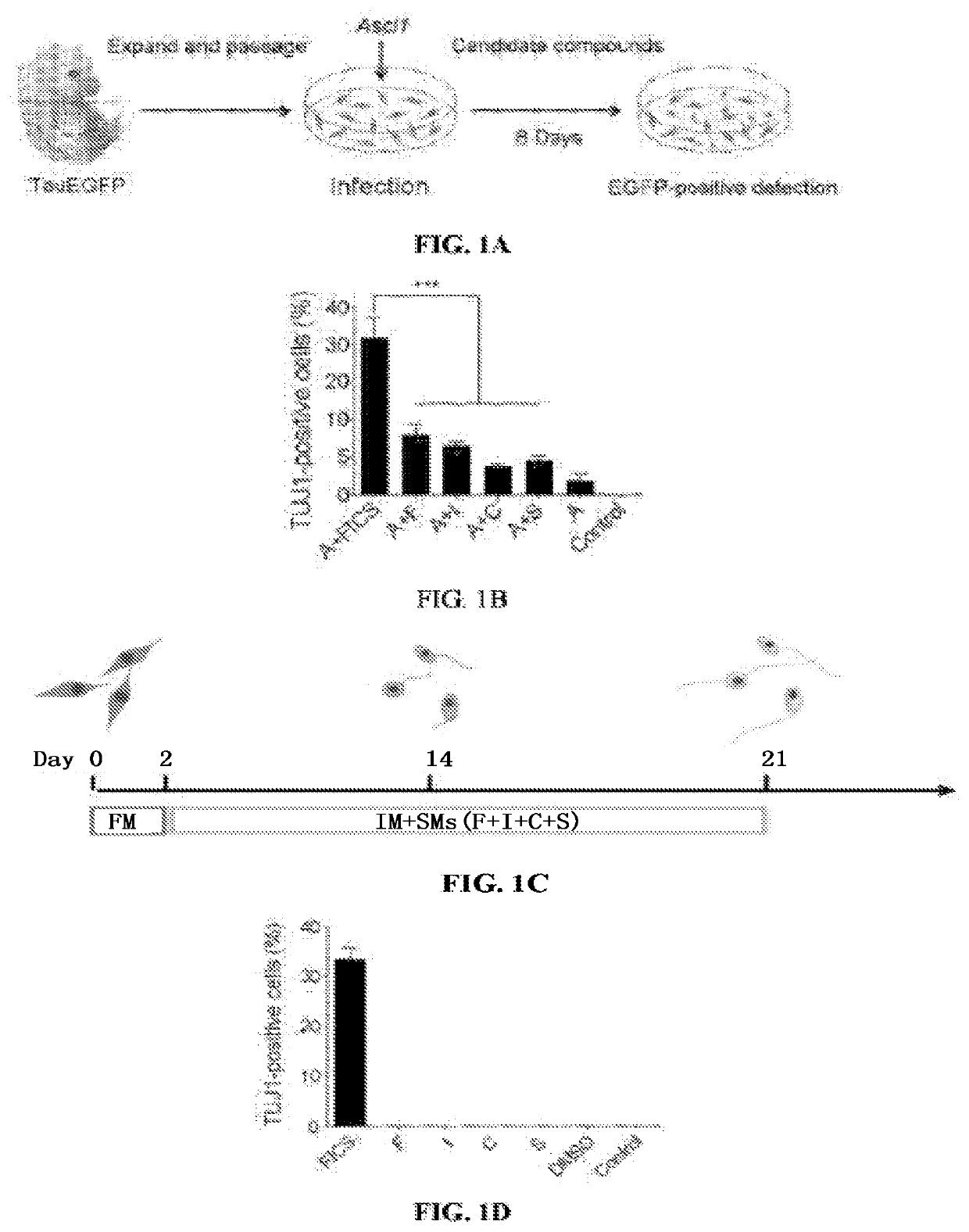
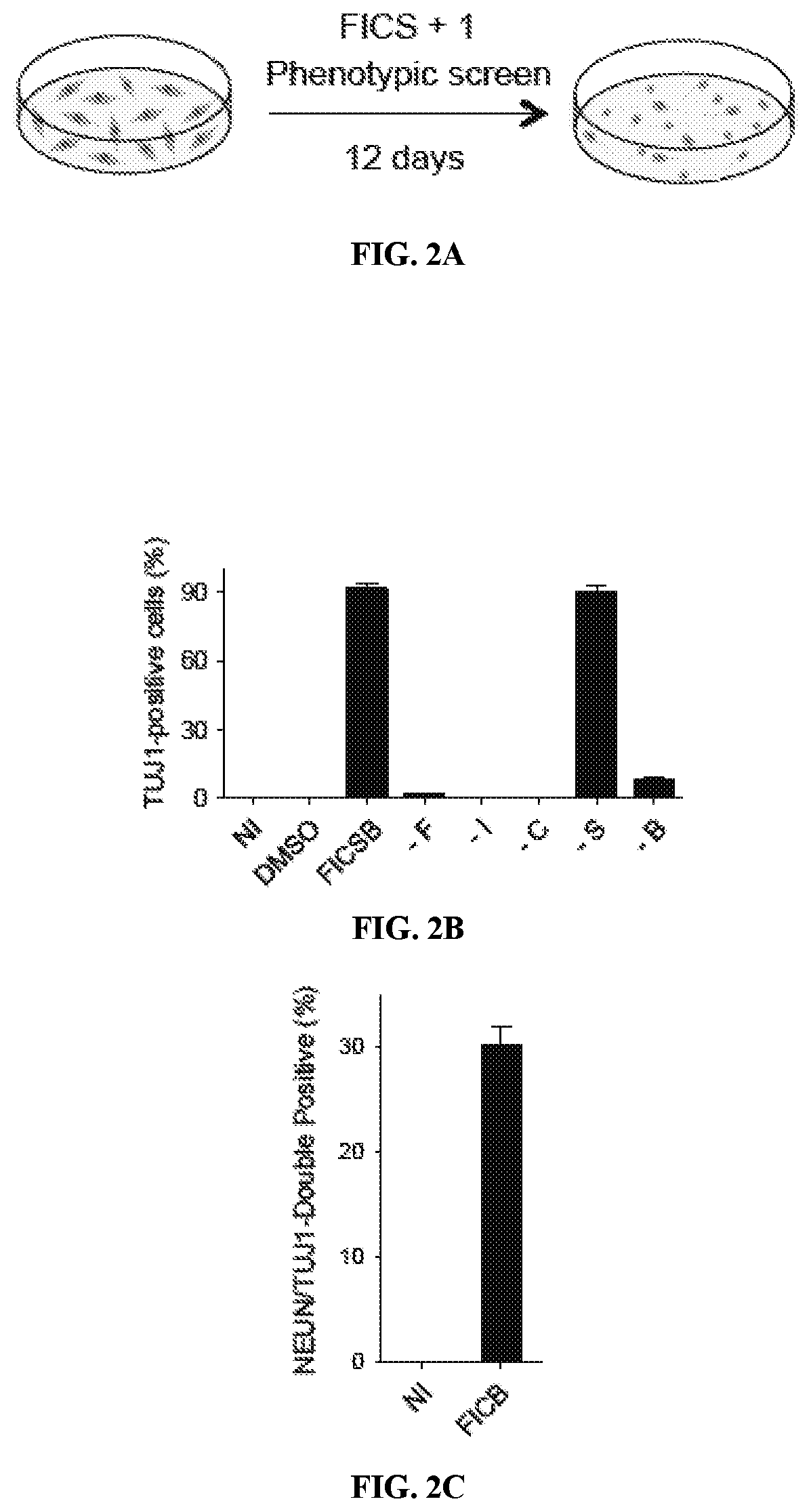
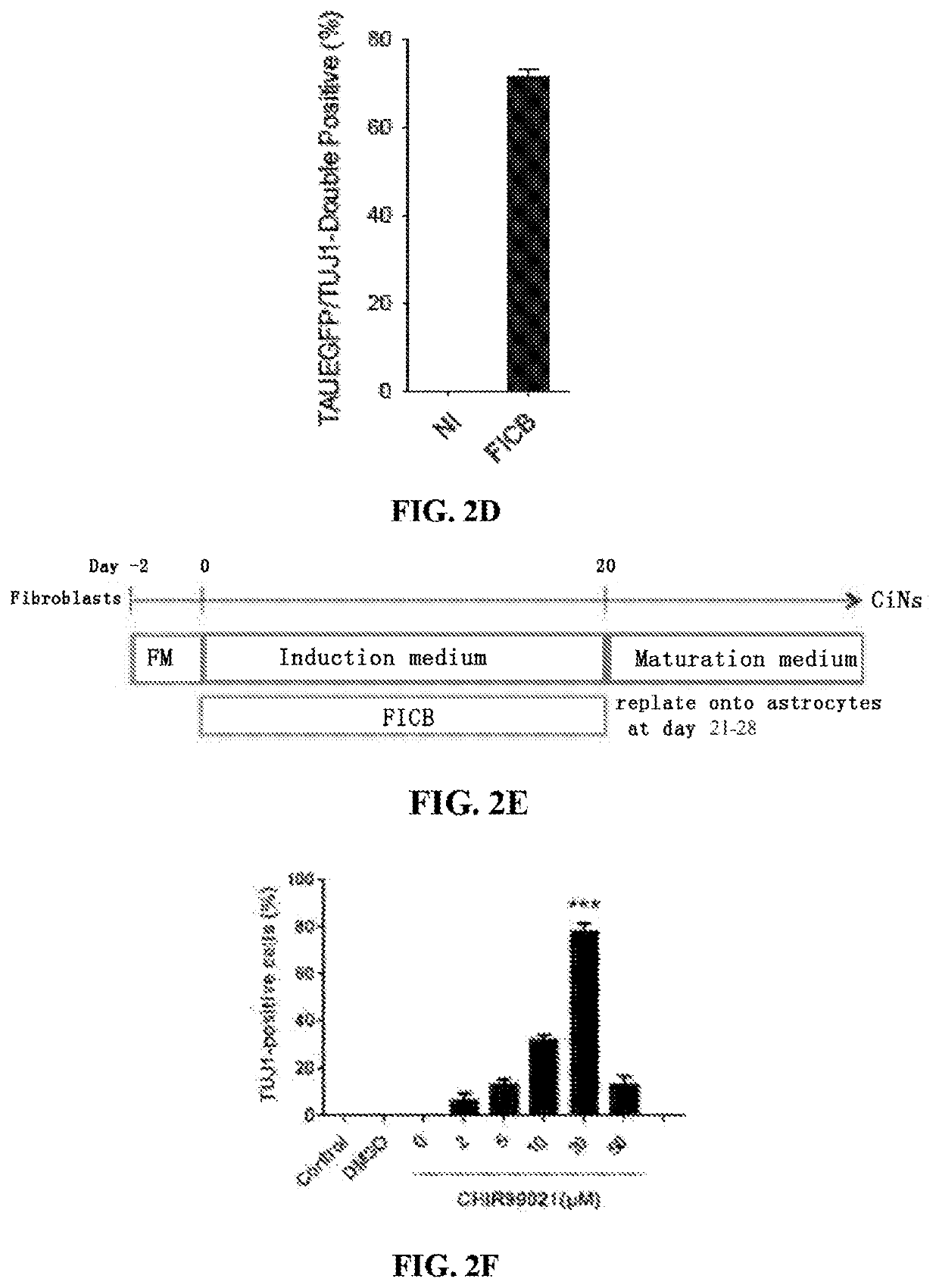
Compositions and methods for reprogramming non-neuronal cells into neuron-like cells
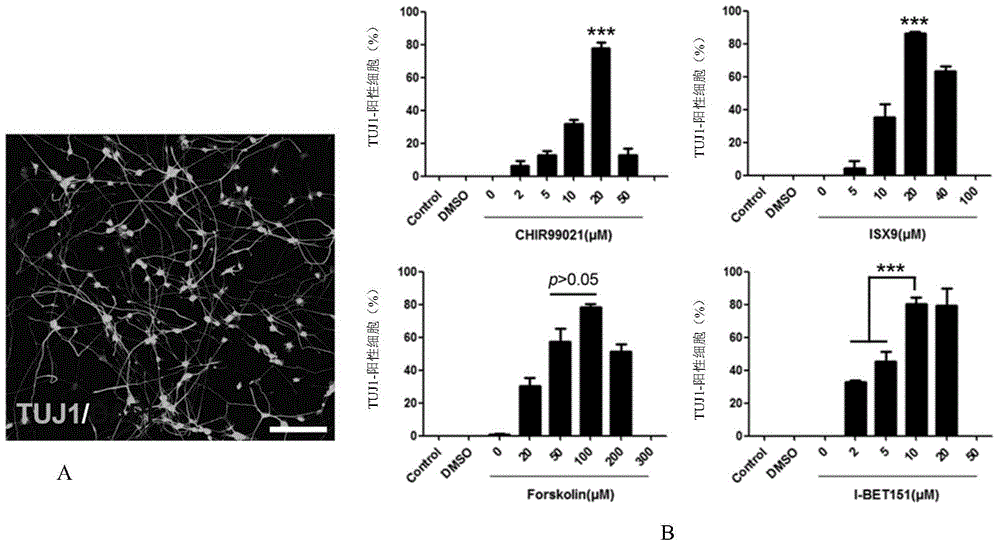
Cocktails of chemical inducers of neuron-like properties (CINP) is provided, which includes cAMP agonists, neurogenic small molecules, glycogen synthase kinase inhibitors, TGFβ receptor inhibitors, and BET family bromodomain inhibitors and optionally, a selective inhibitor of ROCK or p38 MAPK. These cocktails are used in a method of inducing neuron-like properties in partially or completely differentiated non-neuronal cells. The method includes contacting cells of a first type (non-neuronal) with the CINPs for a sufficient period of time to result in reprogramming the cell into cells of a second type having neuron-like characteristics (CiNs). Isolated chemically induced neurons (CiNs) can be used in a number of applications, including but not limited to cell therapy.
