Steering device of railway locomotive
A technology for railway locomotives and steering devices, which is applied in the directions of railway car body parts, bogies, devices for lateral relative movement between the underframe and the bogies, etc. tilt, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
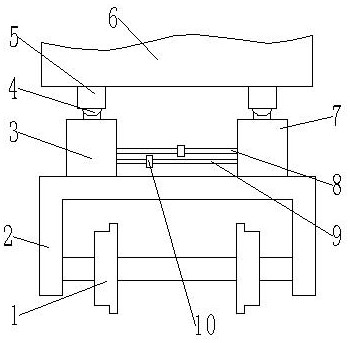
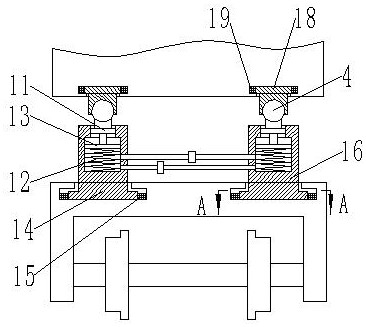
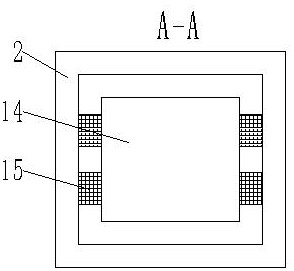
[0036] Such as Figure 1-5 As shown, a steering device of a railway locomotive comprises a main body 2 of a railway locomotive bogie and wheelsets 1 arranged on both sides of the main body 2; both sides of the upper end of the main body 2 are provided with traction devices, and the traction devices are used for The traction compartment 6 moves, and the traction device includes a first traction device 3 and a second traction device 7; symmetrically arranged between the first traction device 3 and the second traction device 7; the other end of the traction device is connected to the carriage 6 connection; a first pipeline 8 and a second pipeline 9 are arranged between the traction devices, and a check valve 10 is arranged on the first pipeline 8 and the second pipeline 9, and the two one-way valves The flow direction of the liquid medium in the valve 10 is opposite; one end of the first pipeline 8 and one end of the second pipeline 9 communicate with the first traction device 3,...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in order to improve the comfort of the cabin when turning, the diameter R1 of the spring, the wire diameter r of the spring, the effective number of coils N of the spring and the diameter R2 of the cavity satisfy the following relationship: R1·R2=α·(N·r) 2 ; Among them, the units of R1, R2, and r are cm; α is the correlation coefficient, and the value range is 3-10. When α is less than 3, the spring stiffness is large and the shock absorption performance is poor, which affects the fluidity of the liquid medium. When α is greater than 10, the spring stiffness is small. The flow between the second traction device 7 and the second traction device 7 is rapid, and the inclination rate of the compartment 6 is relatively large, causing the comfort of the compartment 6 to be poor.
Embodiment 3
[0047] In conjunction with embodiment two, the simulation experiment is carried out to the turning of the locomotive, and the steering angle of the simulated railway curve is 120 degrees, and the angle of the cross section at the turning is 30 degrees, that is, when turning, the angle between the plane where the wheelset 1 is located and the horizontal plane is 30 degrees, in order to simplify the experiment, in the locomotive model, the second spring is freely suspended, the lower end of the spring is connected to the steel ball, the weight of the steel ball is 50N, and the upper end of the second spring is connected to the tension sensor. The locomotive drives through the curve at a constant speed, and the speed is taken as 10m / s, experiment with α as 1, 3, 6, 10, and 12 respectively, and observe the value of the tension sensor. The greater the tension, the worse the stability and comfort of the car when turning; the experimental results are as follows, When α is 1, the pulli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com