Data sharing method based on block chain and federal learning
A data sharing and blockchain technology, applied in machine learning, digital data protection, data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of data owner privacy leakage, data privacy hindering data sharing, and unlikely sharing of local data, etc. The effect of alleviating privacy protection issues, protecting privacy and ensuring reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
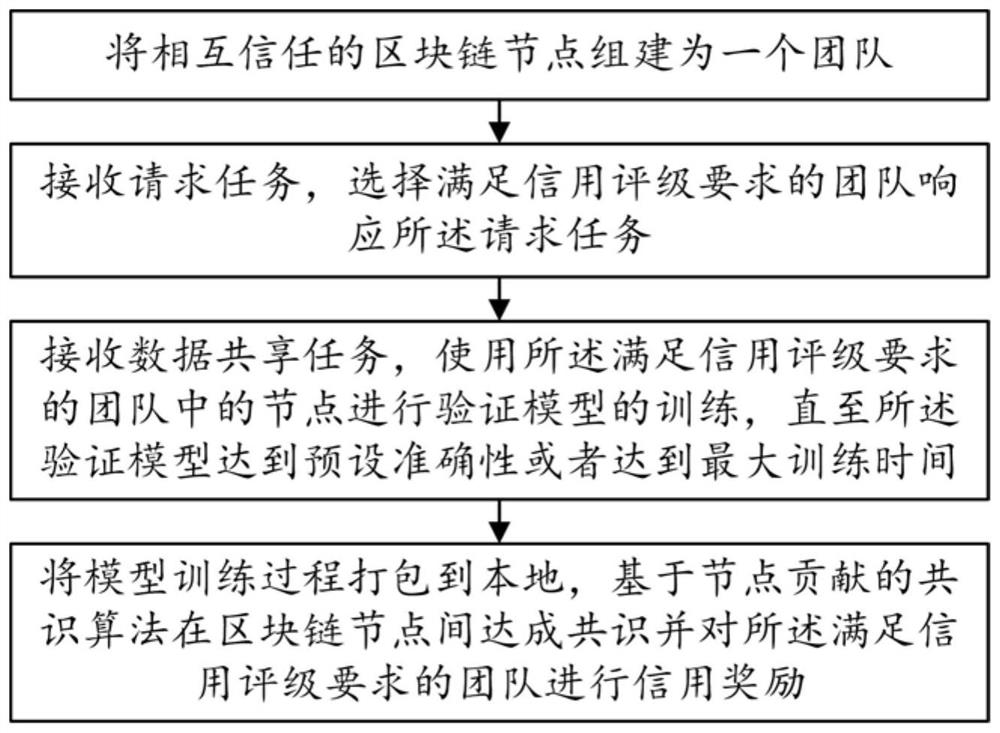
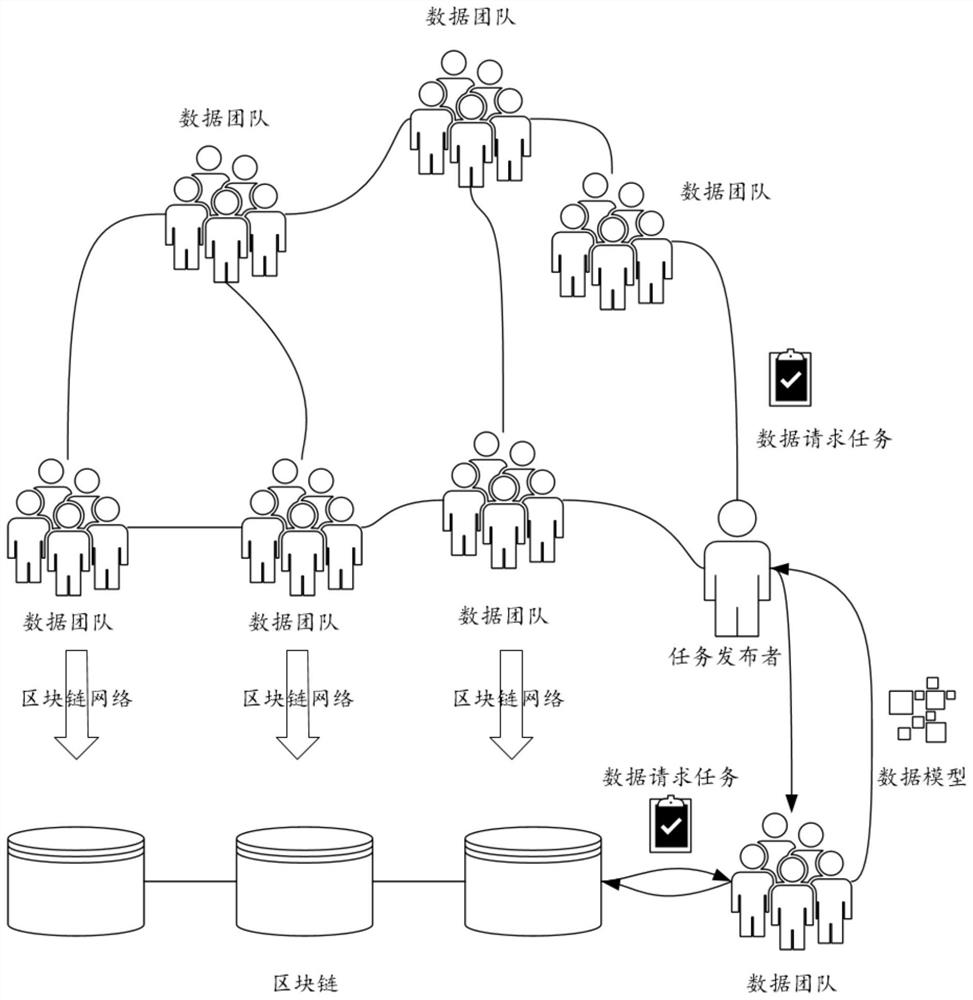
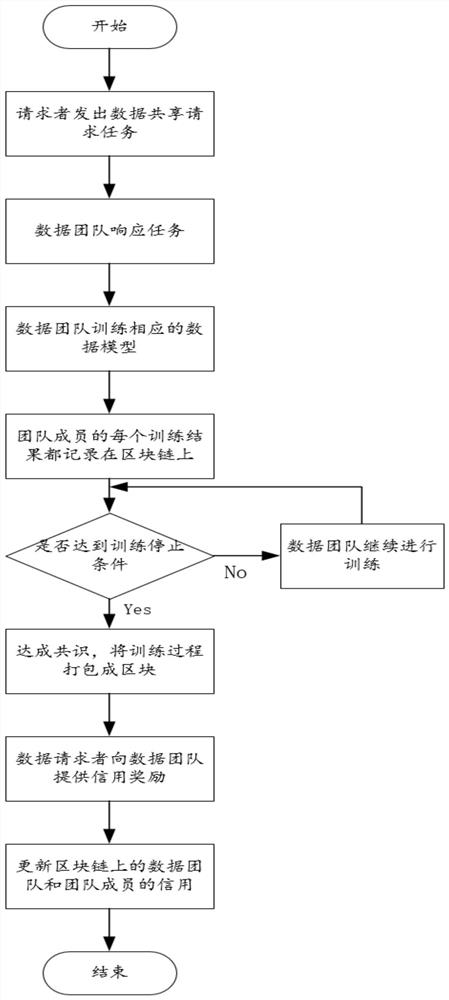
[0088] Please refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , a data sharing method based on blockchain and federated learning, including steps:
[0089] S1. Form a team of blockchain nodes that trust each other.
[0090] Among them, each team has a team leader who is responsible for receiving data sharing tasks, supervising the joint learning process in data sharing, and sending the global model with differential privacy to the task issuer.
[0091] The data nodes in step S1 may have selfish behavior. To solve this problem, an internal team management mechanism based on "mortgage-punishment" is designed, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0092] S11. Provide a preset amount of collateral when forming a team, and calculate the penalty coefficient k for bad behavior nodes:
[0093]
[0094] In the formula, v represents the total number of working rounds for the node to complete the cooperative task, p represents the number of times the node temporarily exits, and q repres...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Please refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that it further limits the application of privacy differences to data sharing. Specifically, considering that malicious data requesters will launch attacks, the team leader should add interference to the model, using the The differential privacy model protection method specifically includes the following steps:
[0129] Given a random algorithm G, two adjacent data sets D1 and D2 with at most one different record;
[0130] After removing two data sets in a row, calculate the probability of the random algorithm G getting the same result according to formula (7):
[0131] Pr[G(D)∈0]≤exp(ε) Pr[G(D′)∈0];
[0132] In the formula, G represents a random algorithm, ε represents a privacy budget, usually a small constant, and D represents a data set;
[0133] Calculate sensitivity:
[0134] Δf=max D,D , ||G(D)-G(G′)||;
[0135] Compute the Laplacian mechanism applied to the g...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Please refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that the steps of the consensus algorithm based on node contributions are further defined, specifically:
[0140] Compute the contribution of each node based on cosine similarity:
[0141]
[0142] in Indicates the actual update gradient k of the node, Indicates the local update gradient of the kth node, Indicates the model gradient before data node k is updated, Represents the gradient of the global model;
[0143] Carry out a reward mechanism based on the contribution weight ratio;
[0144] Calculate the contribution value through the mapping function:
[0145]
[0146] Use the soft-max function to calculate the weight ratio of the node's contribution to the global model;
[0147] Calculate the soft-max function value:
[0148]
[0149] Therefore, the advantage of the consensus mechanism in this embodiment is that it can prevent the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com