Bionic knee joint structure based on tensegrity structure, and control method design
A technology of tensegrity structure and control method, applied in prosthesis, medical science, artificial leg, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the dynamic model of the tensegrity structure, complex structure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] Below in conjunction with embodiment and accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
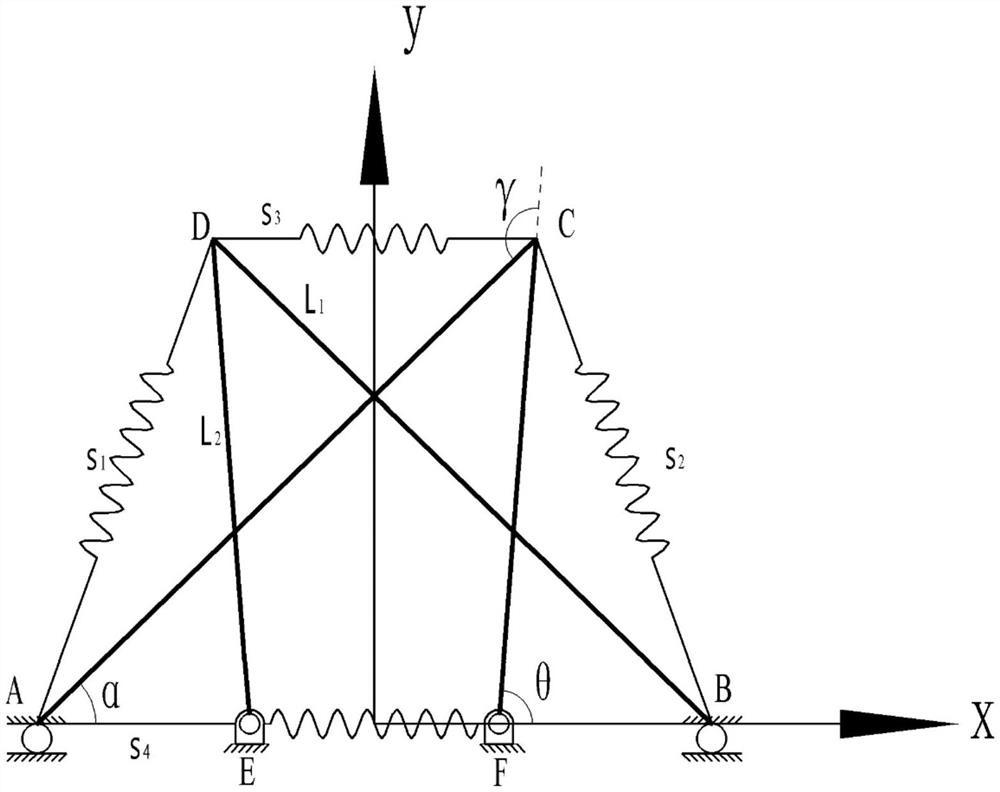
[0051] figure 1 is a geometric structure diagram of a bionic knee joint structure based on a tensegrity structure, such as figure 1 As shown, the structure is specifically as follows:
[0052] S1: The geometric structure of the bionic knee joint structure is as follows:
[0053] S101: The overall structure of the bionic knee joint tension is composed of four rods and four sets of ropes. In the bionic knee joint structure, the rods AC and BD can be regarded as bone structures simplified from the femur, tibia, and fibula, respectively. Rods CF and DE can be viewed as structures with the same function simplified from the patella and nearby tissues. For a two-bar linkage, the lengths of rods AC and CF are L 1 and L 2 , where L 1 greater than L 2 . Similarly, another group of two-link mechanism BD-DE and two-link structure AC-CF are symmetrical about the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com