Integrated mobile collaborative robot control system based on field bus
A fieldbus, mobile collaboration technology, applied in the direction of program control manipulators, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems that robots cannot work continuously and cannot be combined, and achieve the effect of improving completion efficiency, avoiding task delays, and rationally assigning tasks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
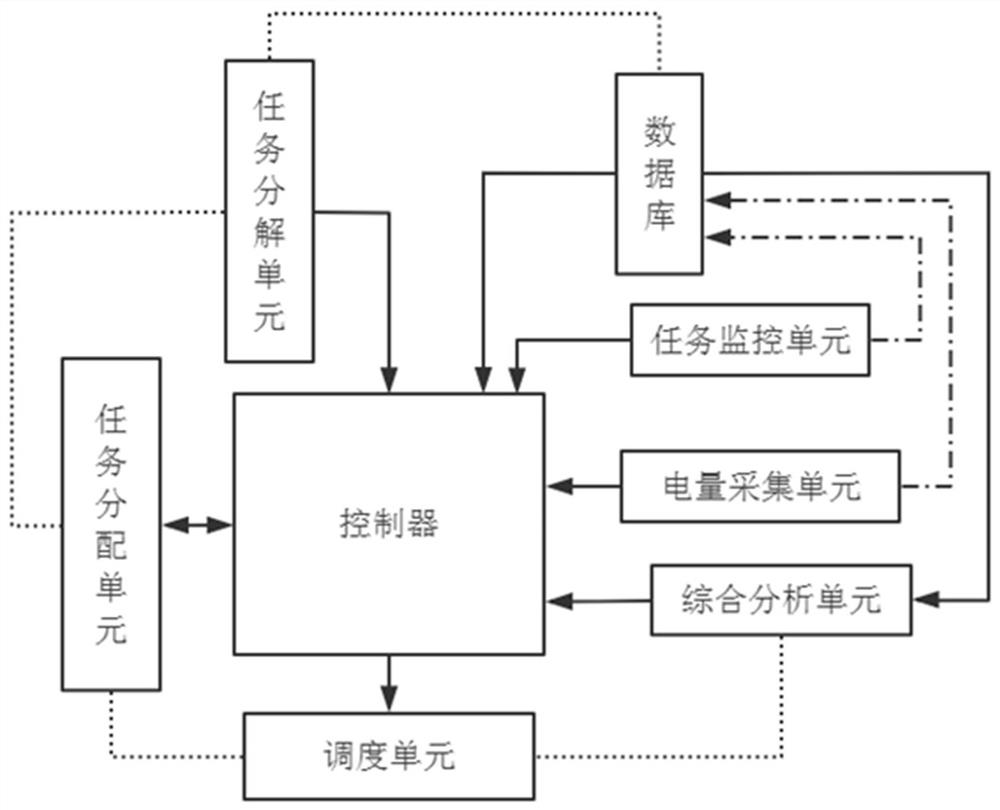
[0060] The present invention is an integrated mobile collaborative robot control system based on the field bus, including: a task decomposition unit, the task decomposition unit is used to respectively decompose the tasks corresponding to each robot, obtain m subtask categories, and respectively m subtasks The class is assigned a priority value Yu, u=1, 2, ..., m; the power collection unit is used to collect the remaining power information corresponding to each robot; the task monitoring unit obtains the remaining task amount of each robot every preset time W1, Rj represents the remaining task amount of robot j; the comprehensive analysis unit analyzes the pre-completion degree Dj of the robot every time it receives the remaining task amount information of the robot; Redistribute the remaining tasks, and return the redistribution results to the controller. Combined with the situation of the tasks and robots, make reasonable scheduling, and redistribute the tasks in time to ensu...
Embodiment 2
[0071] The sub-task classes are respectively core tasks, related tasks, and adjustable tasks, and the division method is as follows:
[0072] Step S001: The task allocation unit allocates a task every time W1 (all tasks allocated each time are guaranteed to have no timing requirements, that is, the tasks allocated this time can be completed within time W1), and obtain all tasks allocated within time W1;
[0073] Step S002: choose a task i from all tasks;
[0074] Step S003: Obtain the task i selected in step S002, and retrieve the number of tasks associated with it, and mark the number of associated tasks as: Gi;
[0075] If Gi>G, mark task i as a core task, that is, such tasks are highly relevant, and if this task cannot be completed, many tasks will not be completed;
[0076] If Gi≦G, task i is marked as a related task, that is, the relevance of such tasks is lower than that of core tasks, and if the task cannot be completed, fewer tasks will not be completed;
[0077] If ...
Embodiment 3
[0086] As an embodiment provided by the present invention, preferably, the steps for the task allocation unit to reassign the remaining tasks according to the pre-completion degree Dj are:
[0087] Determine the size of the pre-completion degree Dj, if Dj≦D, perform the task reassignment step; otherwise, maintain the original assigned task;
[0088] Step F001: Call the robot corresponding to the pre-completion degree Dj≦D, and obtain its remaining tasks;
[0089] Step F002: Obtain the subtask class to which the remaining tasks belong and the priority value Yu corresponding to the subtask class;
[0090] Step F003: Continue to sort the remaining tasks sequentially according to the pre-sorting order rules;
[0091] Step F004: Calculate the number Kj of tasks expected to be performed by the robot according to the prearrangement sequence;
[0092] Step F005: intercepting the first Kj tasks according to the prearrangement order, and marking them as executable tasks, and marking t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com