Robot arm and robot
A robot arm and robot technology, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, claw arms, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the production cost of humanoid robots, increasing robot noise, etc., to achieve optimized anthropomorphic effects, reduce noise, and reduce torque performance the effect of the requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
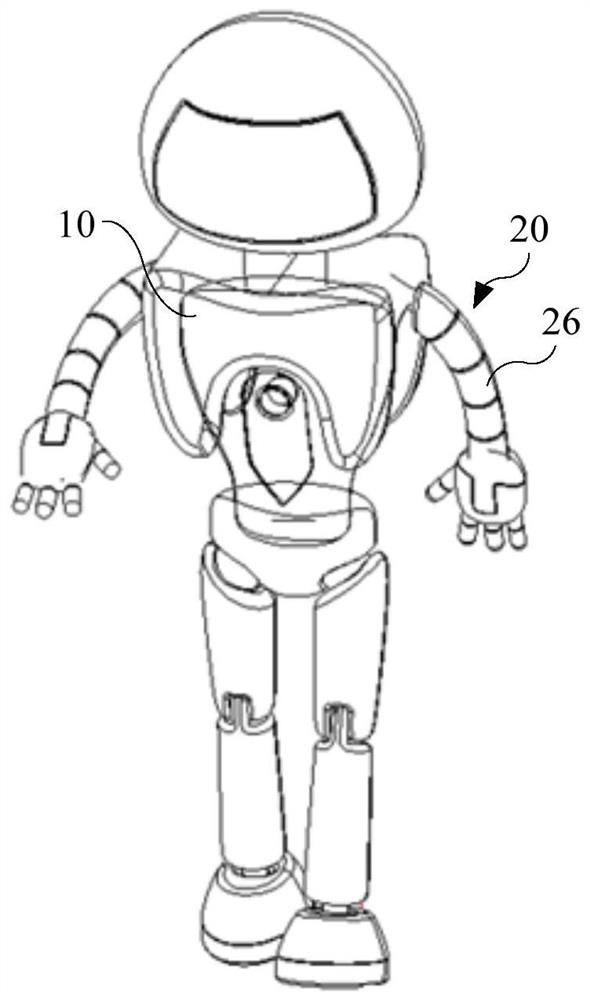
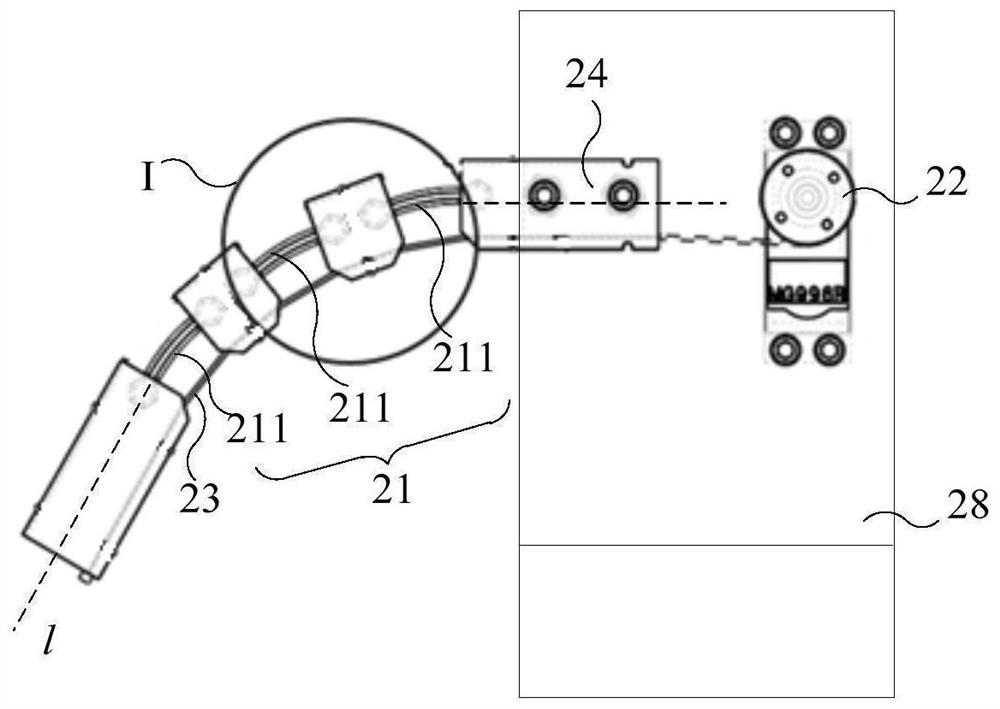
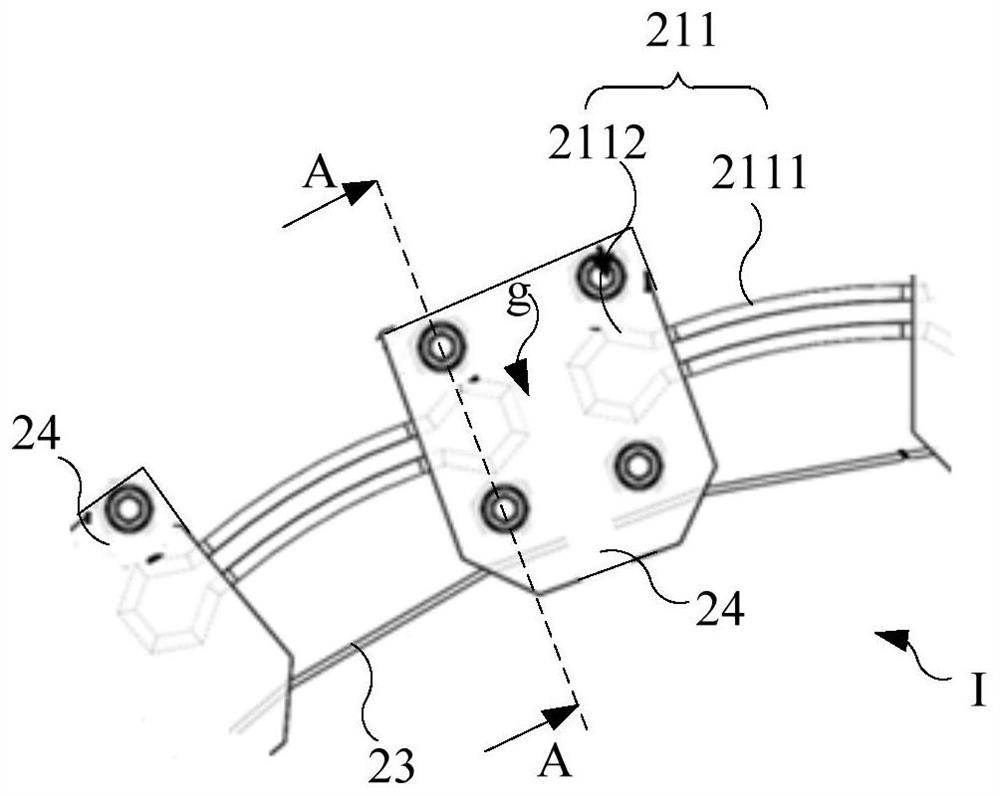
[0080] figure 1 A schematic diagram of the overall structure of the robot provided in Embodiment 1 of the present application; figure 2 for figure 1 One of the structural schematic diagrams of the robot arm; image 3 for figure 2 Partial enlarged view of center I; refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, the present embodiment provides a robot arm 20 including a flexible skeleton 21 and at least one driving component. Wherein, the first end of the flexible skeleton 21 is connected to the main body of the robot 10 as a flexible arm of the robot. For example, the means of the flexible skeleton 21 can be fixed on the shoulders of the robot body 10 .
[0081] refer to figure 1 As shown, it should be noted that the robot arm 20 of this embodiment is mainly used in humanoid robots, especially children's educational companion robots. Of course, the robot arm 20 of the present application can also be applied to other types of robots if there is no contradiction.
[0082] As ...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Figure 7 Schematic diagram of the structure of the robot arm provided in Embodiment 2 of the present application; Figure 8 for Figure 7 Partial enlarged view of II. refer to Figure 7 with Figure 8 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1, the