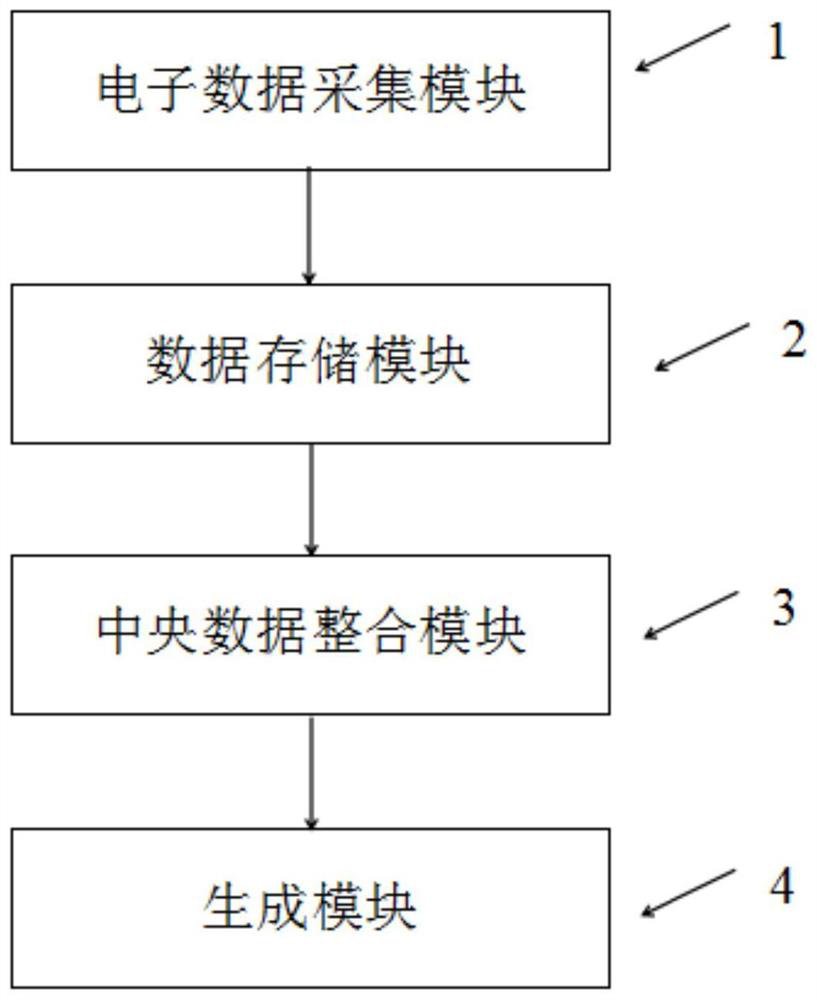
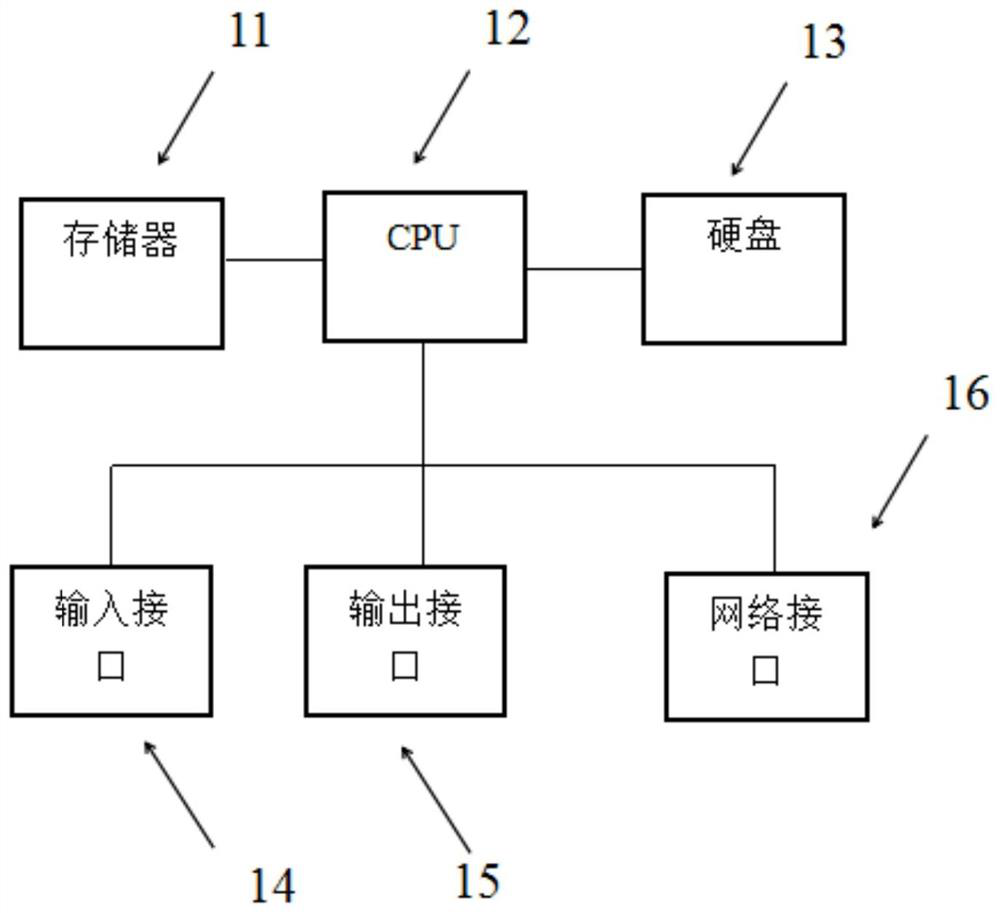
Method, device and equipment for generating clinical test scheme based on BOPII design decision
A technology for clinical trials and design decisions, applied in the field of clinical trials, can solve the problems of slow time-consuming, increased human costs of clinical trials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0073] Example 1: Binary Efficacy Endpoint: A phase II clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of metformin in patients with recurrent small cell lung cancer. The primary endpoint was the objective response rate (ORR) (defined using RECIST version 1.1) of ASO-treated patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC). According to historical data, if the original hypothesis ORR5% is established, the treatment is considered to be ineffective, and if the alternative hypothesis ORR20% is established, it is considered that the therapy has development prospects. This example is used to illustrate the standard case with a binary efficacy endpoint.
example 2
[0074] Example 2: Nested efficacy endpoints: a phase II clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of a novel humanized monoclonal antibody in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma who had failed autologous stem cell transplantation. The effectiveness of lymphoma therapy is defined using the revised International Malignant Lymphoma Working Group Criteria, with one of four reduction level categories including: Complete Response (CR), defined as disappearance of all evidence of disease; Partial Response (PR), defined as regression of measurable lesions with no new lesions; stable disease (SD), defined as failure to meet criteria for CR, PR, or progressive disease (PD); progressive disease (PD), defined as progression of any new lesions Evidence or lesion volume increased by 50% from the nadir of the previously involved site. In this trial, although both CR and PR were considered favorable efficacy responses, CR was actually preferable. The null hypothesis is that Pr(CR+PR) is 30% and Pr(...
example 3
[0075] Example 3: Co-multiple efficacy endpoints: a phase II clinical trial, the protocol name is GOG 0229E, the main purpose is to study the efficacy of bevacizumab in patients with recurrent or persistent endometrial cancer. The trial has two co-primary efficacy endpoints: the objective response rate (ORR) and the probability of 6-month progression-free (or death) survival (PFS6). Objective response rate was defined using Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the time from the start of treatment to disease progression or death from any cause. The null hypothesis is ORR10% and PFS615%. If established, the treatment is considered ineffective. The difference between the clinically significant improvement of the two indicators is 20%, so if the alternative hypothesis ORR≥30% or PFS6≥35% is established, it is considered that the therapy has development prospects.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com