Production of steviol glycosides through whole cell biotransformation
A technology of steviol glycosides and glycosides is applied in the field of producing steviol glycosides through whole-cell biotransformation, and can solve the problems of low popularity of steviol extracts and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
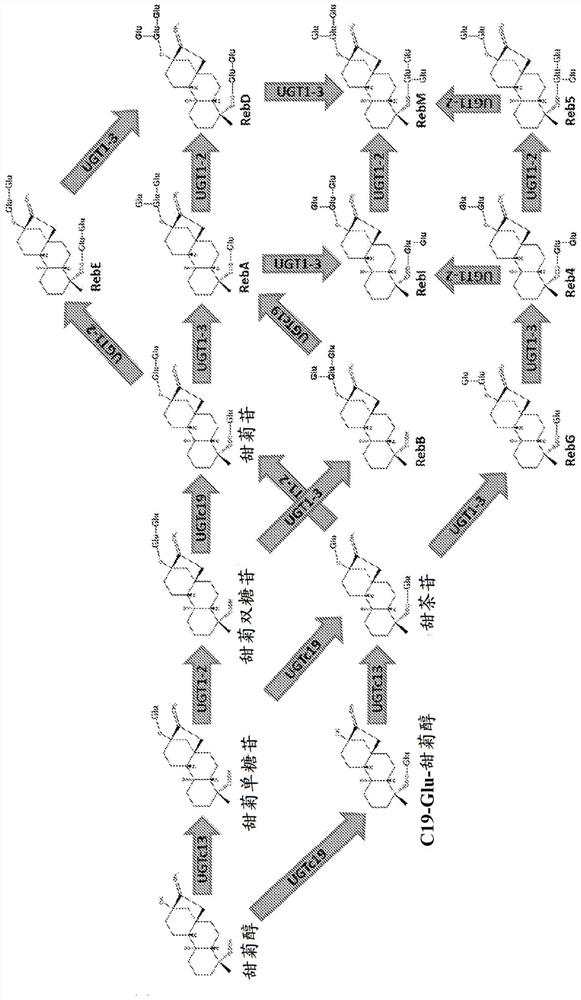
[0115] Table 2 shows the steviol glycoside content of three batches of stevia leaf extract. RebA and stevioside, two intermediates in the RebM pathway, were the two main glycosides in the batch.
[0116] Table 2: Steviol Glycoside Composition of Available Stevia Leaf Extract
