Disease risk prediction modeling method based on LI-RADS classification
A disease risk and modeling method technology, applied in the field of disease risk prediction modeling based on LI-RADS classification, can solve the problems of high sample acquisition cost, low sample accumulation efficiency, and difficulty in iterative upgrade of risk assessment models. Achieve the effect of high feasibility of iterative upgrade and reduce acquisition cost and difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example
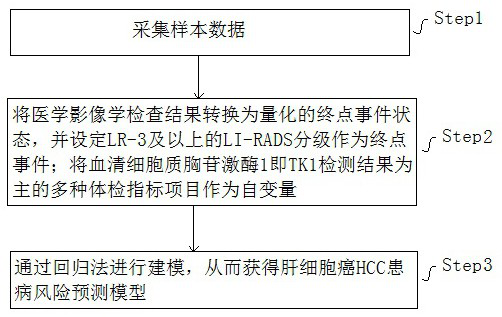
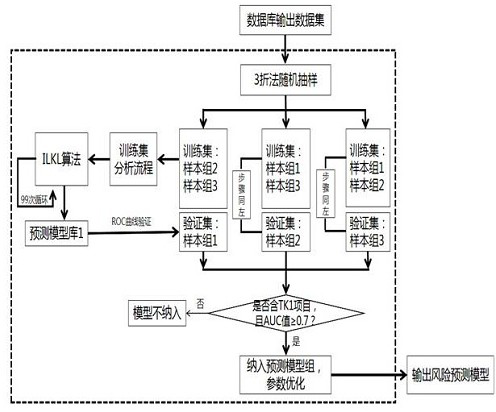
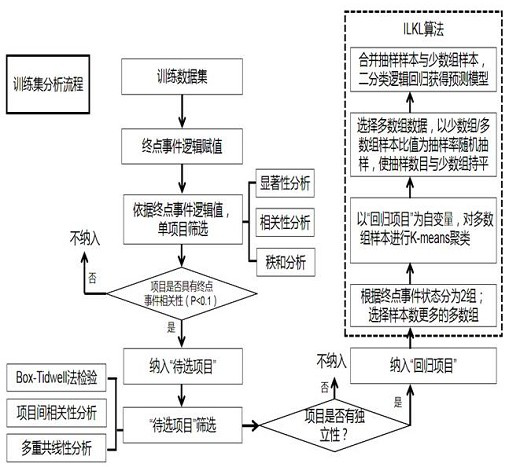
[0126] Using the physical examination data of a hospital of the People's Liberation Army in 2017 (the total number of samples is 10639), of which 130 were in the positive group and 10,509 in the negative group (in line with the true ratio, which improved the scalability of the regression model and the practical significance of the risk evaluation method in this application), based on this application modeling method. The final prediction model included age class and 11 biomarkers or blood indicators as independent variables: cytoplasmic thymidine kinase 1 concentration (TK1), lymphocyte count, mean corpuscular volume, platelet count, leukoglobulin ratio, serum Albumin, aspartate aminotransferase, creatinine, urea creatinine, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
[0127] Among them, the age grade value can be preset as: 20-29 years old is assigned as 1, 30-39 years old is assigned as 2, 40-49 years old is assigned as 3, 50-59 years old is assigned as 4, 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com