Biomarkers and methods for individualized treatment of small cell lung cancer using KDM1A inhibitors
A technology of KDM1A, treatment method, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem that the sensitivity is not SCLC cells and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0143] Example 1: Sorting of KDM1A Inhibitor Sensitive and Resistant Cell Lines
[0144] For biomarker identification, seven SCLC cell lines were assessed for their response to KDM1A inhibitor treatment based on the results of viability assays performed 4 or 10 days after treatment with the KDM1A inhibitor ORY-1001 (as described elsewhere herein). Classification. For the 4-day viability assay, SCLC cell lines were seeded in 384-well plates in a final volume of 40 μL in the optimized medium supplemented with ORY-1001 recommended by the supplier of each cell line (maximum concentration: 50 μM; tested for 18 serial 1:2 dilutions). At 37°C, 5% CO 2 - After 4 days of incubation in a controlled atmosphere, use Assay Cell viability was assessed according to the manufacturer's protocol (Promega). EC50 values were calculated using Microsoft Excel software for untreated cells (100% growth) and without Reagents (100% growth inhibition) were standardized. Viability quantificatio...
Embodiment 2
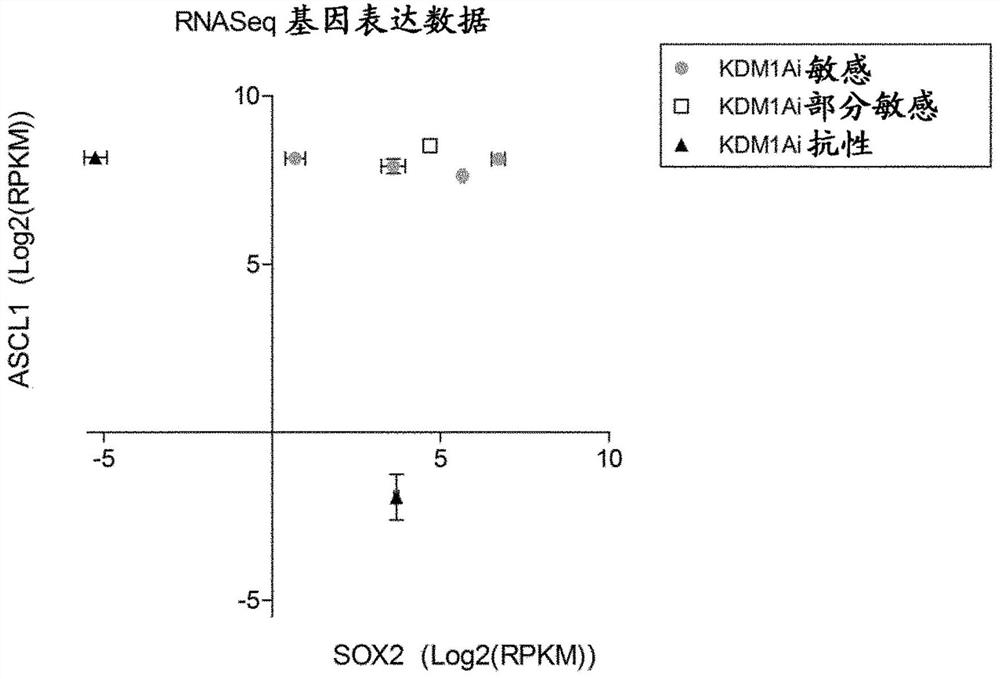
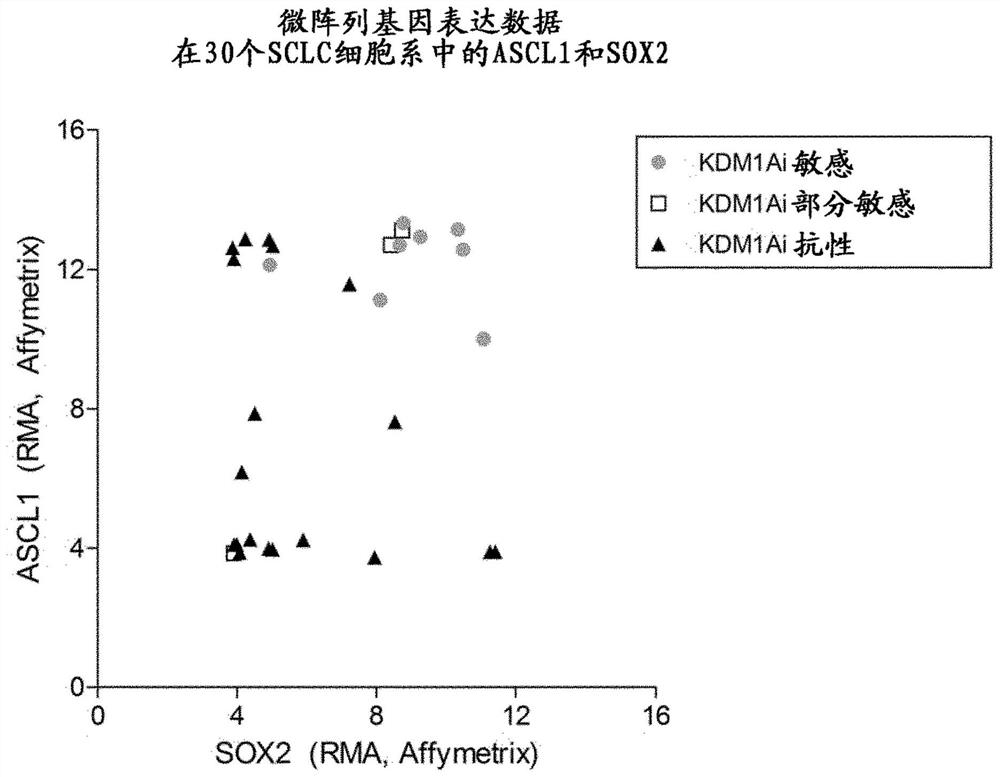
[0148] Example 2 Identification of ASCL1 and SOX2 as biomarkers of responsiveness to KDM1A inhibitors
[0149] To identify genes that can differentiate SCLC cell lines that are sensitive to KDM1A inhibitor therapy from those that are resistant, four KDM1Ai-sensitive, one KDM1Ai-partially sensitive, and two KDM1Ai-resistant SCLC cell lines were subjected to RNASeq analysis. Details on their responsiveness and classification to KDM1Ai are provided in Example 1 above.