[0117] % batch 1 batch 2 batch 3 Rebaudioside A 38.2 10.5 30.3 stevioside 8.5 9.0 18.4 Rebaudioside C 12.9 4.2 16.6 Rebaudioside B 4.3 7.1 1.2 rubusoside 5.0 2.2 2.0 Rebaudioside F 2.0 2.7 2.1 steviolbioside 0.3 3.7 0.3 Rebaudioside D 0.2 2.1 0.9 dulcoside A 0.9 0.4 0.5
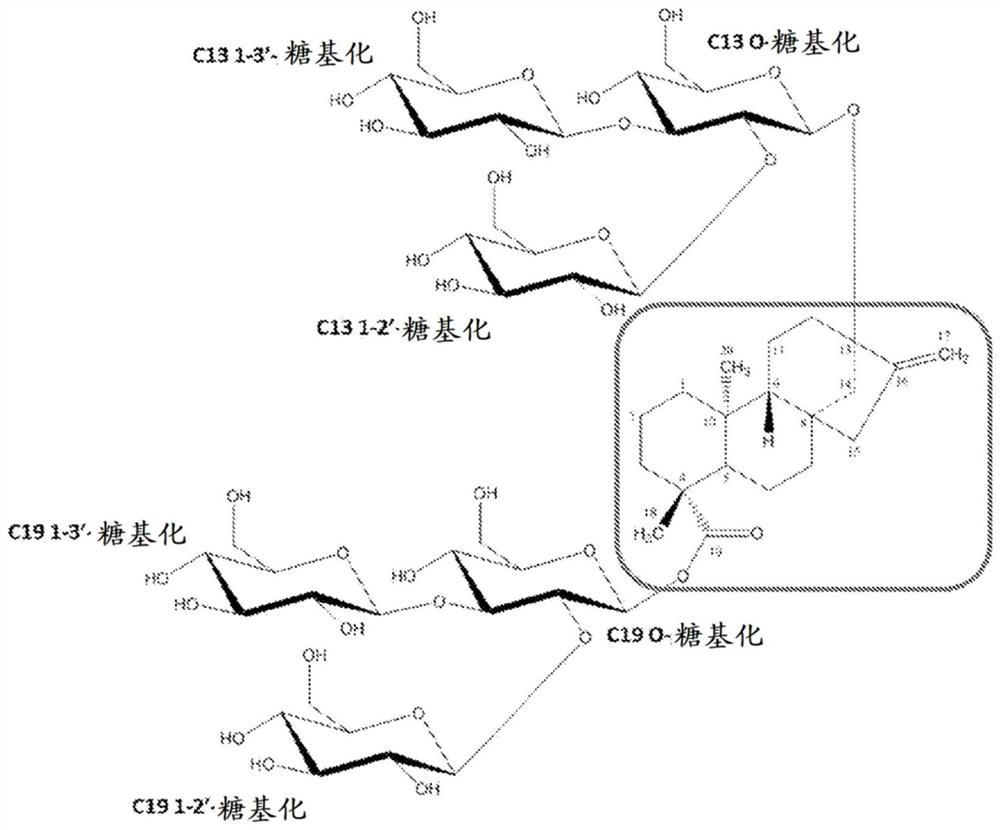
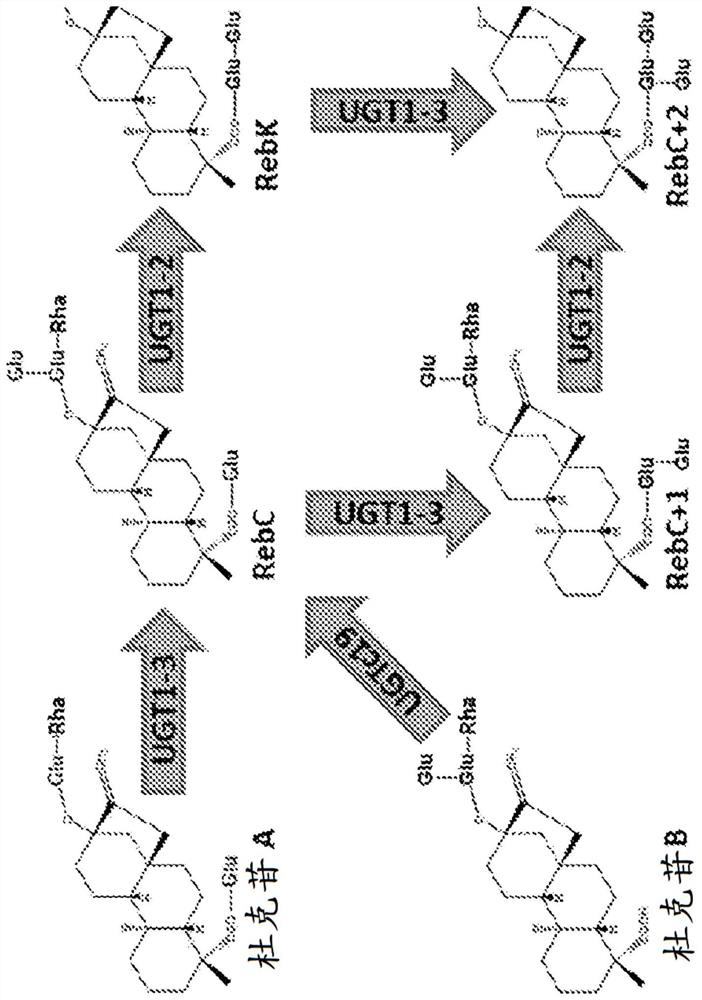
[0118] Figure 4 Biotransformation of glycosylated steviol glycoside intermediates is shown. In the experiments, 0.2 mM steviolbioside was fed to engineered E. coli strains in 96-well plates. Product formation was checked after 48 hours. Even whole-cell biotransformation of early intermediates such as steviolbioside was possible, but for nat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com