Mathematical model-based Lake-entering river pollution influence degree evaluation method
A technology that affects the degree of impact and river pollution. It is applied in data processing applications, general water supply conservation, instruments, etc. It can solve problems such as unmonitored peak concentrations of pollutants, and achieve ecological and environmental protection. Significant economic and social benefits, The effect of easy-to-operate applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
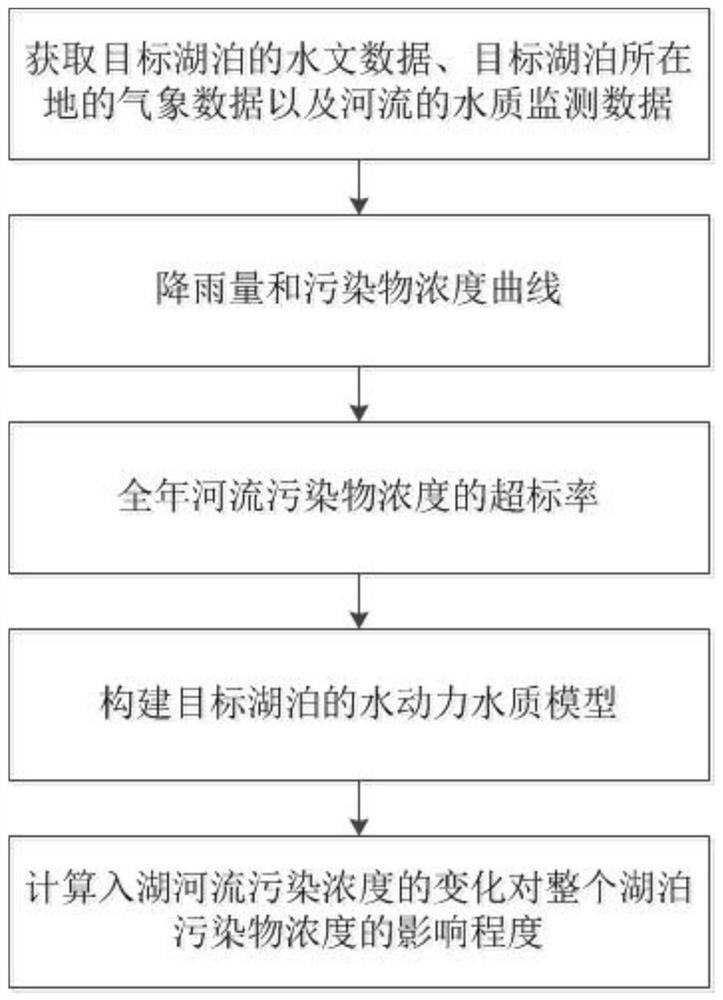
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, a mathematical model-based method for assessing the degree of pollution impact of rivers entering the lake, the specific steps include:
[0055] Step 1: Obtain the hydrological data of the target lake, the meteorological data of the location of the target lake, and the water quality monitoring data of the river.
[0056] Step 2: Based on the water quality monitoring data, extract the river pollutant concentration monitored in rainy days, and use the regression analysis method to obtain the rainfall and pollutant concentration curves.
[0057] Pollutants include at least: permanganate index, COD, ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen, and total phosphorus.
[0058] Obtaining rainfall and pollutant concentration curves include:
[0059] Determining the rainfall level according to the amount of rainfall,
[0060] Filter the function used in the regression analysis for each rainfall class;
[0061] Analyze the results with regression in R 2 Based ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Using the method provided in Example 1, calculate the river X entering the lake 1 The extent to which pollution affects Lake A.
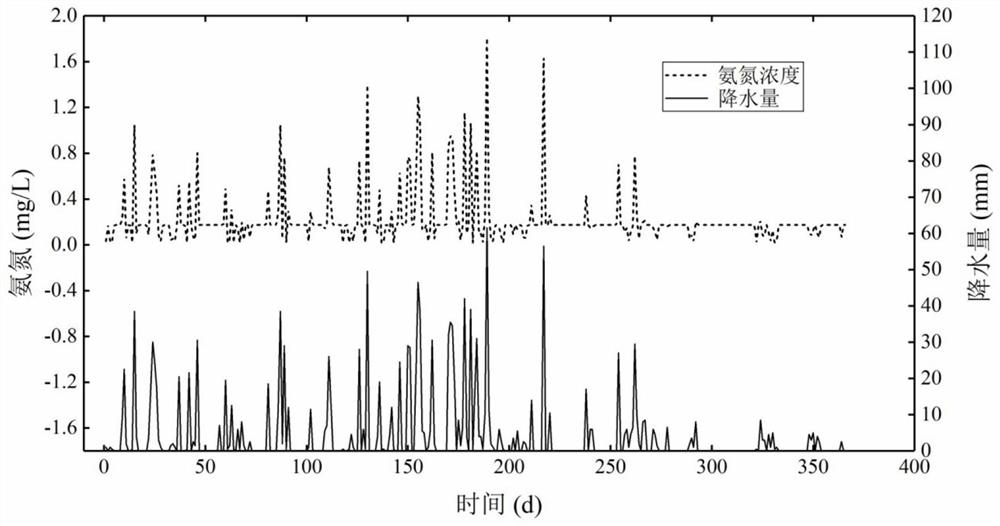
[0094] According to steps 1-3, get as figure 2 Year-round River X shown 1 Pollutant concentration distribution map.
[0095] According to step 4, the hydrodynamic water quality model of lake A is established. Using the established hydrodynamic water quality model, the concentration of river pollutants monitored in rainy days is calculated to obtain the model mean value. Compare the measured mean value of rainy day monitoring with the model mean value, as shown in Table 1:
[0096] Table 1: Lake A model validation results
[0097]
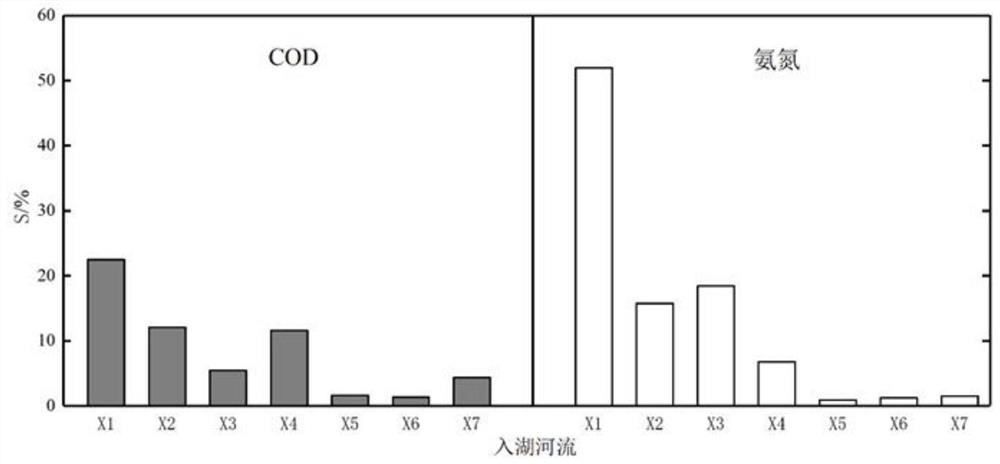
[0098] According to step 5, under the condition that the boundary disturbance is 30% increase or decrease in the pollution load of the river entering the lake, the degree of influence is calculated, as follows: image 3 Shown are the results of the degree of pollution impact on rivers entering the lake. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com