Intelligent welding device and method for wind power stator core
A stator core and welding device technology, applied in auxiliary devices, welding equipment, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of poor welding effect, reduced penetration depth, and low intelligence, so as to avoid the reduction of penetration depth and scientific method design , to meet the effect of continuous welding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
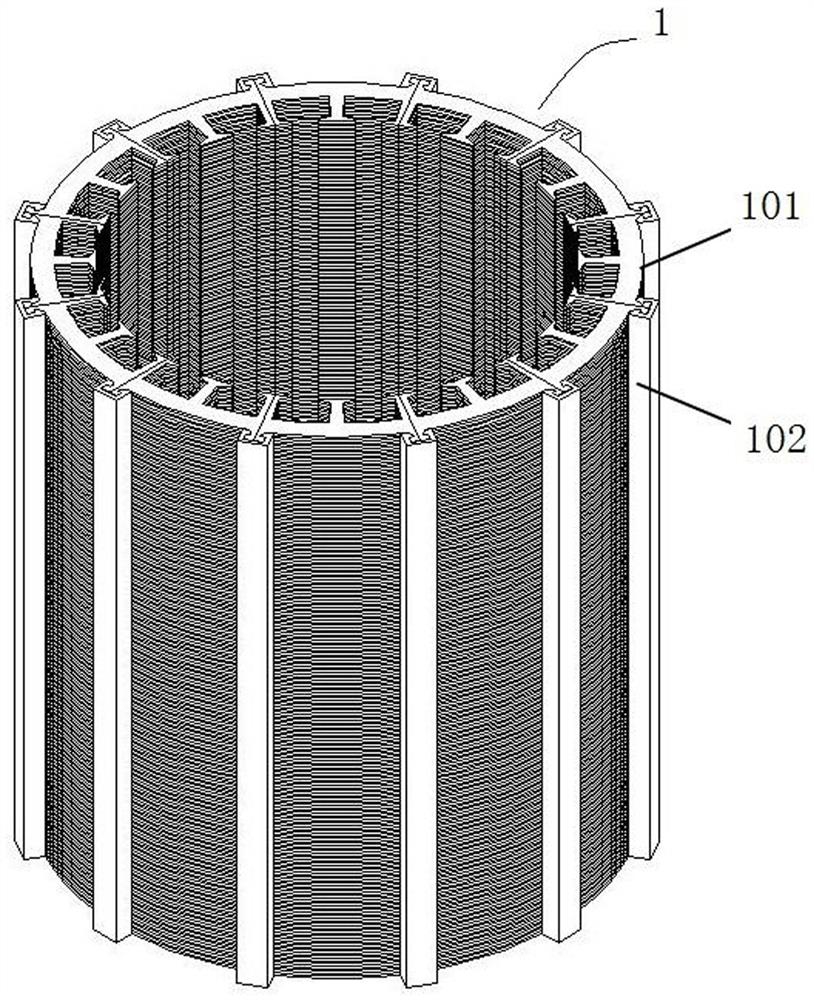
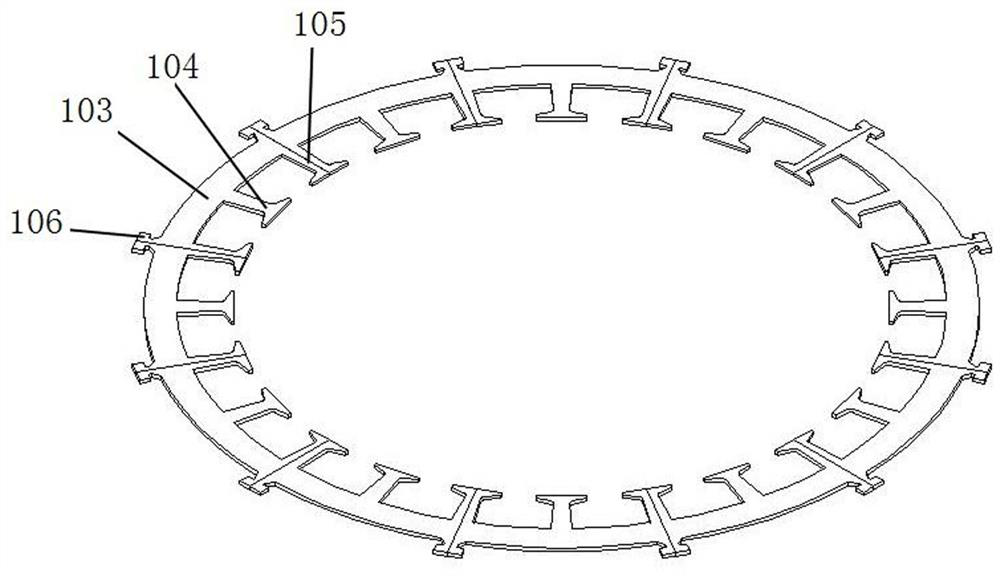
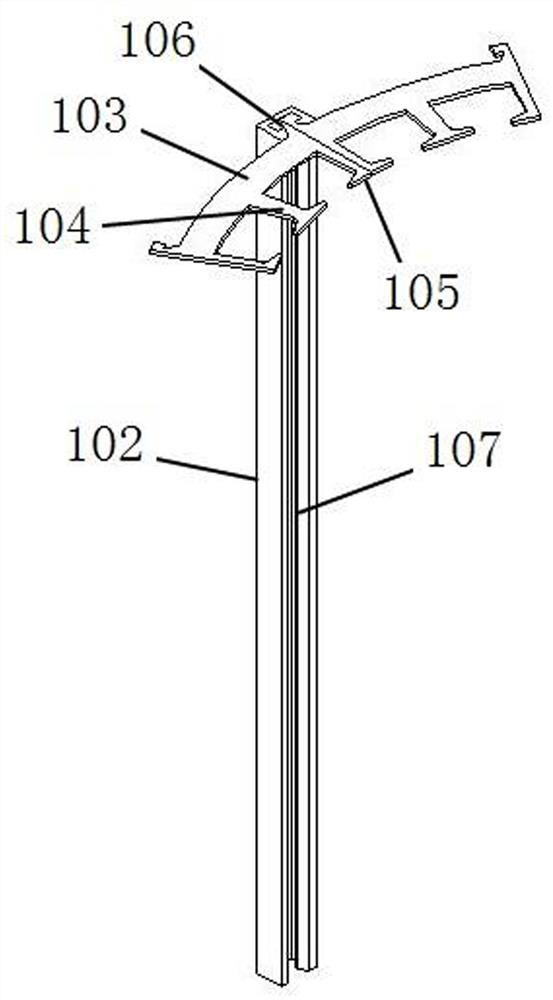
[0042] This embodiment is an intelligent welding device for a wind power stator core, which is used for welding the segmented laminated stator core 1, such as Figure 1-Figure 3 As shown, the segmented laminated stator core 1 is composed of several layers of segmented laminations 101 distributed in a circular array and locking strips 102 for fixing the segmented laminations 101 in circles. The block lamination 101 includes an arc-shaped sheet body 103, at least one complete winding board 104 is provided at the inner middle of the arc-shaped sheet body 103, and semi-complete winding boards 105 are provided at both ends of the inner side. The semi-complete winding boards of two adjacent arc-shaped sheets 103 can be assembled into a complete winding board; the outer two ends of the arc-shaped sheets 103 are provided with semi-complete locking plates 106, and the two adjacent arc-shaped sheets The semi-complete lock plate 106 of 103 can be assembled into a complete lock plate. Th...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The structure and application of this embodiment are basically the same as those of Embodiment 1, and the differences are as follows: Figure 11 As shown, the round mounting column 9 and the retaining ring 10 are locked in position through threaded socketing. Specifically, an external thread groove 904 can be provided on the outer surface of the cylinder part 901, and an internal thread part can be added inside the retaining ring 10 to realize position locking. . In order to facilitate manual rotation of the retaining ring 10, a handle can be added on its outside.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The structure and application of this embodiment are basically the same as those of Embodiment 1, and the differences are as follows: Figure 12 As shown, the round mounting column 9 and the retaining ring 10 are locked in position by screw locking. Specifically, a number of fastening screws 15 can be threaded through the retaining ring 10, and the fastening screws 15 are screwed inward to the cylinder part 901. The unslotted position offsets to achieve position locking. The position locking principle of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, which uses the friction resistance between the fastening screw 15 and the round mounting column 9 to replace the friction resistance between the round mounting column 9 and the stop ring 10 in Embodiment 1 . A loose fit is adopted between the round mounting column 9 and the retaining ring 10, and the position between the two can be adjusted freely before the fastening screw 15 is locked.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com