Method for determining harmful element lead or cadmium in food additive
A technology for food additives and elemental lead, which is applied in measuring devices, color/spectral characteristic measurement, material analysis through optical means, etc. It can solve problems such as large background interference, deviation of measurement results, and great influence on measurement results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Instrument model used: PerkinElmer PinAAcle D900 atomic absorption spectrophotometer
[0025] When the graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer is used for the determination of harmful elements such as lead and cadmium in food additive phosphate, the different ratios of the matrix modifier and the sample solution (standard sample) are discussed, and it includes the following steps:
[0026] 1) Use a 1000mg / L lead standard solution to prepare a 10mg / L standard solution;
[0027] 2) Use 10mg / L lead standard solution to prepare 100μg / L lead standard solution;
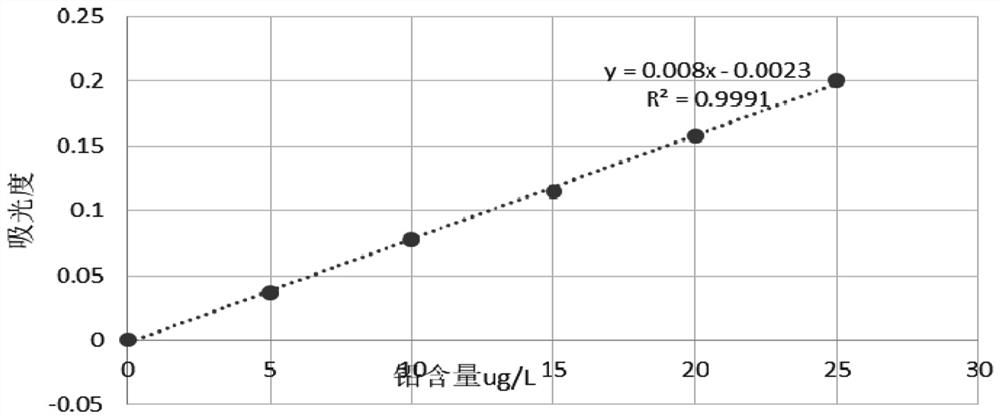
[0028] 3) Prepare 20 μg / L lead standard with 100 μg / L lead standard solution, specific steps: pipette 12.50 ml of 100 μg / L lead standard into a 50 mL volumetric flask, add a certain volume of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate matrix modifier, Use 1% nitric acid (volume concentration) to make up to the scale, shake well, use 1% nitric acid (volume concentration) as standard blank, use graphite furnace atomic...
Embodiment 2
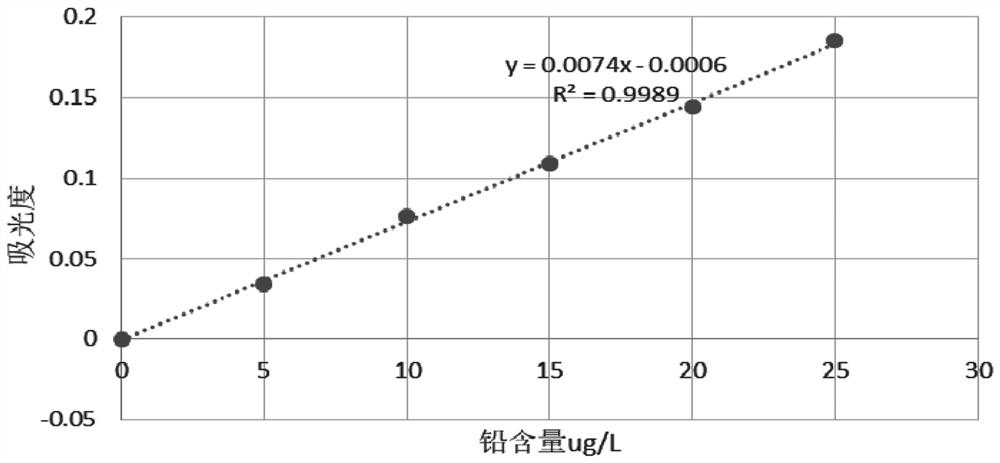
[0034] Change the matrix improver in embodiment 1 into diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution (20g / L), step is the same as embodiment 1, draw standard curve and see attached figure 2 , the measurement results are shown in Table 2:
[0035] Table 2-diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution is used as matrix improver determination result (71% of standard addition recovery rate)
[0036]
[0037]
Embodiment 3
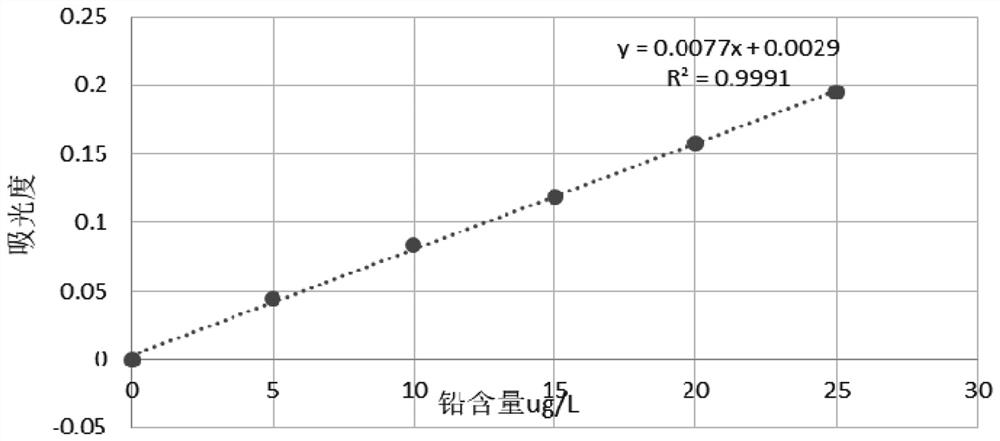
[0039] Change the matrix improver in embodiment 1 into ammonium nitrate solution (20g / L), step is with embodiment 1, standard curve sees attached image 3 , the measurement results are shown in Table 3:
[0040] Table 3—Ammonium nitrate solution is used as matrix improver determination result (87% of standard addition recovery rate)
[0041]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com