robot arm of this embodiment also includes an elastic member 25, and the elastic member 25 and the transmission member 23 are respectively arranged on both sides of the central axis of the flexible skeleton 21. In other words, the elastic The member 25 and the transmission member 23 are symmetrical with respect to the central axis of the flexible frame 21 , and the elastic member 25 is arranged along the extending direction of the flexible frame 21 . When specifically configured, the elastic member 25 may be a telescopic spring.
[0134] During specific implementation, the quantity of the elastic member 25 can be multiple, and the plurality of elastic members 25 are arranged in one-to-one correspondence with the plurality o...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Figure 10 A schematic diagram of the first structure of the robot arm provided in Embodiment 3 of the present application; Figure 11 for Figure 10 Partial enlarged view of III. refer to Figure 10 with Figure 11 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the flexible skeleton 21 of this embodiment includes a flexible segment 211. In other words, the flexible skeleton 21 of this embodiment is composed of a flexible segment 211, and the head end of the flexible segment 211 is connected to On the robot main body 10, it is used as a flexible arm of the robot. For example, the head end of the flexible section 211 can be fixed on the robot main body 10 through the connecting piece 24 .
[0147] In this embodiment, by setting the flexible skeleton 21 as a flexible segment 211, while ensuring that the flexible skeleton 21 can simulate the bending or stretching of the human arm under the driving action of the drive assembly, the structure of the robot arm is sim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com