[0150] Cell pellets for gene expression analysis
[0151] Cells were grown continuously in flasks for 6 days. On the last day of the assay, cells were collected in Falcon tubes, counted, and then centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 4 minutes. Discard the supernatant, suspend the cells in 1 mL of PBS and transfer to an eppendorf sample, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 5 min in an eppendorf centrifuge at 4 °C. Finally, the supernatant was discarded and the pellet was frozen at -80°C.
[0152] RNA sequencing
[0153] To...
Embodiment 3
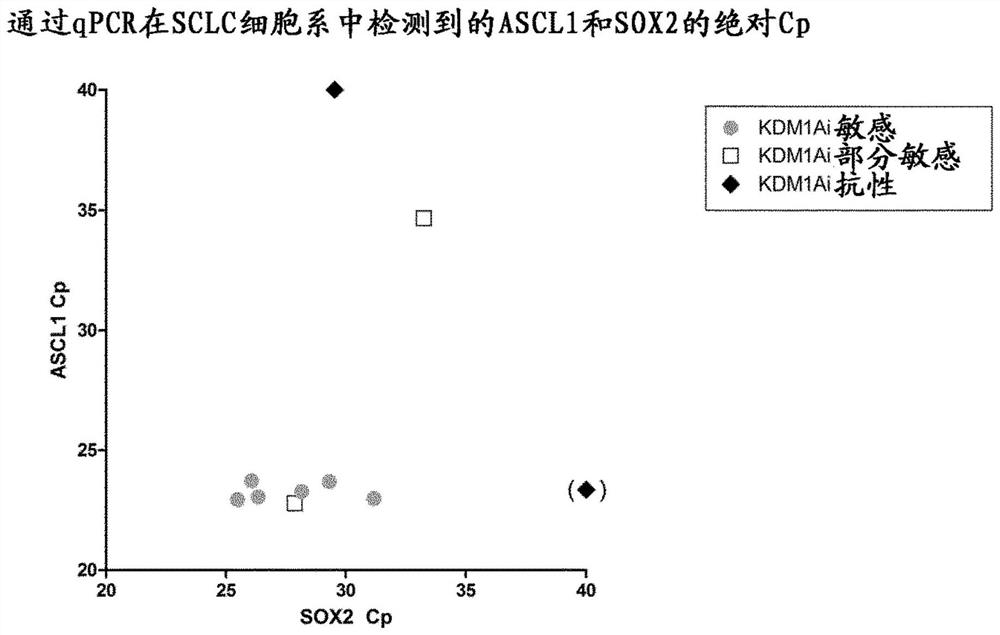
[0163] Example 3 Verification of ASCL1 and SOX2 using qRT-PCR
[0164] The same panel of SCLC cell lines described in Examples 1 and 2 (including two additional SCLC cell lines, one identified as sensitive to KDM1Ai treatment (DMS53) and the other identified as sensitive to KDM1Ai treatment) were then analyzed by Taqman qRT-PCR. KDM1Ai Treatment Partial Sensitivity (NCIH526)) The biomarkers of responsiveness to KDM1A inhibitors identified in Example 2, ASCL1 and SOX2, were validated.
[0165] Gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR
[0166] Total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Mini kit, and cDNA was obtained using the High Capacity RNA-to-cDNA Master Mix (ThermoFisher Scientific #4390779) according to standard procedures. qRT-PCR was performed using a LightCycler 480 Probes Master (PNT-L-034; Roche #04887301001) and using a predesigned and preoptimized TaqMan gene expression assay from ThermoFisher Scientific. qRT-PCR was performed in triplicate using a Lightcycler 480 Ins...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap