Method for acquiring transmission performance evaluation data for data distribution service
A technology of data distribution service and transmission performance, applied in the field of communication transmission, can solve the problems of inability to adapt to the characteristics of data distribution service scenarios, reduce the flexibility of distribution service deployment, occupy network overhead and performance overhead, etc., to achieve low network overhead, low cost The effect of running overhead, low complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
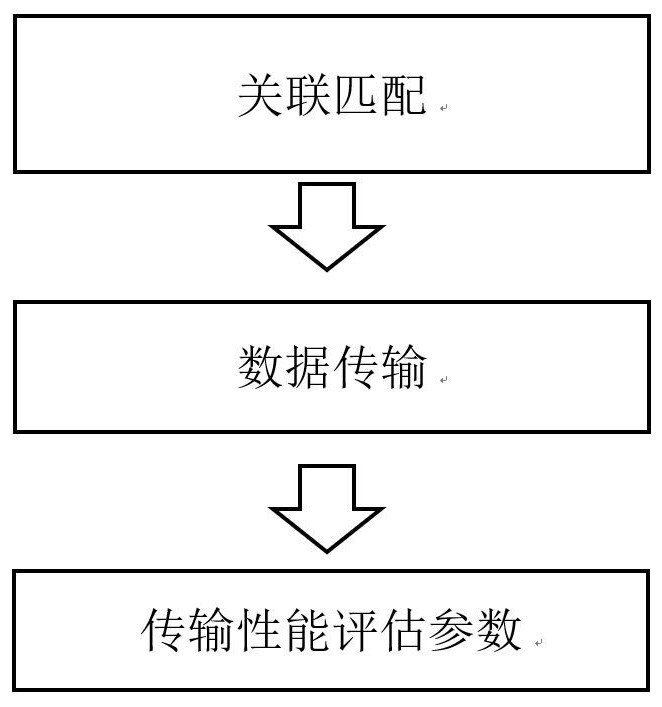
[0032] A method for obtaining transmission performance evaluation data for data distribution services in this embodiment, such as image 3 As shown, perform the following steps:
[0033] Step 1, association matching;
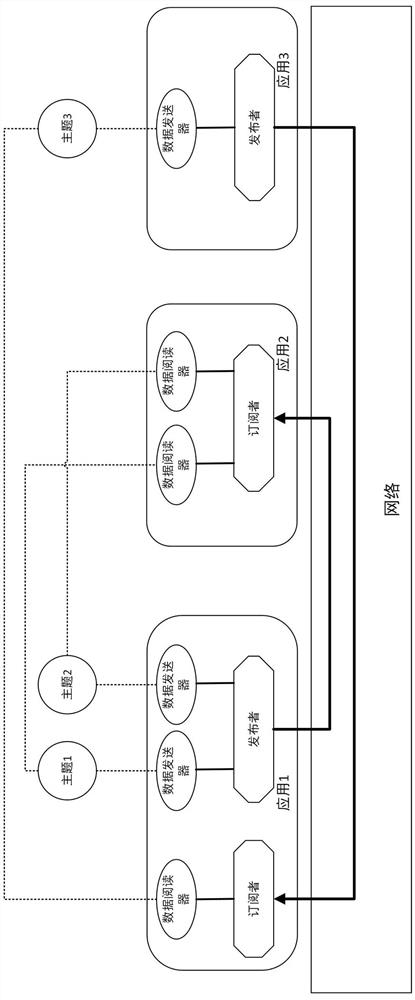
[0034] Publishers and subscribers in each application involved in the data distribution service are matched through topics;
[0035] Step 2, data transmission;
[0036] Obtain the transmission performance evaluation parameters of a single data transmission from the publisher to the subscriber based on the RTPS message and the RTPS protocol standard;
[0037] RTPS messages include data sub-messages, heartbeat sub-messages, confirmation sub-messages and timestamp sub-messages;
[0038] Wherein, there is a timestamp sub-message carrying at least one timestamp before the confirmation sub-message of the message in the data transmission;
[0039] Step 3, obtaining transmission performance evaluation parameters;
[0040] Obtain transport performance evaluation par...
Embodiment 2
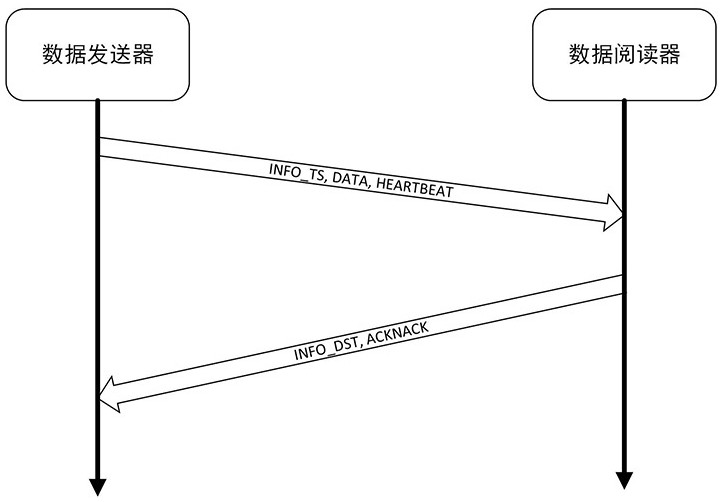
[0052] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that the round-trip time delay of this embodiment is more accurate than that of Embodiment 1, and the effects of factors such as performance and scheduling on the time delay are considered. Such as Figure 6 As shown, the data sender sends a message carrying a time stamp (T1), data and heartbeat at time T1. The data reader receives at time T2 and records T1 and T2. The data reader replies with a message carrying a timestamp (T1, T2, T3) and confirmation at T3, and the data sender receives it at T4 and calculates that the round-trip delay between the data sender and the data reader is T4 -T1-(T3-T2). That is to exclude the delay caused by the non-immediate transmission of the data reader due to various reasons, so as to show the round-trip delay that has nothing to do with external factors and is completely based on the deployment of the data distribution service, so as to provide a reference.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com