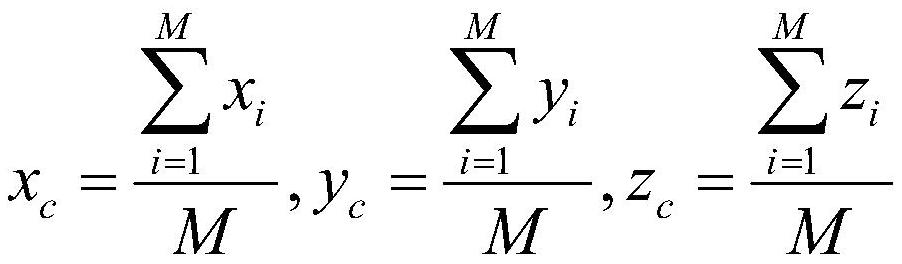Automatic calibration method for millimeter-wave radar and camera
A millimeter-wave radar and automatic calibration technology, applied in neural learning methods, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, radio wave measurement systems, etc., can solve the problems of complicated calibration process, camera can not directly get the actual distance, manual measurement, etc. To achieve the effect of ensuring good operation and reducing the workload of calibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
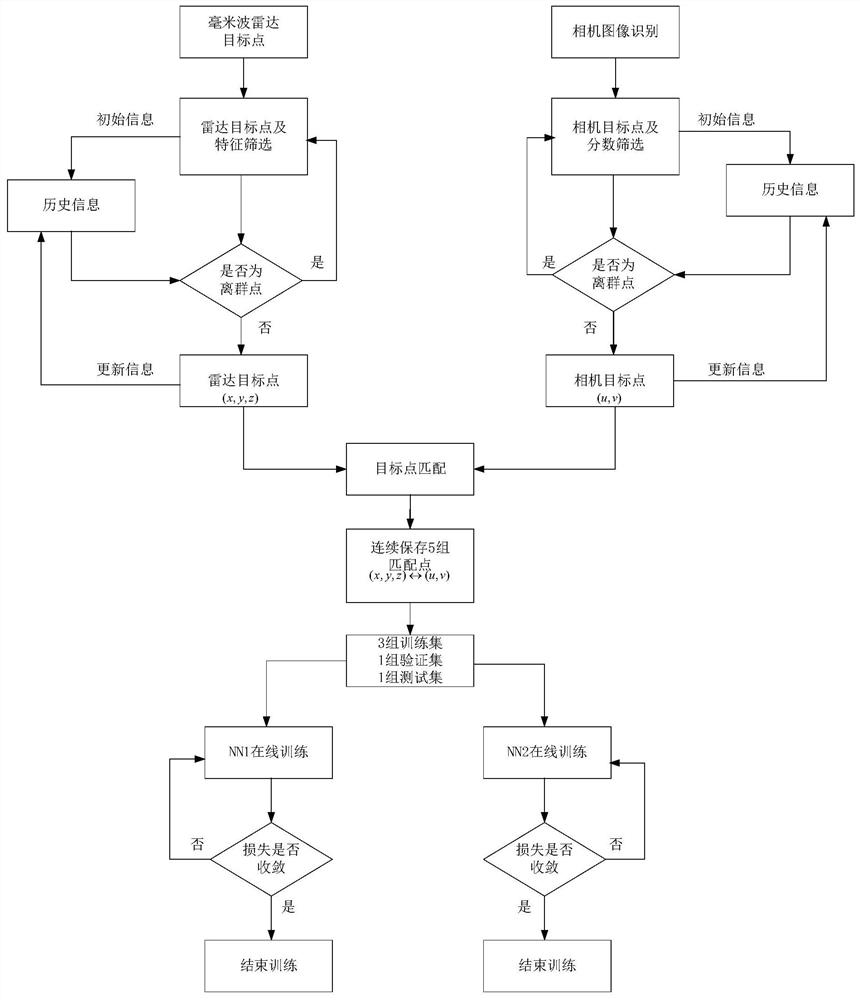
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides an automatic calibration method for a millimeter-wave radar and a camera, comprising the following steps:
[0051] S1. This method needs to be implemented in an open field to ensure that there is only one moving target within the cross-visual range of the millimeter-wave radar and the camera. The moving target needs to move as many positions as possible within the cross-visual range. Sampling is performed at the same starting time and at the same frequency. The sampling period of this embodiment is 0.08s, and calibration begins after 5 sampling periods;
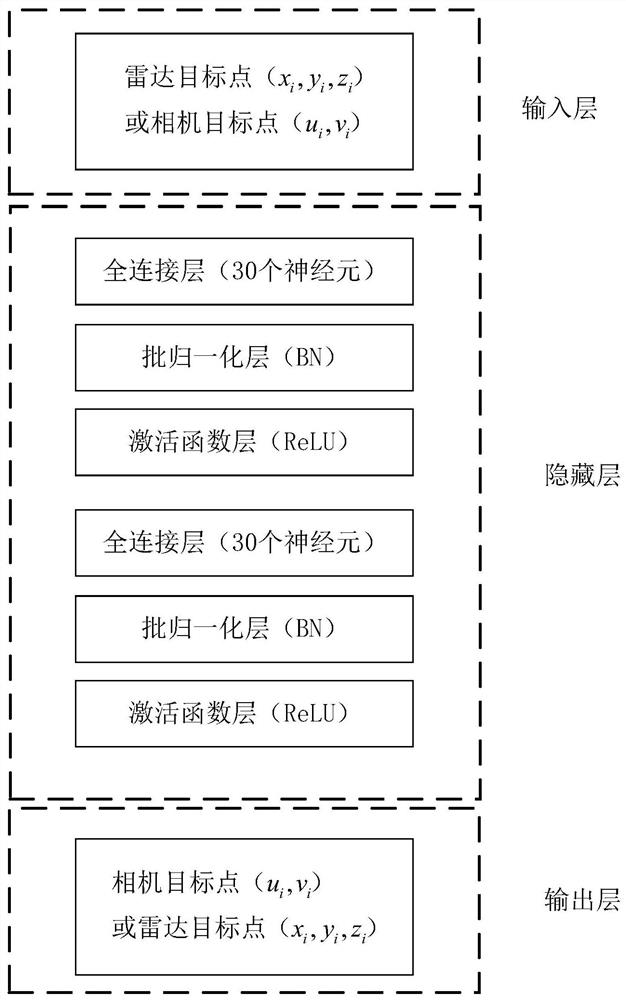
[0052] S2. Use the millimeter-wave radar and camera for sampling, and obtain the coordinates of n millimeter-wave radar target points in each sampling period Coordinates of m camera target center pixel points There are many classic open source algorithms for image-based target detection. The algorithm used in this embodiment is YOLOV2, and an appropriate ima...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com