System for determining prognosis of hepatitis B related liver cancer by using TIGIT and TIM-3 on NK cell
A technology of TIM-3 and NK cells, applied in instruments, biomaterial analysis, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of lack of reliable biomarkers, and achieve the effect of convenient method and good adaptability of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 TIGIT for patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer + TIM-3 + Increased expression of NK cells
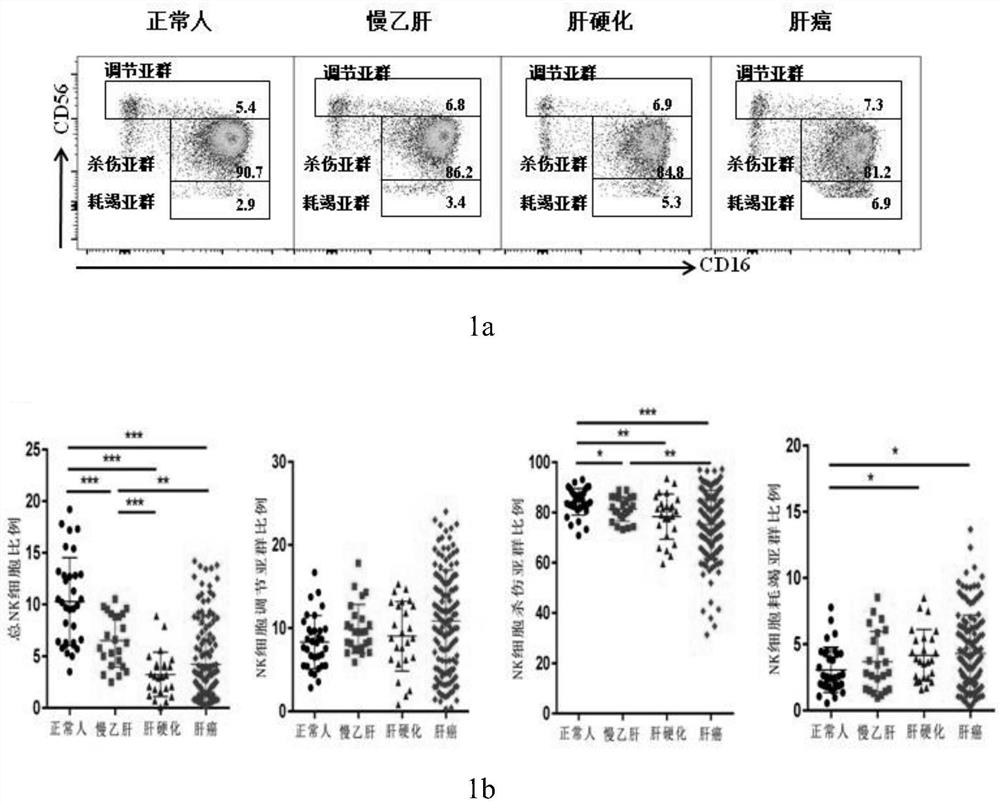
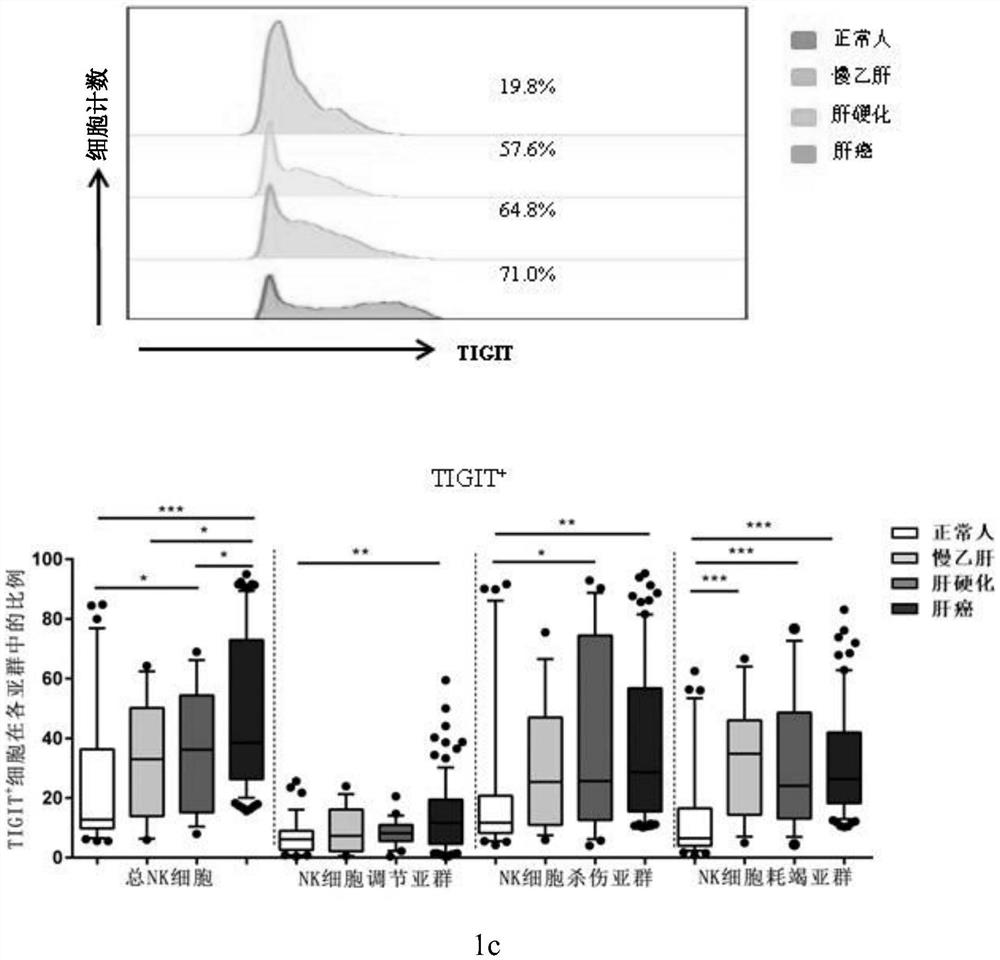
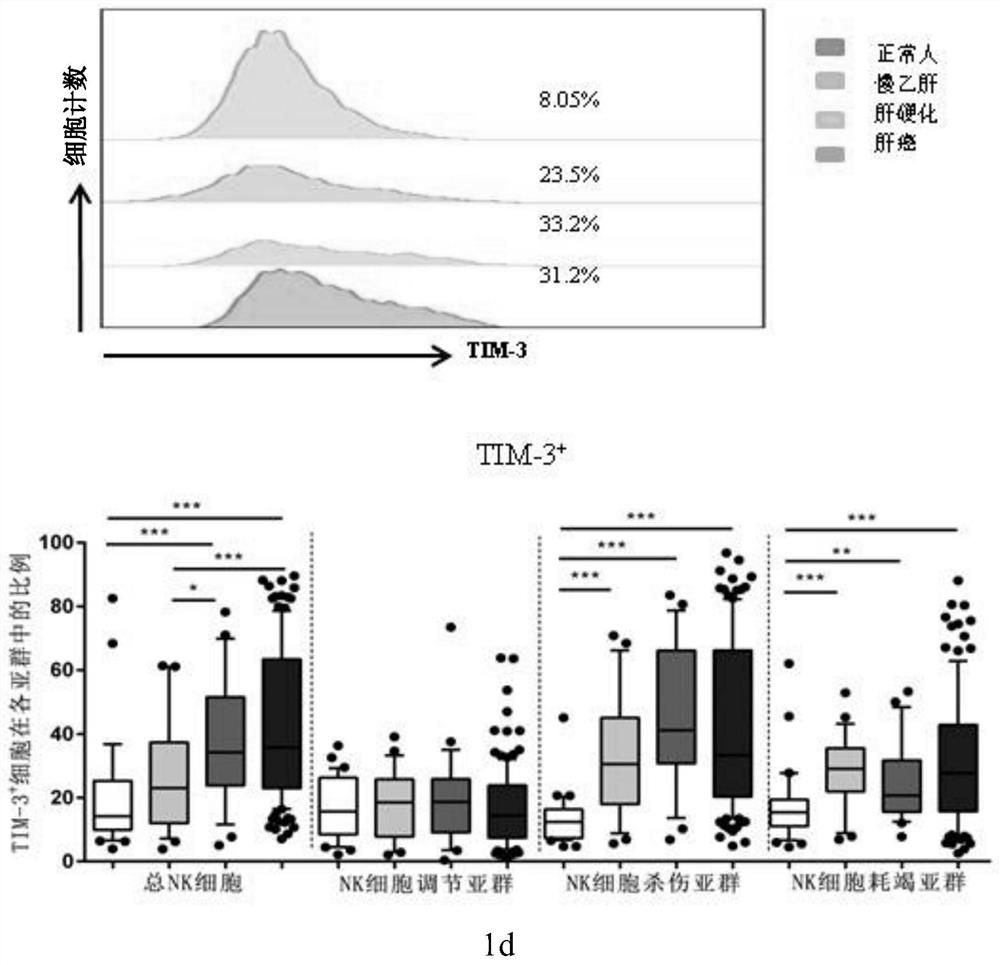
[0054] To evaluate the expression levels of TIGIT and TIM-3, we analyzed the expression levels of TIGIT and TIM-3 in normal subjects, patients with chronic hepatitis B, patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis, and patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer by flow cytometry.
[0055] First, we found that the proportion of total NK cells in patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer was significantly lower than that of normal people and patients with chronic hepatitis B (Pfigure 1 a, 1b). Subsequently, we compared the proportion changes of TIGIT and TIM-3 in total NK cells and each subpopulation in normal subjects, patients with chronic hepatitis B, patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis, and patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer. TIGIT in patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer compared with the proportion of total NK cells in normal peopl...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 TIGIT + TIM-3 + High expression of NK cells is associated with progression in patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer
[0057] To discuss TIGIT + TIM-3 + The relationship between NK cells and the clinical outcome of patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer, we studied 133 patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer. According to whether progress occurred or not, it was divided into progress group and non-progression group. Compare TIGIT + NK cells, TIM-3 + NK cells and TIGIT + TIM-3 + The proportion of NK cells in the two groups. We found that TIGIT + TIM-3 + The proportion of NK cells was significantly higher than that of the non-progressive group (P figure 2 d, 2e). According to TIGIT + TIM-3 + NK cell ratio to TIGIT + TIM-3 +The median (20.5%) of NK cell proportion was the cut-off value. We divided 133 patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer into two groups: TIGIT + TIM-3 + High expression group (>20.5%) and TIGIT...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3 TIGIT + TIM-3 + High expression of NK cells is associated with poor prognosis in hepatitis B-related liver cancer
[0062] To further determine the effect of tumor progression on TIGIT + TIM-3 + For the effect of co-expression, we used survival curves to compare the two groups in clinical subgroups (TIGIT + TIM-3 + High expression group and TIGIT + TIM-3 + low expression group) progression-free survival time. In the total population of HBV-related HCC, we found that TIGIT + TIM-3 + The progression-free survival rate of the high expression group was lower than that of TIGIT + TIM-3 + low expression group ( image 3 ; HR=2.05, 95% CI 1.24-3.04, P=0.005).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com