Hydrophilic interface for holding biological tissues
A biological tissue and hydrophilic technology, applied in the direction of instruments, computer materials science, molecular design, etc., can solve problems such as tissue damage and slippage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] In the present invention, the maximum slipping force is defined as the minimum clamping force that can hold the biological tissue along the vertical direction of the tissue surface and prevent the tissue from slipping off from the forceps, and the minimum damage force is defined as the ability to clamp the living tissue along the vertical direction of the tissue surface. The above-mentioned biological tissue is the minimum clamping force that causes tissue damage; since the maximum slipping force and the minimum damage force are related to the clamping force, the clamping force is defined as the force that pulls up or unfolds the tissue horizontally.
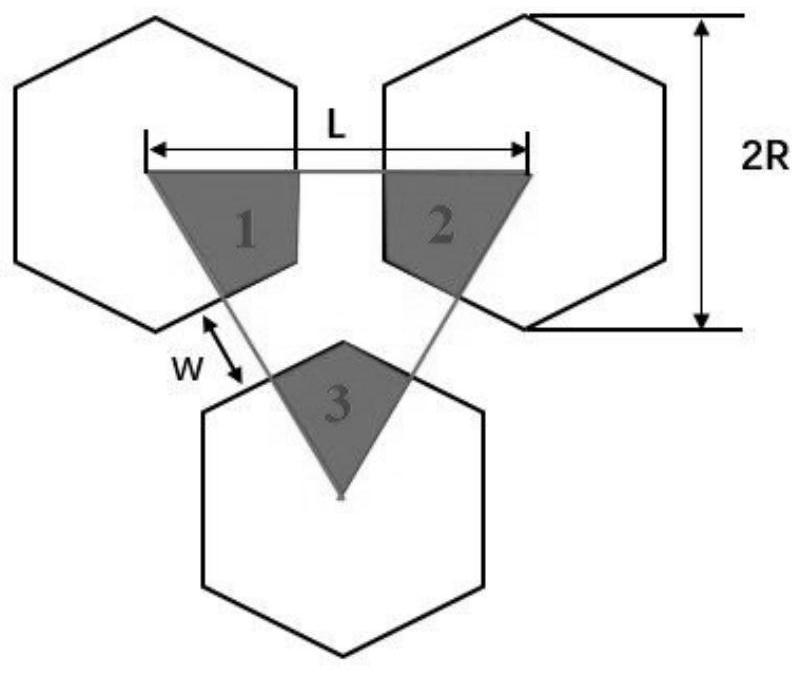
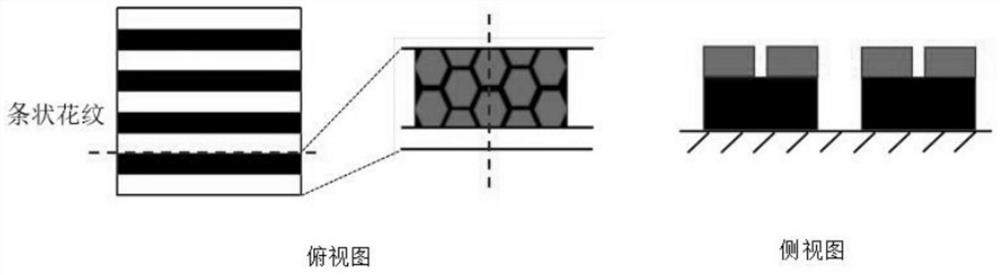
[0046] The source of the adsorption force of the hydrophilic interface is the liquid film tension, the viscosity-dependent hydrodynamic pressure and the intermolecular force (Van der Waals force), among which the liquid film tension plays a major role, and the liquid film tension is affected by the structure of the hydrophi...
Embodiment 2
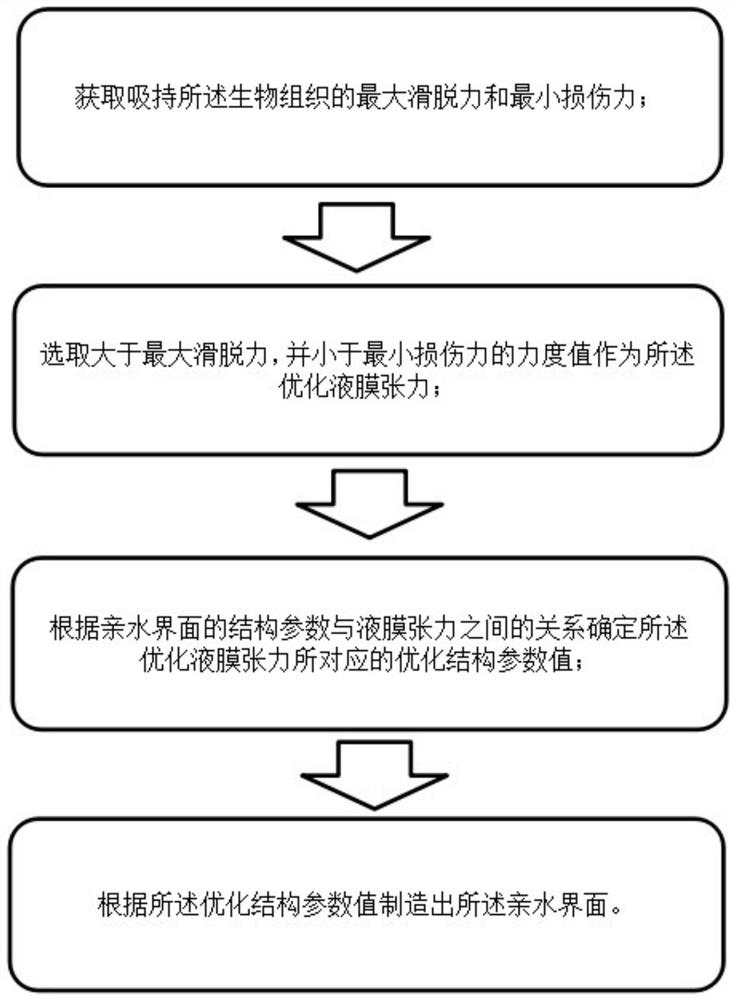
[0051] Embodiment 2 is an extended embodiment of the embodiment. It differs from Embodiment 1 in that it introduces the manufacturing method of the hydrophilic interface used to absorb biological tissue, and introduces the hydrophilic interface used to absorb biological tissue. The interface has been refined, among them, the hydrophilic interface fabrication method for adsorbing biological tissue, such as figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0052] (1) Obtain the maximum slipping force and the minimum damage force for holding the biological tissue:
[0053] Step 1: Use the clamp head to clamp the biological tissue with a clamping force (such as 1N) of the initial strength along the vertical direction of the surface of the biological tissue, and observe whether the clamp head under this force can clamp the biological tissue;
[0054] 1A: If the biological tissue cannot be clamped (that is, when there is a visible movement between the forceps head ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com