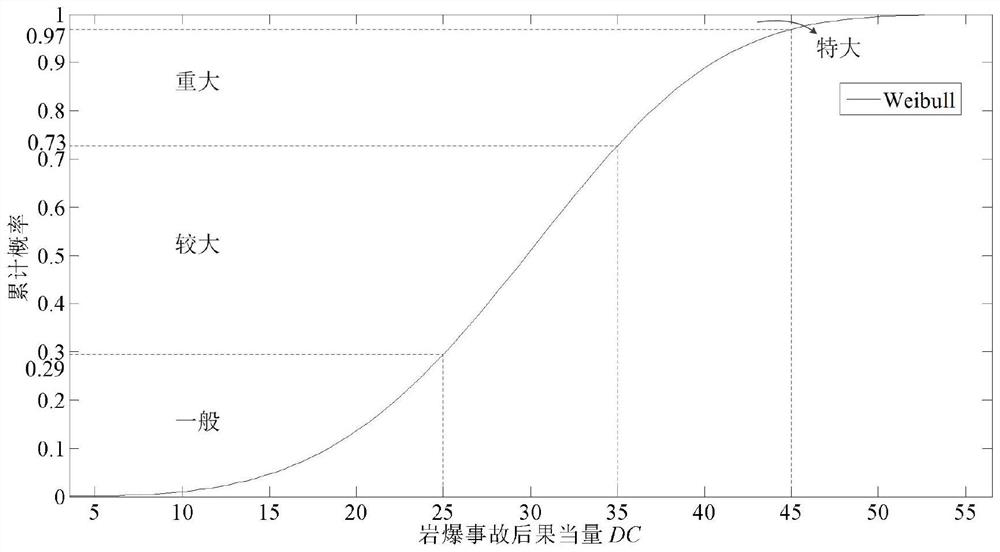
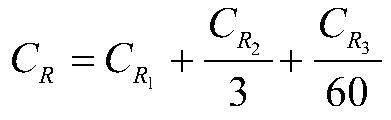Deep hard rock tunnel rockburst risk consequence equivalent grading method
A grading method and equivalent technology, applied in the field of rockburst risk, can solve problems such as inconsistent measurement methods, casualties, direct economic losses, social impacts, environmental impacts, and different grading standards for construction delays, and achieve the goal of overcoming poor accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1: A method for grading equivalent grading of rockburst risk consequences in deep-buried hard rock tunnels, the specific steps are as follows:
[0062] (1) Establishment of rockburst risk consequence equivalent calculation model
[0063] DC=C R +C Z +C S +C H +C G
[0064] In the formula, DC is the equivalent of rockburst risk consequences; C R Casualty equivalent; C Z is the direct economic loss equivalent; C S is the social impact equivalent; C H is the environmental impact equivalent; C G is the equivalent of construction delay;
[0065] Casualty Equivalent C R The calculation method is
[0066] According to the "Classification of Casualty Accidents for Enterprise Employees", the degree of injury is divided by the value of lost working days, among which, minor injury refers to the disabling injury with less than 105 lost working days, serious injury refers to the disabling injury with not less than 105 lost working days, and serious injury The...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Embodiment 2: Calculate the risk consequence equivalent classification of specific engineering cases with the equivalent classification method of rockburst risk consequences of deep-buried hard rock tunnels in Embodiment 1;
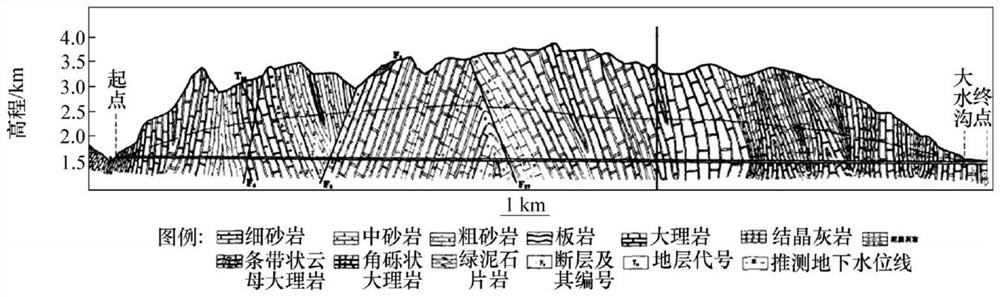
[0089] The Jinping II Hydropower Station is located in Sichuan Province, China. It is a super-large underground hydropower project with an ultra-deep buried long tunnel. The strata it traverses are all Triassic strata, respectively T 1 , T 2y , T 2b , T 2z , T 3 , the rock mass along the line is mainly composed of marble, limestone, sandstone and slate, and its geological section is shown in figure 2 , a total of four diversion tunnels, the average length of the tunnel line is about 16.67km, and the excavation diameter is 13m. Among them, the TBM excavation sections of the 1# and 3# diversion tunnels are circular sections with an excavation diameter of 12.4m, the excavation sections of the 1# and 3# diversion tunnels by drilling and blasting m...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Example 3: Based on the equivalent classification method for rockburst risk consequences of deep-buried hard rock tunnels in Example 1, three rockburst accident cases were selected from the water diversion tunnel of Jiulongxia Power Station, the Dulongjiang Highway Tunnel, and the NJ Hydropower Station in Pakistan to further verify the equivalent classification method Applicability, the actual consequences of specific rockburst accidents and the equivalent prediction results are shown in Table 12 below;
[0094] Table 12 Comparison of the risk equivalent prediction results and actual results of three rockburst accidents
[0095]
[0096] It can be seen from Table 12 that the equivalent prediction results of rockburst consequences in the three cases are ordinary, major and extra large, except that the rockburst prediction consequences of Dulongjiang Highway Tunnel K3+856.5~K3+854.5 are slightly lower than those calculated by the International Tunnel and Underground Space...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com