Owner:BEIHAO STEM CELL & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST CO LTD +1
A cell co-culture method for the analysis of synapse formation
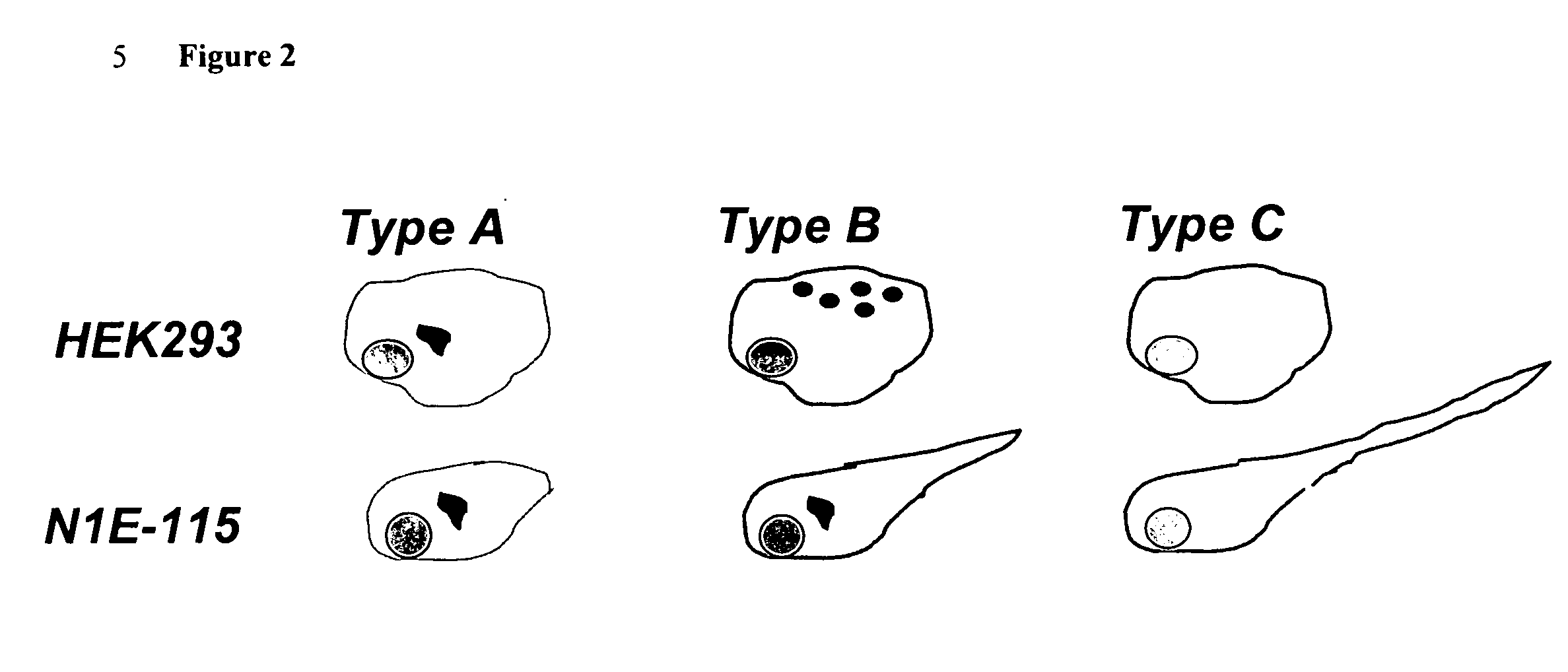
The invention provides a cell co-cultivation method used in the analysis of synapse formation, comprising the following steps: adding subcultured non-neuronal cells, namely HEK293 T cells, to 24-well primary cultured neuronal cells in an in vitro environment Medium, mixed and cultured for more than 24 hours; PEI transfection method was used to transfect HEK293 T cells, and the exogenous genes transfected in each well were different, and the transfected HEK293 T cells overexpressed exogenous genes, Under these conditions, co-culture was carried out for more than 48 hours; the presynaptic marker protein synapsin was immunostained to determine whether a synaptic structure was formed in each well. The co-cultivation method provided by the present invention solves the deficiencies in the prior art. The method is simple and convenient to operate, relatively low in cost and short in time, can screen genes well and verify gene functions, and can be widely used in laboratories .
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com