Nuclear power station radioactive liquid effluent discharging and conveying method
A radioactive and effluent technology, applied in the field of nuclear power, can solve the problems of high initial investment, interference, and failure to monitor and timely repair the damage of external protective trenches, and achieve the effect of reducing initial investment and reducing environmental risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] In order to make the purpose, technical solution and beneficial technical effects of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be understood that the specific implementations described in this specification are only for explaining the present invention, not for limiting the present invention.
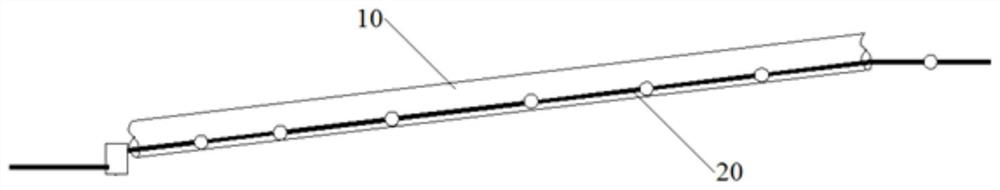
[0026] Please refer to figure 1 As shown, the nuclear power plant radioactive liquid effluent discharge delivery method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0027] Laying of non-radioactive liquid effluent discharge pipeline 10;
[0028] Putting the radioactive liquid effluent discharge pipeline 20 into the non-radioactive liquid effluent discharge pipeline 10 for laying, and the radioactive liquid effluent discharge pipeline 20 is laid on the inner bottom of the non-radioactive liquid effluent discharge pipeline 10; and
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com